Biostar N4SIE-A7 N4SIE-A7 user's manual - Page 32
RAID 1, Spanning JBOD - downloads
 |
View all Biostar N4SIE-A7 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
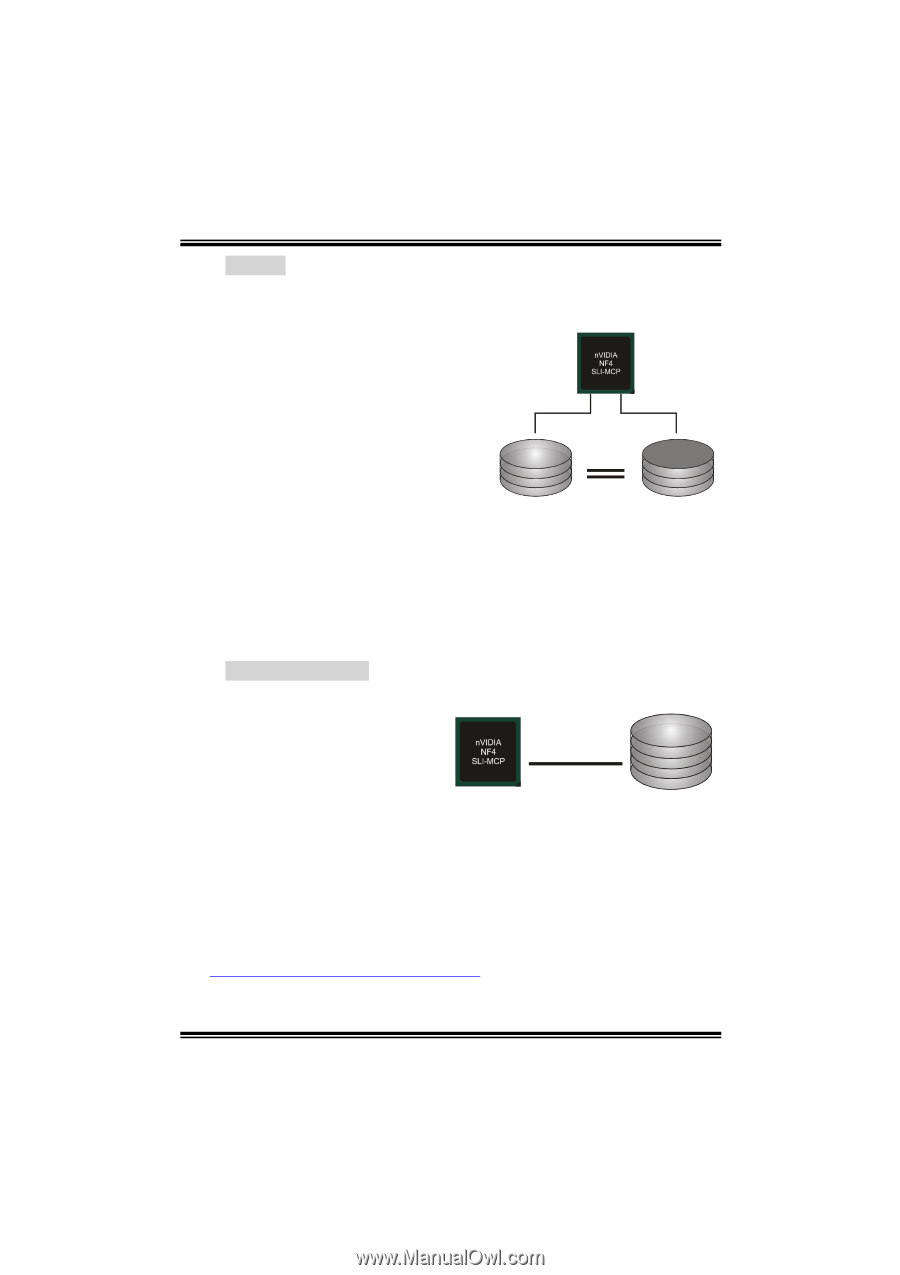
N4SIE-A7 RAID 1: Every read and write is actually carried out in parallel across 2 disk drives in a RAID 1 array system. The mirrored (backup) copy of the data can reside on the same disk or on a second redundant drive in the array. RAID 1 provides a hot-standby copy of data if the active volume or drive is corrupted or becomes unavailable because of a hardware failure. RAID techniques can be applied for high-availability solutions, or as a form of automatic backup that eliminates tedious manual backups to more Block 1 Block 1 expensive and less reliable media. Block 2 Block 2 Block 3 Block 3 Features and Benefits - Drives: Minimum 2, and maximum is 2. - Uses: RAID 1 is ideal for small databases or any other application that requires fault tolerance and minimal capacity. - Benefits: Provides 100% data redundancy. Should one drive fail, the controller switches to the other drive. - Drawbacks: Requires 2 drives for the storage space of one drive. Performance is impaired during drive rebuilds. - Fault Tolerance: Yes. Spanning (JBOD): JBOD stands for "Just a Bunch of Disks". Each drive is accessed as if it were on a standard SCSI host bus adapter. This is useful when a single drive configuration is needed, but it offers no speed improvement or fault tolerance. Single Logical Drive Disk 1: 40GB Disk 2: 80GB Disk 3: 40GB Disk 4: 120GB Features and Benefits - Uses: JBOD works best if you have odd sized drives and you want to combine them to make one big drive. - Benefits: JBOD provides the ability to combine odd size drives using all of the capacity of the drives. - Drawbacks: Decreases performance because of the difficulty in using drives concurrently. - Fault Tolerance: Yes. ※ For more detailed setup information, please refer to the Driver CD, or go to http://www.nvidia.com/page/pg_20011106217193.html to download NVIDIA nForce Tutorial Flash. 30