Netgear Wg111v2 WG111v2 User Manual - Page 44
How to Con WPA-PSK Encryption Security, To con WPA-PSK security
 |
UPC - 012495805855
View all Netgear Wg111v2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
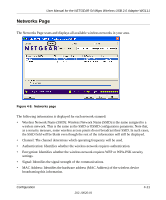
Page 44 highlights
User Manual for the NETGEAR 54 Mbps Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter WG111 5. The default key setting must match what is set in the access point and the other 802.11 wireless devices. 6. Click Apply for the changes to take effect. How to Configure WPA-PSK Encryption Security Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is wireless security with far greater protection than WEP. WPA-PSK (pre-shared key) uses encryption of a shared key as the starting point. WPA has a significant advantages over WEP - an encryption key differing in every packet. It is extremely difficult for hackers to read messages even if they have intercepted the data. To configure WPA-PSK security, click the Advanced Security button. The Advanced Security button is located in the Settings page, Security section. Figure 4-7: Advanced Security page The Passphrase can be between 8 and 63 characters. Select TKIP or AES for the security mechanism. TKIP stands for Temporal Key Integrity Protocol. TKIP replaces WEP with a new encryption algorithm that is stronger than the WEP algorithm, but that uses the calculation facilities present on existing wireless devices to perform encryption operations. One of the encryption methods supported by WPA, besides TKIP, is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). This is viewed as the optimal choice for security conscience organizations, but the problem with AES is that it requires a fundamental redesign of the NIC's hardware in both the station and the access point. TKIP is a pragmatic compromise that allows organizations to deploy better security while AES capable equipment is being designed, manufactured, and incrementally deployed. For more information on WPA security, see "WPA Wireless Security" on page B-8. 4-10 202-10026-01 Configuration