Dell Brocade M5424 Brocade 7.1.0 Access Gateway Administrator's Guide - Page 21
Access Gateway Basic Concepts, Brocade Access Gateway overview - manual
 |
View all Dell Brocade M5424 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
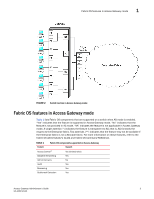
Chapter Access Gateway Basic Concepts 1 •Brocade Access Gateway overview 1 •Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode 3 •Access Gateway port types 9 •Access Gateway hardware considerations 11 Brocade Access Gateway overview Brocade Access Gateway (AG) is a Fabric OS feature that you can use to configure your Enterprise fabric to handle additional devices instead of domains. You do this by configuring F_Ports to connect to the fabric as N_Ports, which increases the number of device ports you can connect to a single fabric. Multiple AGs can connect to the DCX enterprise-class platform, directors, and switches. Access Gateway is compatible with M-EOS v9.1 or v9.6 or later, and Cisco-based fabrics v3.0 (1) or later and v3.1 (1) or later. You can use the command line interface (CLI), Web Tools, or Brocade Network Advisor (BNA) to enable and disable AG mode and configure AG features on a switch. This document describes configurations using the CLI commands. Refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference Manual, the Web Tools Administrator's Guide, or the Brocade Network Advisor User Guide for more information about AG support in those tools. After you set a Fabric OS switch to AG mode, the F_Ports connect to the Enterprise fabric as N_Ports rather than as E_Ports. Figure 1 shows a comparison of a configuration that connects eight hosts to a fabric using AG to the same configuration with Fabric OS switches in Native mode. Switches in AG mode are logically transparent to the host and the fabric. Therefore, you can increase the number of hosts that have access to the fabric without increasing the number of switch domains. This simplifies configuration and management in a large fabric by reducing the number of domain IDs and ports. Comparing Native Fabric and Access Gateway modes The following points summarize the differences between a Fabric OS switch functioning in Native operating mode and a Fabric OS switch functioning in AG operating mode: • The Fabric OS switch in Native mode is a part of the fabric; it requires two to four times as many physical ports, consumes fabric resources, and can connect to a Fabric OS fabric only. • A switch in AG mode is outside of the fabric; it reduces the number of switches in the fabric and the number of required physical ports. You can connect an AG switch to a Fabric OS, M-EOS, or Cisco-based fabric. For comparison, Figure 1 illustrates switch function in Native mode and Figure 2 illustrates switch function in AG mode. Access Gateway Administrator's Guide 1 53-1002743-01