3Com 3C17300A Implementation Guide - Page 55
Identify Service Levels, Apply Traffic classification
 |
UPC - 662705493169
View all 3Com 3C17300A manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 55 highlights
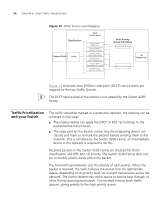
Traffic Prioritization and your Switch 55 How traffic is processed to provide Quality of Service A received packet at the ingress port is checked for its DSCP and IEEE 802.1D attributes to determine the level of service that the packet should receive. 802.1D packets are categorized into the 8 traffic classes defined by IEEE 802.1D; the higher the class the higher the priority given the packet on transmission. DSCP packets are categorized into the six service levels as shown in Figure 14 and mapped to the appropriate queue. The priority defined in the service level directs the packet to the appropriate egress queue. When a packet comes in with both 802.1D and DSCP priority markings, the higher of the priorities will be used. Received packets in the Switch 4200 Family are only checked for DSCP and 802.1D attributes. No other attributes are supported. Traffic queues are preset on a per-unit basis on the Switch 4200 Family. Configuring traffic prioritization for QoS on a 4200 Family QoS can be configured on your Switch using the 3Com Network Supervisor or via the Command Line Interface (CLI). You can also configure QoS via the command line interface (CLI). For a detailed description of the commands that you require, refer to the Management Interface Reference Guide supplied in HTML format on the CD-ROM that accompanies your Switch. Configure Quality of service in the Switch 4200 Family in the following way: 1 Apply Traffic classification First identify the types of traffic requiring special treatment. These types are defined in the QoS feature through the creation of classifiers. The Switch 4200 Family supports two types of packet attributes on which to classify incoming traffic, Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) and IEEE 802.1D. 2 Identify Service Levels You must then identify the level of service each classifier should receive. Note that DSCP service levels will be set somewhere else in the network and not in the Switch 4200 Family. Note also that 802.1D service levels are fixed and cannot be altered.