Dell PowerEdge External Media System 1434 Improving NFS performance on HPC clu - Page 36
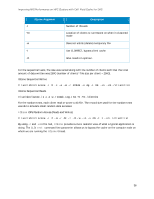
IOzone Argument, Description, IOPs Random Access Reads and Writes
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge External Media System 1434 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 36 highlights
Improving NFS Performance on HPC Clusters with Dell Fluid Cache for DAS IOzone Argument -t +m -w -I -O Description Number of threads Location of clients to run IOzone on when in clustered mode Does not unlink (delete) temporary file Use O_DIRECT, bypass client cache Give results in ops/sec. For the sequential tests, file size was varied along with the number of clients such that the total amount of data written was 256G (number of clients * file size per client = 256G). IOzone Sequential Writes # /usr/sbin/iozone -i 0 -c -e -w -r 1024k -s 4g -t 64 -+n -+m ./clientlist IOzone Sequential Reads # /usr/sbin/iozone -i 1 -c -e -w -r 1024k -s 4g -t 64 -+n -+m ./clientlist For the random tests, each client read or wrote a 4G file. The record size used for the random tests was 4k to simulate small random data accesses. IOzone IOPs Random Access (Reads and Writes) # /usr/sbin/iozone -i 2 -w -r 4k -I -O -w -+n -s 4G -t 1 -+m ./clientlist By using -c and -e in the test, IOzone provides a more realistic view of what a typical application is doing. The O_Direct command line parameter allows us to bypass the cache on the compute node on which we are running the IOzone thread. 36