Dell PowerEdge R350 EMC BIOS and UEFI Reference Guide - Page 15
Table 20. System Security details continued, Table 21. Secure Boot Mode
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge R350 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
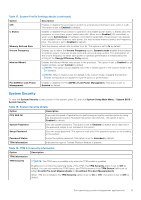
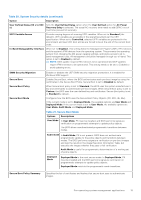
Table 20. System Security details (continued) Option Description User Defined Delay (60 s to 600 s) Sets the User Defined Delay option when the User Defined option for AC Power Recovery Delay is selected. The actual AC recovery time needs to add iDRAC root of trust time (around 50 seconds). UEFI Variable Access Provides varying degrees of securing UEFI variables. When set to Standard (the default), UEFI variables are accessible in the operating system per the UEFI specification. When set to Controlled, selected UEFI variables are protected in the environment and new UEFI boot entries are forced to be at the end of the current boot order. In-Band Manageability Interface When set to Disabled , this setting hides the Management Engine's (ME), HECI devices, and the system's IPMI devices from the operating system. This prevents the operating system from changing the ME power capping settings, and blocks access to all inband management tools. All management should be managed through out-of-band. This option is set to Enabled by default. NOTE: BIOS update requires HECI devices to be operational and DUP updates require IPMI interface to be operational. This setting needs to be set to Enabled to avoid updating errors. SMM Security Migration Secure Boot Secure Boot Policy Secure Boot Mode Enables or disables the UEFI SMM security migration protections. It is enabled for Windows 2022 support. Enables Secure Boot, where the BIOS authenticates each pre-boot image by using the certificates in the Secure Boot Policy. Secure Boot is set to Disabled by default. When Secure Boot policy is set to Standard, the BIOS uses the system manufacturer's key and certificates to authenticate pre-boot images. When Secure Boot policy is set to Custom, the BIOS uses the user-defined key and certificates. Secure Boot policy is set to Standard by default. Configures how the BIOS uses the Secure Boot Policy Objects (PK, KEK, db, dbx). If the current mode is set to Deployed Mode, the available options are User Mode and Deployed Mode. If the current mode is set to User Mode, the available options are User Mode, Audit Mode, and Deployed Mode. Table 21. Secure Boot Mode Options Descriptions User Mode In User Mode, PK must be installed, and BIOS performs signature verification on programmatic attempts to update policy objects. The BIOS allows unauthenticated programmatic transitions between modes. Audit mode In Audit Mode, PK is not present. BIOS does not authenticate programmatic update to the policy objects and transitions between modes. The BIOS performs a signature verification on pre-boot images and logs the results in the image Execution Information Table, but executes the images whether they pass or fail verification. Audit Mode is useful for programmatic determination of a working set of policy objects. Deployed Mode Deployed Mode is the most secure mode. In Deployed Mode, PK must be installed and the BIOS performs signature verification on programmatic attempts to update policy objects. Deployed Mode restricts the programmatic mode transitions. Secure Boot Policy Summary Specifies the list of certificates and hashes that secure boot uses to authenticate images. Pre-operating system management applications 15