HP BL260c Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades
HP BL260c - ProLiant - G5 Manual
 |
UPC - 883585668663
View all HP BL260c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
HP BL260c manual content summary:
- HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 1
iSCSI boot for Linux ...12 Virtual Connect ...13 Configuration and management technologies 14 BladeSystem Onboard Administrator 14 ProLiant Onboard Administrator (Integrated Lights-Out 2) for ProLiant server blades 15 HP Insight Control suite ...15 Power management technologies...15 Power meter - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 2
describes the architecture and the implementation of major technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class server blades based on Intel® Xeon® and AMD Opteron™ processors. These technologies include processors, memory, connections, power, management, and the latest serial input/output (I/O) technologies. It - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 3
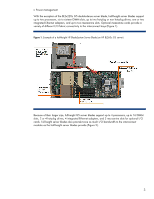
to the interconnect bays (Figure 1). Figure 1. Example of a half-height HP BladeSystem Server Blade (an HP BL260c G5 server) Because of their larger size, full-height G5 server blades support up to 4 processors, up to 16 DIMM slots, 2 or 4 hot-plug drives, 4 integrated Ethernet adapters, and - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 4
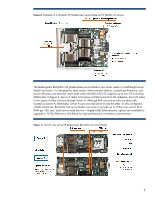
dense server blade is two server nodes in a half-height server blade form factor. It is designed for data centers where extreme density, compute performance, and power efficiency are essential. Each node within the BL2x220c G5 supports up to two CPUs and four DIMM slots. In Figure 3, Server A refers - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 5
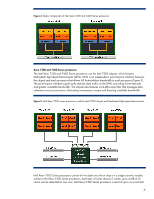
5200, 5300 and 5400 Series processors ProLiant G5 server blades with two Intel processors use the Intel 5000P chipset. This chipset contains two main components: the Memory Controller Hub (MCH) and the I/O controller hub. The Northbridge MCH supports DDR2 fully-buffered DIMMs. The 64-bit Intel Xeon - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 6
processors consist of two dual-core silicon chips on a single ceramic module, similar to the Xeon 5300 Series processors. Each pair of cores shares L2 cache; up to 4 MB of L2 cache can be allocated to one core. Intel Xeon 7400 Series processors consist of up to six cores that 6 - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 7
share a 16 MB L3 cache (Figure 6). Intel Xeon 7300 and 7400 Series processors are available on the ProLiant BL680 G5 server blade. Figure 6. Major components of Intel Xeon 7300 and 7400 Series processors AMD Opteron™ quad-core processors Third generation, quad-core AMD Opteron 2300 and 8300 - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 8
server blades for DIMM slots and hard drives. Precise ducting on ProLiant c-Class server blades server blade and to obtain the most thermal work from the least amount of air moved. Ducting produces high pressure that reduces the amount of required airflow, which in turn reduces the power HP engineers - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 9
how the processor installation tool simplifies installation Memory technologies Depending on the model, HP ProLiant c-Class G5 Server Blades support the following memory technologies: • Registered PC2 (DDR2) DIMMs • Fully buffered PC2 (DDR2) DIMMs DDR2 memory devices operate at 1.8V. DDR2 devices - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 10
cache module and disks to a working controller where the cache will be flushed out to the disks. The battery will last up to two days without receiving any power titled "HP local I/O technology for ProLiant and BladeSystem servers": http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c00231623 - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 11
storage. HP ProLiant c-Class server blades use two types of mezzanine cards that connect to the various interconnect fabrics such as Fibre Channel, Ethernet, serial-attached SCSI, or InfiniBand. Type I and Type II mezzanine cards differ only in the amount of power allocated to them by the server and - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 12
located on a SAN within a Red Hat or SUSE Linux environment. The host server uses an iSCSI firmware image (iSCSI boot option ROM), making the remote disk drive appear to be a local, bootable C: drive. Administrators can configure the server to connect to and boot from the iSCSI target disk on the - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 13
Connect Manager Virtual Connect implements server-edge virtualization so that server administrators can upgrade, replace, or move server blades within their enclosures without changes being visible to the external LAN and SAN environments. HP recommends using Virtual Connect or managed switches - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 14
Memory (EEPROM) that contains specific factory information about the component, such as product name, part number, and serial number. The BladeSystem Onboard Administrator accesses server blade FRU EEPROMs through their ProLiant Onboard Administrator (iLO 2) management processors. The server blades - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 15
x 7 HP Software Technical Support and Update Service. Power management technologies Three HP power management tools help to accurately monitor and provision server power use, which improves power efficiency in HP BladeSystem c-Class server blades: • Power meter • HP Power Regulator for ProLiant • HP - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 16
BladeSystem server blades with iLO 2 version 1.30 or later and system BIOS 2007.05.01 or later. Support for Dynamic Power Capping requires iLO 2 version 1.70 or later, system BIOS 2008.11.01 or later, and BladeSystem Onboard Administrator firmware version 2.32 or later for HP BladeSystem enclosures - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 17
Select ProLiant G5 server blades support power loads, and memory formats requiring more power. This architecture makes network, compute, and storage resources modular, enabling a truly adaptive infrastructure that can accommodate continually changing business needs. HP ProLiant c-Class Server Blades - HP BL260c | Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 18
-based HP BladeSystem and HP ProLiant servers" technology brief General HP BladeSystem information HP BladeSystem c-Class documentation HP BladeSystem c-Class Enclosure Setup and Installation Guide HP BladeSystem c-Class interconnects Technology briefs about HP BladeSystem HP BladeSystem Power Sizer

Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class
server blades
technology brief
Abstract
..............................................................................................................................................
2
Introduction
.........................................................................................................................................
2
ProLiant c-Class server blade architecture
................................................................................................
2
Processor technologies
.........................................................................................................................
5
Intel processors
................................................................................................................................
5
Xeon 5200, 5300 and 5400 Series processors
...............................................................................
5
Xeon 7300 and 7400 Series processors
.........................................................................................
6
AMD Opteron™ quad-core processors
...............................................................................................
7
Thermal Logic technologies
...................................................................................................................
8
Processor socket technology
..................................................................................................................
8
Memory technologies
...........................................................................................................................
9
I/O technologies
.................................................................................................................................
9
PCI Express technology
.....................................................................................................................
9
Serial Attached SCSI technology
......................................................................................................
10
SAS and SATA Small Form Factor hard drives
...................................................................................
10
Solid state drives
............................................................................................................................
11
Optional mezzanine cards
..............................................................................................................
11
Networking technologies
................................................................................................................
11
TCP/IP Offload Engine
................................................................................................................
12
Receive-side Scaling (RSS)
...........................................................................................................
12
iSCSI Acceleration
......................................................................................................................
12
iSCSI boot for Linux
....................................................................................................................
12
Virtual Connect
..........................................................................................................................
13
Configuration and management technologies
.......................................................................................
14
BladeSystem Onboard Administrator
................................................................................................
14
ProLiant Onboard Administrator (Integrated Lights-Out 2) for ProLiant server blades
...............................
15
HP Insight Control suite
...................................................................................................................
15
Power management technologies
.........................................................................................................
15
Power meter
..................................................................................................................................
16
HP Power Regulator for ProLiant
.......................................................................................................
16
HP Dynamic Power Capping and HP Power Capping
........................................................................
16
Data security technology with the Trusted Platform Module
.....................................................................
17
Conclusion
........................................................................................................................................
17
For more information
..........................................................................................................................
18
Call to action
....................................................................................................................................
18