Motorola E680 Technical Manual - Page 98
Verifying the Signer Certificate, Verifying the MIDlet Suite JAR
 |
View all Motorola E680 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 98 highlights
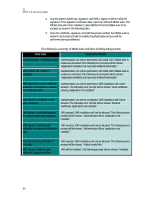
Verifying the Signer Certificate The signer certificate will be found in the application descriptor of the MIDlet suite. The process for verifying a Signer Certificate is outlined in the steps below: 1. Get the certification path for the signer certificate from the JAD attributes MIDletCertificate-1, where starts a 1 and is incremented by 1 until there is no attribute with this name. The value of each attribute is abase64 encoded certificate that will need to be decoded and parsed. 2. Validate the certification path using the basic validation process as described in RFC2459 using the protection domains as the source of the protection domain root certificates. 3. Bind the MIDlet suite to the corresponding protection domain that contains the protection domain root certificate that validated the first chain from signer to root. 4. Begin installation of MIDlet suite. 5. If attribute MIDlet-Certificate-- with being greater than 1 are present and full certification path could not be established after verifying MIDletCertificate-- certificates, then repeat step 1 through 3 for the value greater by 1 than the previous value. The following table describes actions performed upon completion of signer certificate verification: Result Action Attempted to validate paths. No public keys of the Authentication fails, JAR installation is not issuer for the certificate can be found, or none of the allowed. certificate paths can be validated. More than one full certification path is established and validated. Implementation proceeds with the signature verification using the first successfully verified certificate path for authentication and authorization. Only one certification path established and validated. Implementation proceeds with the signature verification. Verifying the MIDlet Suite JAR The following are the steps taken to verify the MIDlet suite JAR: 1. Get the public key from the verified signer certificate. 2. Get the MIDlet-JAR-RSA-SHA1 attribute from the JAD. 3. Decode the attribute value from base64 yielding a PKCS #1 signature, and refer to RFC 2437 for more detail. 98