Asus P4P800 Deluxe Motherboard DIY Troubleshooting Guide - Page 85
Glossary, Small Computer System Interface
 |
View all Asus P4P800 Deluxe manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 85 highlights
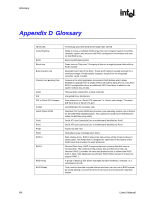
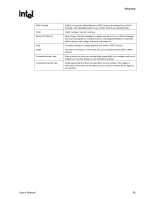
Glossary R RAID Volume SCSI Serial ATA (SATA) Strip Stripe Sustained transfer rate Theoretical transfer rate A block of capacity, allocated from a RAID Array and arranged into a RAID topology. The operating system sees a RAID Volume as a physical disk. Small Computer System Interface New storage interface designed to replace parallel ATA (e.g. IDE technology). SATA was designed for a variety reasons, including performance headroom, cabling issues, and voltage tolerance requirements. Grouping of data on a single physical disk within a RAID Volume The sum of all strips in a horizontal axis across physical disks within a RAID Volume Rate at which the drive can transfer data sequentially from multiple tracks and cylinders on the disk (closer to real-world file transfers) Actual speed that the drive can read bits from the surface of the platter or write bits to the surface of the platter (can be used to compare drives against one another) User's Manual 85