Compaq 307560-001 PCI Bus Balancing and Optimization on Compaq ProLiant Server - Page 5
Performance Optimization Using PCI Bus Balancing, Bus Balancing Rules
 |
UPC - 743172470379
View all Compaq 307560-001 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
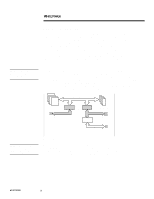
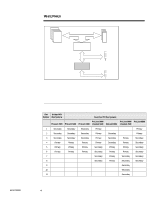
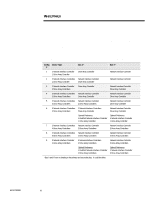
ECG073/0398 WHITE PAPER (cont.) ... PCI LOAD BALANCING One key to procuring peak server performance is optimal configuration of the I/O (Input/Output) subsystems. Because of architectural changes and enhancements incorporated into these systems, careful consideration of load balancing must be given before the initial system setup and configuration take place. For example, the Intel Pentium Pro processor is optimized for performance using PCI peripherals. The Compaq ProLiant servers that support dual-peer PCI bus architectures provide aggregate I/O throughput capability as high as 267 MB/s. The dual-peer PCI bus architecture increases configuration flexibility and allows higher levels of overall performance. However, attaining peak performance requires careful evaluation of I/O loading across both PCI buses. This means the administrator must carefully plan expansion slot usage for each device before initial configuration, as well as plan for future expansion. Performance Optimization Using PCI Bus Balancing Bus balancing is achieved by balancing the I/O throughput on each bus, thus producing the optimum performance on a system. However, not all PCI systems (i.e., bridged PCI systems) achieve performance gains when implementing bus balancing; therefore, the customer has to know when to balance the load on the system. Here are some brief recommendations. Detailed configurations are described later in the document: • For bridged architectures, load balancing is not required nor recommended. To obtain the best performance on a bridged PCI system, the primary bus should be populated first. • For dual-peer architectures load balancing is recommended. It could be helpful to split the workload between buses when I/O throughput is high. • For dual-peer architectures that have PCI Hot Plug slots, customers must consider the trade-off between high availability and high performance. This is discussed in more detail later in this document. Bus Balancing Rules Understanding how to balance the PCI load on a system can be confusing; therefore, some general guidelines or rules for balancing bus traffic are provided: 1. When installing multiple network or array controllers, split the controllers between the buses. 2. If installing an "odd" number of controllers, for example, two NICs (Network Interface Controller) and one drive array controller, split the two network controllers between the buses. Network controllers consume more bandwidth than array controllers do, so it is best to split the workload between two buses if possible. 3. Avoid putting two network controllers together in the same bus unless both buses already have a network controller installed. Note that it is better to have a system with one dual-port NIC in each bus than to have two single-port NICs in each bus. 5