Autodesk 24009-050008-1610A User Guide - Page 8
Sharing the Same Revit Model
 |
UPC - 606121693468
View all Autodesk 24009-050008-1610A manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
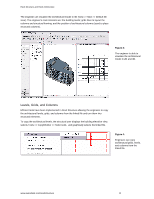
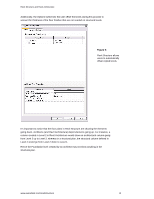
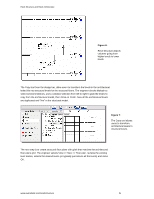
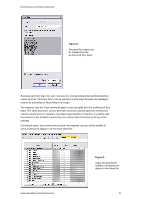
Revit Structure and Revit Architecture Sharing the Same Revit Model In some situations, structural engineering firms using Revit Structure may want to share the same RVT file with architects using Revit Architecture software (versus cross-linking RVT files). For instance, if the architect and the structural engineer are in the same organization (such as an A/E firm) and both have access to the same network, they can work directly on a combined architectural and structural model. Each team uses their appropriate software applications: the engineering team works on the building information model in Revit Structure while the architectural team works on the same model in Revit Architecture. Users can simultaneously work on different portions of a single building information model at the same time via Revit Worksharing (visit the White Papers Section on Autodesk's website at www.autodesk.com/revit to learn more about Multi-user Collaboration with Revit Worksharing). Worksharing Revit Worksharing allows both the architectural and the structural teams to share a single building information model by using worksets - which are logical groupings of objects in a building project that is reserved for editing by a single user at a time. Worksets function like the External Reference (xref) capability in AutoCAD® software, but with the additional ability to propagate and coordinate changes between designers. Worksets usually correspond to specific zones of responsibility, such as: building disciplines (structural, architectural, etc.); building systems (shell, core, interior, etc.); physical features (levels, wings, etc.); or model representation (physical or analytical). For example, the structural engineers and structural drafters may use two separate structural worksets: a drafting workset with the physical model for structural documentation, details, and views; and an engineering workset with the analytical representation of the structure for export to third-party analysis software. Figure 11: The worksets tool allows one user to own structural elements while other users can borrow them at the same time. www.autodesk.com/revitstructure 8