HP Cisco MDS 9216A HP StorageWorks C-Series iSCSI Configuration Guide (AA-RW7P - Page 16
Presenting iSCSI hosts as virtual Fibre Channel hosts, Transparent mode static mapping
 |
View all HP Cisco MDS 9216A manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 16 highlights
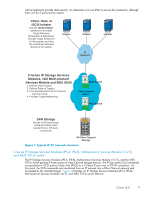
To configure IP for subsequent use by iSCSI initiators: 1. Enter configuration mode: switch# config terminal 2. Enter the interface configuration mode on the Gigabit Ethernet interface (slot 2, port 2): switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet 2/2 3. Enter the IP address (33.33.33.170) and subnet mask (255.255.255.0) for the Gigabit Ethernet interface: switch(config-if)# ip address 33.33.33.170 255.255.255.0 4. Enable the interface: switch(config-if)# no shutdown Presenting iSCSI hosts as virtual Fibre Channel hosts Because you are converting SCSI commands to and from an iSCSI IP server to Fibre Channel storage, the C-Series IP Storage Services Modules (IPS-4, IPS-8), Multi-protocol Services Module (14/2), and MDS 9216i switch must map the ISCSI server's IP address to a unique WWPN that the Fibre Channel Storage recognizes. The IP Storage Services Modules (IPS-4, IPS-8), Multi-protocol Services Module (14/2), and MDS 9216i switch have two modes to present iSCSI hosts in the Fibre Channel fabric: transparent mode and proxy initiator mode. HP recommends the use of transparent mode as described in this guide. The benefit of transparent mode is that it allows a finer level of access control configuration. In transparent mode, each iSCSI host is presented as one virtual Fibre Channel host on the Fibre Channel fabric. Because of the one-to-one mapping of IP-to-WWPN translation from iSCSI to Fibre Channel, each host can have different zoning in the Fibre Channel SAN or LUN access control on the Fibre Channel storage. Transparent mode static mapping The C-Series IP Storage Services Modules (IPS-4, IPS-8), Multi-protocol Services Module (14/2), and MDS 9216i switch have two modes of mapping IP addresses: transparent-mode dynamic mapping and transparent-mode static mapping. Because the Microsoft iSCSI Initiator does not support Dynamic partitions, you must configure using transparent mode static mapping. Static mapping must be enabled for each iSCSI Initiator to guarantee persistent LUN mapping from the HP Fibre Channel controller to the iSCSI Initiator. See Configuring transparent mode static mapping for instructions. Installing an iSCSI Initiator on a Windows server The IP host or iSCSI Initiator uses the Microsoft iSCSI Initiator to enable target resource recognition and attachment to the C-Series IP Storage Services Modules (IPS-4, IPS-8), Multi-protocol Services Module (14/2), and MDS 9216i switch over IP. The Microsoft iSCSI Initiator is configured with the Gigabit Ethernet IP address of each iSCSI interface running on the C-Series IP Storage Services Modules (IPS-4, IPS-8), Multi-protocol Services Module (14/2), and MDS 9216i to which the host is to transport SCSI requests and responses. The iSCSI Initiator sees the storage resources (LUNs) as if they were local drives attached directly to the server. HP configuration utility for network interface cards With HP ProLiant servers, an iSCSI Initiator may use multiple NIC cards with HP teaming enabled for failover. The term team refers to the concept of multiple network adapters working together as a single network adapter, commonly referred to as a virtual network adapter. Setup Download the iSCSI Initiator from Microsoft's download page, and follow the installation instructions. The download includes copying the user guide to your local disk. You can refer to the user guide in C:\Program Files\Microsoft iSCSI Initiator\uguide.doc for further information. The first use of the Microsoft iSCSI initiator, requires a manual log in to the Available Targets. After the Available Target logins are completed with the Restore Connection button enabled, the iSCSI Initiator automatically logs in whenever the server powers up or reboots. 16