Cisco CISCO1005-CH Deployment Guide - Page 28
Basic Guidelines with Optional Site Survey, Example Basic Guidelines Process
 |
UPC - 746320013343
View all Cisco CISCO1005-CH manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 28 highlights
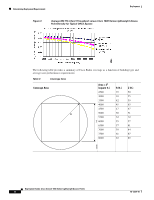
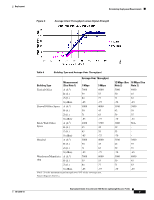
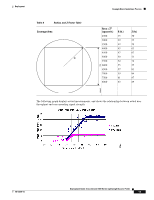
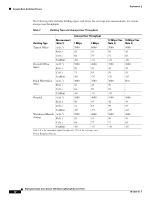
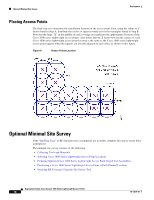
Example Basic Guidelines Process Deployment Basic Guidelines with Optional Site Survey The Basic Guideline approach is based on empirical data from existing wireless deployments and is adequate for most deployments. This approach is based on most enterprise buildings having common RF characteristics, and that only a part of the building needs to be characterized to verify the access point coverage for the entire building. This approach leverages the algorithms built into the Cisco WLAN Solution Radio Resource Management (RRM) that ensure that the overlap between access points is minimized and that coverage holes are detected and eliminated before clients find them. When deploying 802.11 wireless LANs to support Voice over IP (VoIP) telephones, such as SpectraLink NetLink Telephones, a few special considerations are needed in the deployment process. When deploying an 802.11 voice system, full coverage with an average user throughput of 5 Mbps or more should be used. Areas such as stairways, bathrooms, cafeterias and outside areas may require special consideration and access points. These are areas that are not typically critical for data users but are critical coverage areas for voice users who want seamless coverage. Example Basic Guidelines Process This section describes the basic factors that you need to consider before deploying access points. Refer to each of the sections below for a detailed explanation: • Determining the Radius and Z Factor • Determining How Many Access Points are Needed • Optional Minimal Site Survey • Placing Access Points Determining the Radius and Z Factor This section helps you to determine the coverage area of a Cisco Radio based on the building type and desired average user performance using the table below. The Z factor represents the length of a square that corresponds to the coverage area of the access point. Deployment Guide: Cisco Aironet 1000 Series Lightweight Access Points 10 78-17279-01