Biostar N4SIE-A7 N4SIE-A7 user's manual - Page 31
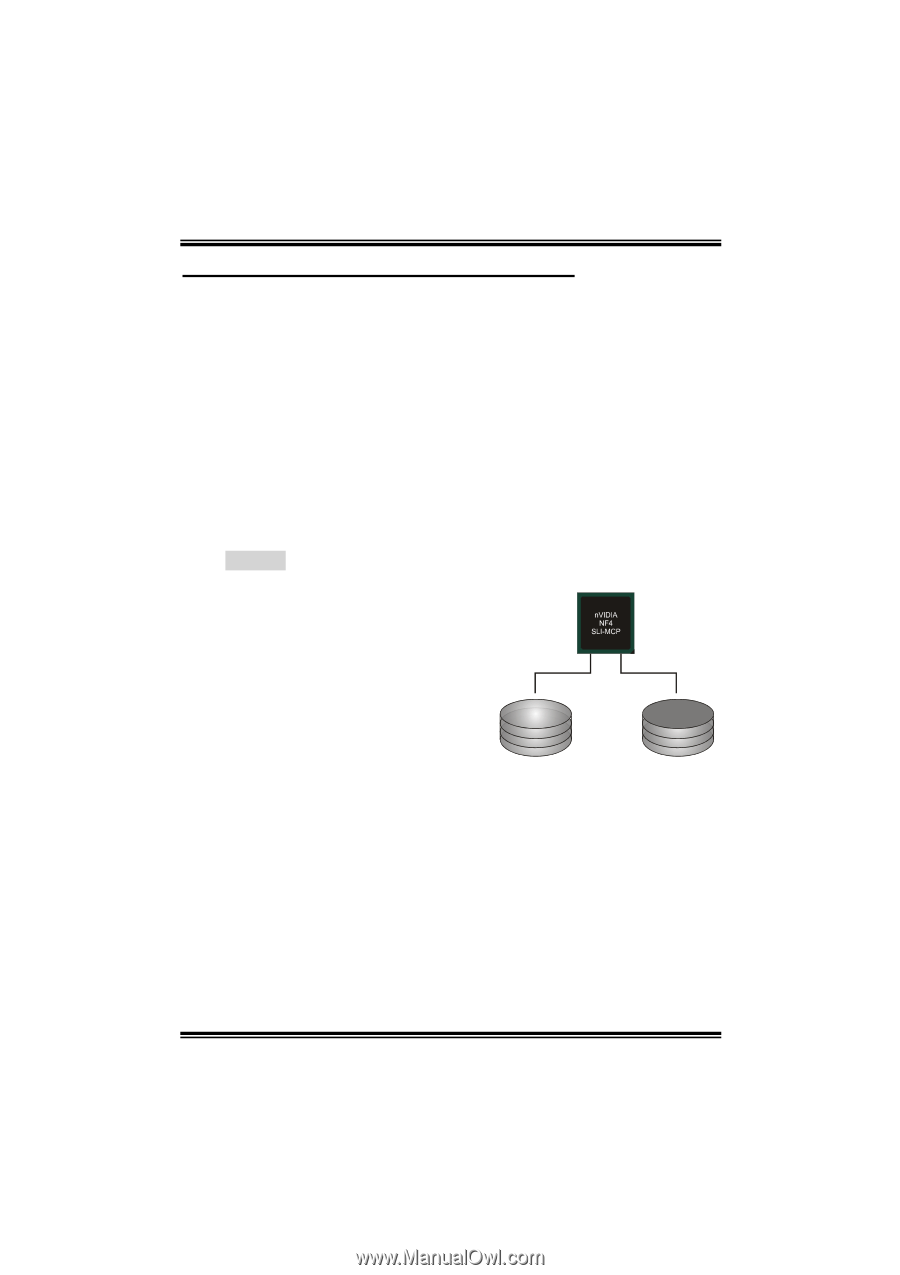
Nvidia Raid Functions
 |
View all Biostar N4SIE-A7 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 31 highlights
N4SIE-A7 CHAPTER 6: NVIDIA RAID FUNCTIONS 6.1 OPERATION SYSTEM λSupports Windows XP Home/Professional Edition, and Windows 2000 Professional. 6.2 RAID ARRAYS NVRAID supports the following types of RAID arrays: RAID 0: RAID 0 defines a disk striping scheme that improves disk read and writes times for many applications. RAID 1: RAID 1 defines techniques for mirroring data. RAID 0+1: RAID 0+1 combines the techniques used in RAID 0 and RAID 1. Spanning (JBOD): JBOD provides a method for combining drives of different sizes in to one large disk. 6.3 HOW RAID WORKS RAID 0: The controller "stripes" data across multiple drives in a RAID 0 array system. It breaks up a large file into smaller blocks and performs disk reads and writes across multiple drives in parallel. The size of each block is determined by the strip size parameter, which you set during the creation of the RAID set based on the system Block 1 Block 2 environment. This technique reduces Block 3 Block 4 overall disk access time and offers high Block 5 Block 6 bandwidth. Features and Benefits - Drives: Minimum 1, and maximum is up to 6 or 8. Depending on the platform. - Uses: Intended for non-critical data requiring high data throughput, or any environment that does not require fault tolerance. - Benefits: provides increased data throughput, especially for large files. No capacity loss penalty for parity. - Drawbacks: Does not deliver any fault tolerance. If any drive in the array fails, all data is lost. - Fault Tolerance: No. 29