Biostar TFORCE 6100 AM2 Setup Manual - Page 28
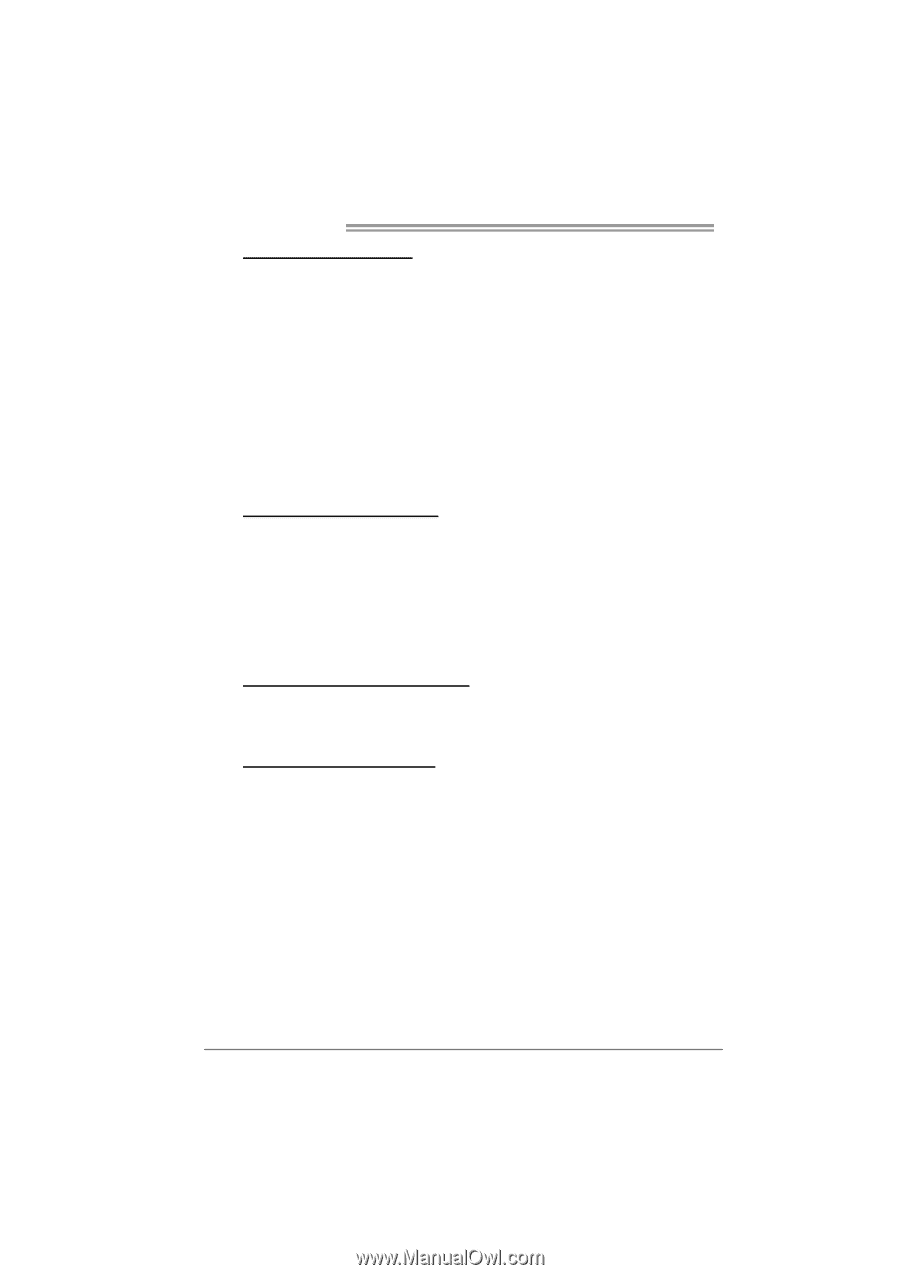
CPU Voltage, CPU Frequency, Hammer CPU Multiplier, Memory Voltage, Memclock Frequency, PCIE Clock,
 |
View all Biostar TFORCE 6100 AM2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 28 highlights
Motherboard Manual CPU Overclock Setting: CPU Voltage: This function will increase CPU stability when overclocking. However, the CPU temperature will increase when CPU voltage is increased. Choices: The range is from 1.2V to 1.725V, with an interval of 0.0.25V. CPU Frequency: CPU Frequency is directly in proportion to system performance. To maintain the system stability, CPU voltage needs to be increased also when raising CPU frequency. Choices: This range is from 200 to 450, with an interval of 1MHz. Hammer CPU Multiplier: The MOS allows users to downgrade the CPU ratio when overclocking. Choices: The lower limit is x4 (800MHz). The upper limit is decided by different CPU type. With an x1 (200MHz) interval. Memory Overclock Setting: Memory Voltage: This function will increase memory stability when overclocking. Choices: The range is from 1.85V to 2.0V, with an interval of 0.05V. Memclock Frequency: To get better system performance, sometimes downgrading the memory frequency is necessary when CPU frequency is adjusted over the upper limit. Choices: DDR400, DDR 533, DDR 667, DDR 800 (MHz). PCI-Express Overclock Setting: PCIE Clock: It helps to increase VGA card performance. Choices: The range is from 100 to 145, with an interval of 1MHz. Chipset Overclock Setting: NB/SB Voltage Regulator: This function will increase chipset stability when overclocking. Choices: 1.52V, 1.60V, 1.68V, 1.76V. HT Frequency: We recommend users to set this item at "x4" when overclocking. Choices: x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, Auto. 26