Dell PowerStore 5200T Common Event Enabler 8.9.7.1 Release Notes - Page 2
Product description
 |
View all Dell PowerStore 5200T manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 2 highlights
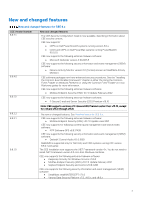
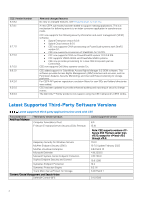
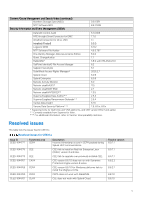
Document revision 02 01 Date April 2017 December 2016 Description Updated for release 8.2.0.0 Initial release for 8.0.0.0 Product description The Dell Common Event Enabler (CEE) framework is used to provide a working environment for the following facilities. • CEE Common AntiVirus Agent (CAVA) provides an antivirus solution for Dell systems (for example, the Dell Unity or PowerStore series). It uses an industry-standard Common Internet File System (CIFS) or Server Message Block (SMB) protocol in a Microsoft Windows Server® environment. CAVA uses third-party antivirus software to identify and eliminate known viruses before they infect files on the system. The Using the Common Event Enabler on Windows Platforms guide contains information for CAVA customers. VNXe customers should refer to Using a VNXe System with CIFS Shared Folders for specific CAVA information. Both documents are available on Online Support. Refer to the Dell Unity system's online help for antivirus details. • CEE Common Event Publishing Agent (CEPA) is a mechanism whereby applications can register to receive event notification and context from sources such as Dell Unity or PowerStore systems. The event publishing agent delivers to the consuming application both event notification and associated context in one message. Context may consist of file metadata or directory metadata that is needed to decide business policy. The Using the Common Event Enabler on Windows Platforms and Using the Common Event Enabler on Linux Platforms guides on Online Support contain information about using CEPA for Windows and Linux customers, respectively. Refer to the Dell Unity system's online help for details about using Events Publishing. • The CEPA sub-facilities include: Auditing-A mechanism for delivering post-events to registered consumer applications in a synchronous manner. Events are delivered individually in real-time. Backup-A mechanism for delivering post-events in bulk mode to backup applications. A backup-specific delivery cadence is based on either a time period or a number of events. CQM-A mechanism for delivering pre-events to registered consumer applications in a synchronous manner. Events are delivered individually in real-time, allowing the consumer application to exercise business policy on the event. Index-A mechanism for delivering events to Splunk Enterprise or the Splunk Cloud in asynchronous mode. The delivery cadence is based on a time period or a number of events. MessageExchange-A mechanism for delivering post-events in asynchronous mode, when needed, without consumer use of the CEPA API. Events are published from CEPA to the RabbitMQ CEE_Events exchange. A consumer application creates a queue for itself in the exchange from which it can retrieve events. Note: RabbitMQ is supported only for Dell Unity and VNX systems running CEE version 8.8.2.1 and earlier. VCAPS-A mechanism for delivering post-events in asynchronous mode. The delivery cadence is based on a time period or a number of events. Note: If both CQM events and Auditing events are present, CEPA delivers events to the CQM application first, and then delivers events to the Auditing application. While the CEE framework includes the CAVA and CEPA facilities and their associated sub-facilities, they can run independently of each other or run together. 2