HP ProLiant DL288 HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 6
Power consumption and system performance, DL380 G5 Power Savings and Performance Impact - proliant dl380
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL288 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
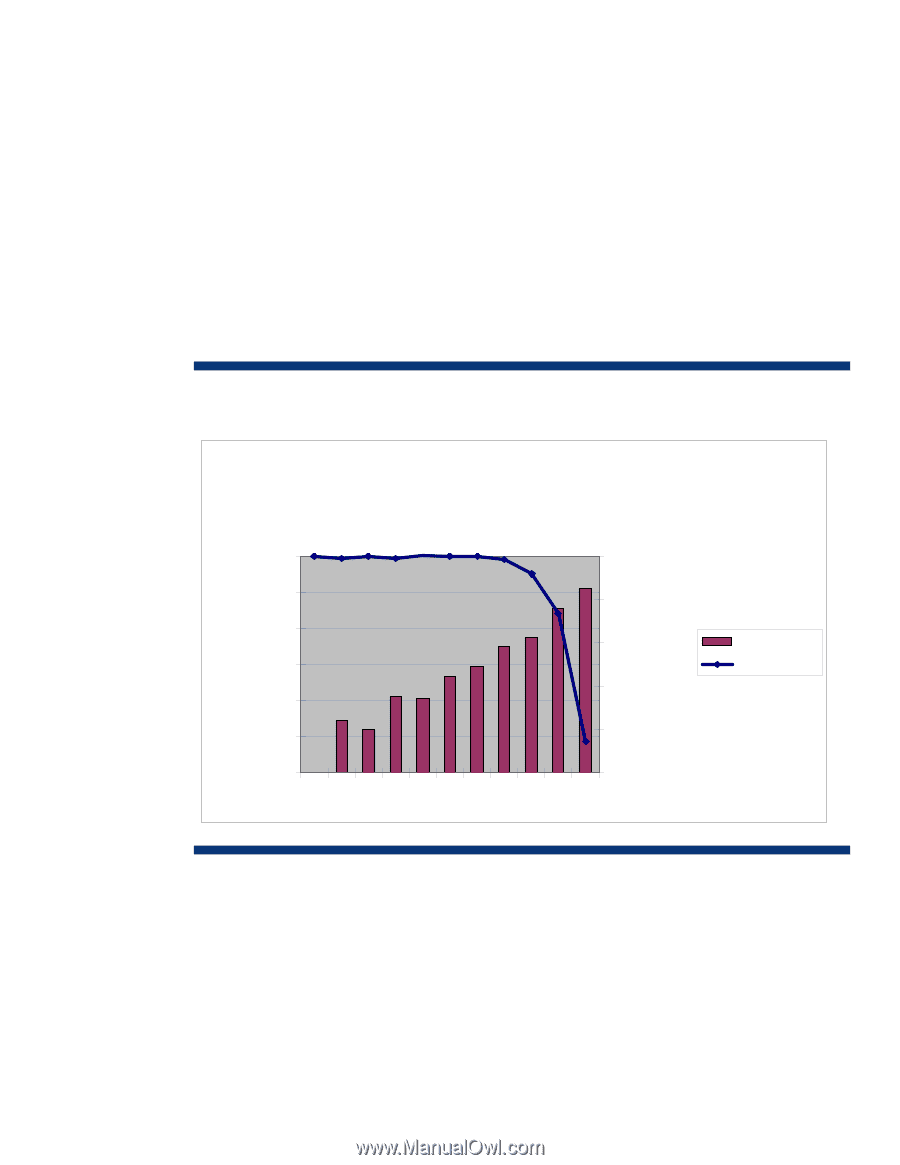
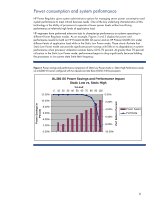
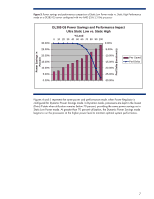
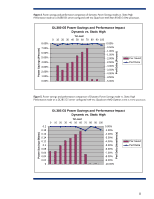
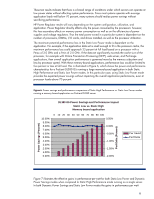
Power consumption and system performance HP Power Regulator gives system administrators options for managing server power consumption and system performance to meet critical business needs. One of the key underlying characteristics of this technology is the ability of processors to operate at lower power levels without sacrificing performance at relatively high levels of application load. HP engineers have performed extensive tests to characterize performance on systems operating in different Power Regulator modes. As an example, Figures 2 and 3 display the power and performance results for both an HP ProLiant DL380 G5 server and an HP ProLiant DL385 G5 under different levels of application load while in the Static Low Power mode. These charts illustrate that Static Low Power mode can provide significant power savings with little or no degradation in system performance when processor utilization remains below 60 to 70 percent. At greater than 70 percent utilization in the Static Low Power mode, performance begins to drop significantly because holding the processors in low power state limits their frequency. Figure 2. Power savings and performance comparison of Static Low Power mode vs. Static High Performance mode on a DL380 G5 server configured with two Quad-core Intel Xeon E5450 3 GHz processors Power Savings in Percent Perf Delta in Percent DL380 G5 Power Savings and Performance Impact Static Low vs. Static High 12.00% % Load 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 0.00% 10.00% 8.00% 6.00% 4.00% 2.00% -2.00% -4.00% -6.00% -8.00% Power Saved Perf Delta 0.00% -10.00% 6