Casio FX 115ES User Guide - Page 38
Differential Calculations - derivatives on
 |
UPC - 079767171131
View all Casio FX 115ES manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
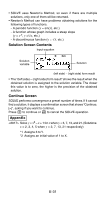
k Differential Calculations Your calculator performs differential calculations by approximating the derivative based on centered difference approximation. d/dx( f(x), a, tol ) f(x): Function of X (All non-X variables are treated as constants.) a: Input a value to specify the point for which the derivative should be obtained (differential point) tol: Tolerance range (input/output format: Linear) • You can omit specification of the tolerance range. A default value of 1 × 10-10 is used when you do. • ∫(, d/dx(, Pol(, Rec(, and Σ( cannot be used within f(x), a, or tol. • Differential calculations can be performed in the COMP Mode only. • When performing a differential calculation involving trigonometric functions, specify Rad as the calculator's default angle unit. • A "Time Out" error occurs when a differential calculation ends without the ending condition being fulfilled. • A smaller tol value provides better precision, but it also causes the calculation to take more time. Specify a tol value that is 1 × 10-14 or greater. • You cannot input a tol value when using Math format. • Inaccurate results and errors can be caused by the following : - discontinuous points in x values - extreme changes in x values - inclusion of the local maximum point and local minimum point in x values - inclusion of the inflection point in x values - inclusion of undifferentiable points in x values - differential calculation results approaching zero • Pressing A will interrupt an ongoing differential calculation. Appendix Determine f '( π ) when f(x) = sin(x) 2 (tol specification omitted.) d (3x2 - 5x + 2, 2, 1×10-12) = 7 dx E-36