Compaq 307560-001 PCI Bus Balancing and Optimization on Compaq ProLiant Server - Page 3
Xecutive, Ummary, Rchitecture
 |
UPC - 743172470379
View all Compaq 307560-001 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
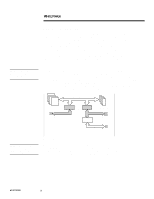
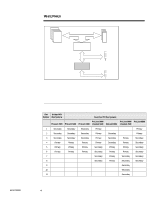
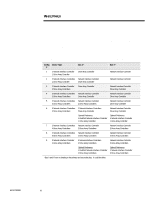
WHITE PAPER (cont.) NOTE: Table 1 lists the Compaq ProLiant family of servers that embody the dual-peer PCI bus architecture. NOTE: Table 1 lists the Compaq ProLiant family of servers that embody the bridged PCI bus architecture. ECG073/0398 ... EXECUTIVE SUMMARY With the introduction of the Compaq ProLiant 5000 Server and its dual-peer PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) bus architecture, Compaq recommended certain configurations to balance the load between the two PCI buses and achieve optimal performance on the server. Customers now question what load balancing means, how it affects server performance and what to consider for future planning and implementation of PCI bus loading. This white paper identifies the overall importance of PCI bus balancing and provides technical configurations for achieving high performance and availability on bridged and dual-peer PCI bus architectures. The supporting facts presented along with recommendations will assist system administrators and network operators in attaining and maintaining this goal. PCI ARCHITECTURE Two basic architectures are used to connect the primary and secondary PCI bus to the host bus: the dual-peer PCI bus or the bridged PCI bus. The dual-peer bus architecture, as shown in Figure 1, provides two PCI buses independently linked to the host processor bus by means of two Host-to-PCI Bridges. Since each PCI bus runs independently, it is possible to have two PCI bus masters transferring data simultaneously thus producing more overall throughput. This is an advantage with systems that have two or more high-bandwidth peripherals. Splitting these peripherals between the two buses provides an uniformed load. Host Bus 540 MB/s Processors HostBridge to-PCI Bridge Memory Slots 133 MB/s Secondary PCI Bus 133 MB/s Primary PCI Bus PCI-to-EISA Bridge Slots 33 MB/s EISA Bus Slots Figure 1: Dual-peer PCI architecture. The bridged PCI architecture, as shown in Figure 2, requires all processed transactions on the bridged PCI bus (the secondary bus) to go through the PCI-to-PCI Bridge to reach the primary bus, then through the Host-to-PCI Bridge. In effect there is only one path to the host bus; therefore, no load balancing is required on a system with this type of architecture. 3