HP BL260c Technologies in HP ProLiant G5 c-Class Server Blades - Page 9
Memory technologies, PCI Express technology - proliant g5 server
 |
UPC - 883585668663
View all HP BL260c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
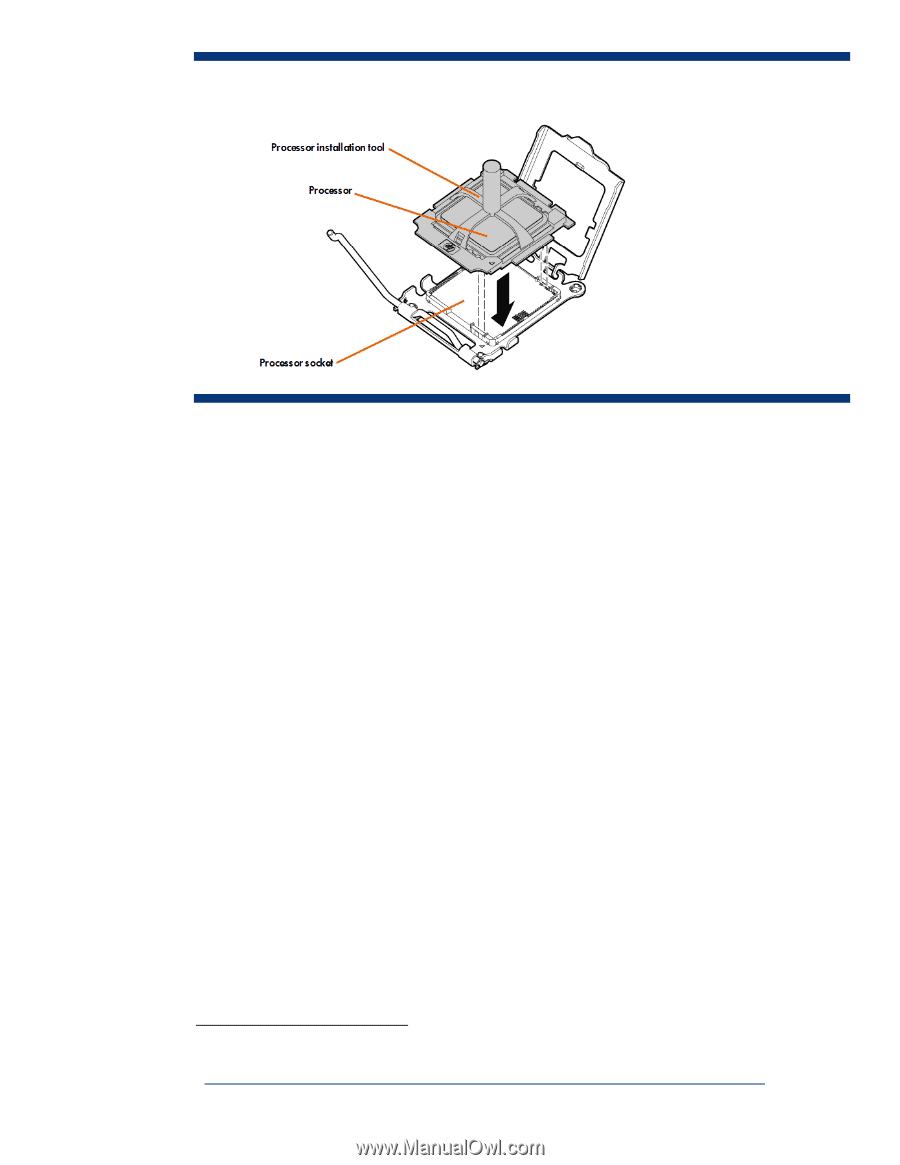
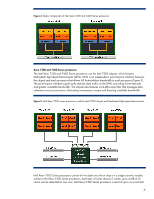
Figure 9. Diagram showing how the processor installation tool simplifies installation Memory technologies Depending on the model, HP ProLiant c-Class G5 Server Blades support the following memory technologies: • Registered PC2 (DDR2) DIMMs • Fully buffered PC2 (DDR2) DIMMs DDR2 memory devices operate at 1.8V. DDR2 devices use high clock frequencies to increase data transfer rates and on-die termination control to improve signal quality. For example, at a clock frequency of 400 MHz, the data transfer rate is 800 megatransfers per second (MT/s), which translates to a memory bandwidth of 6400 MB/s per DIMM. Single-rank registered DDR2 DIMMs place only one load per DIMM on the memory bus. Fully buffered DIMMs implement a serial architecture to increase memory bandwidth and capacity.5 I/O technologies HP ProLiant c-Class Server Blades support PCI Express (PCIe), serial attached SCSI (SAS), serial ATA (SATA) I/O technologies, Multifunction 1 Gb or 10 Gb Ethernet, 4 Gb Fibre Channel, and 4X DDR (20 Gb) InfiniBand. PCI Express technology The PCI Express (PCIe) serial interface provides point-to-point connections between the chipset I/O controller hub and I/O devices. Each PCIe serial link consists of one or more dual-simplex lanes. Each lane contains a send pair and a receive pair to transmit data at the signaling rate in both directions simultaneously (Figure 10). ProLiant G5 server blades support PCIe 1.0 slots, which have a signaling rate of 2.5 Gb/s per direction per lane. After accounting for 20 percent serializing/deserializing encoding overhead, the resulting effective maximum bandwidth is 2 Gb/s (250 MB/s) per direction per lane. Therefore, a x4 link with 4 send and receive pairs has an effective bandwidth of 2 GB/s. A 5 For additional information, refer to the HP technology brief titled "Memory technology evolution: an overview of system memory technologies": http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c00256987/c00256987.pdf. 9