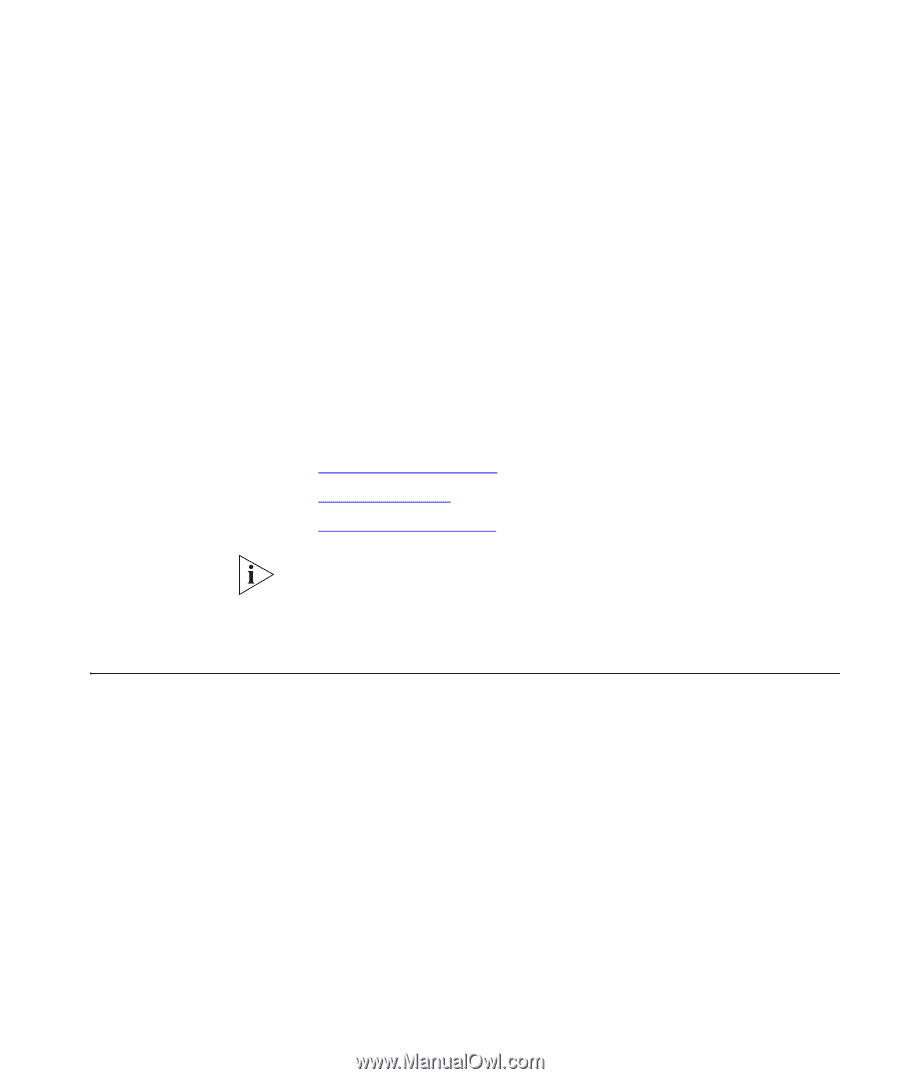3Com 3C17300A Implementation Guide - Page 33
Using Multicast Filtering, What is an IP Multicast
 |
UPC - 662705493169
View all 3Com 3C17300A manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 33 highlights
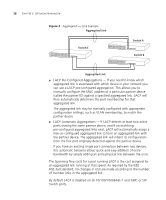
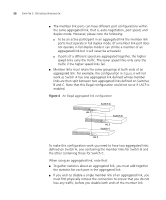
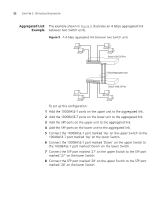
3 USING MULTICAST FILTERING What is an IP Multicast? Multicast filtering improves the performance of networks that carry multicast traffic. This chapter explains multicasts, multicast filtering, and how multicast filtering can be implemented on your Switch. It covers the following topics: ■ What is an IP Multicast? ■ Multicast Filtering ■ IGMP Multicast Filtering For detailed descriptions of the web interface operations and the command line interface (CLI) commands that you require to manage the Switch please refer to the Management Interface Reference Guide supplied in HTML format on the CD-ROM that accompanies your Switch. A multicast is a packet that is intended for "one-to-many" and "manyto-many" communication. Users explicitly request to participate in the communication by joining an endstation to a specific multicast group. If the network is set up correctly, a multicast can only be sent to an endstation or a subset of endstations in a LAN, or VLAN, that belong to the relevant multicast group. Multicast group members can be distributed across multiple subnetworks; thus, multicast transmissions can occur within a campus LAN or over a WAN. In addition, networks that support IP multicast send only one copy of the desired information across the network until the delivery path that reaches group members diverges. It is only at these points that multicast packets are replicated and forwarded, which makes efficient use of network bandwidth.