HP BL260c Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 2
Abstract, Introduction, ProLiant c-Class server blade architecture, Thermal Logic technologies - proliant g5
 |
UPC - 883585668663
View all HP BL260c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 2 highlights
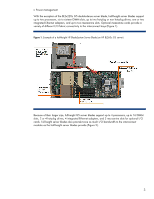
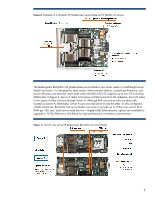
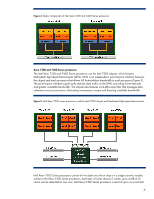
Abstract This technology brief describes the architecture and the implementation of major technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class server blades based on Intel® Xeon® and AMD Opteron™ processors. These technologies include processors, memory, connections, power, management, and the latest serial input/output (I/O) technologies. It is assumed that the reader is familiar with HP ProLiant server technology and has some knowledge of BladeSystem architecture. For more information about the infrastructure components, see the HP website: www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/. Introduction As HP began planning the next generation of BladeSystem architecture, it became clear that significant changes affecting I/O, processor, and memory technologies were on the horizon. HP designed the BladeSystem architecture to accommodate these new technologies. HP BladeSystem architecture uses full-featured server blades. For complete specifications of each server blade, see the HP website: http://www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/. ProLiant c-Class server blade architecture An HP ProLiant c-Class Server Blade is a complete server that slides into an HP BladeSystem c-Class Enclosure. Three different c-Class enclosures are available to meet the needs of large or small IT environments: • The HP BladeSystem c7000 rack enclosure is 10U high and holds up to 16 ProLiant c-Class server blades. • The HP BladeSystem c3000 rack enclosure is 6U high and holds up to 8 ProLiant c-Class server blades. • The HP BladeSystem c3000 tower enclosure is designed with casters for sites without racks. It holds up to 8 ProLiant c-Class server blades inserted vertically. The rack enclosures fit in HP 10000 series racks and can operate with as few as one server blade installed. The greatest advantage of blade architecture, however, is the ease of adding more server blades. ProLiant c-Class server blades are built in standard form-factors, referred to as half-height (4U) and full-height (8U). Both half-height and full-height server blades fit into any device bay in a BladeSystem c-Class enclosure.1 ProLiant c-Class server blades include enterprise-class technologies: • Two or four AMD or Intel x86 processors • Thermal Logic technologies • Advanced memory technologies • Multiple slots for I/O cards • Integrated multifunction Ethernet network adapters that support TCP/IP offload engine (TOE)2 and iSCSI acceleration • Hot-plug internal disk drives 1 More information about BladeSystem c-Class enclosure configuration options can be found at http://www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/. 2 TOE technology is designed to move processing transactions from the main processor on a server blade to a processor embedded on the network interconnect card. This frees the main processor for other work. 2