Dell PowerVault TL2000 Dell PowerVault ML6000 Encryption Key Manager User's - Page 18
Encryption Key Processing by Other Applications, PowerVault TL2000 and TL4000 Tape Libraries - backup exec
 |
View all Dell PowerVault TL2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
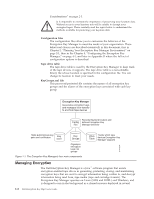
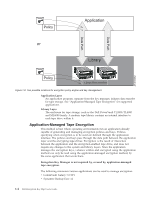
written to tape. The Encryption Key Manager selects a pre-generated DK in round robin fashion. DKs are reused on multiple tape cartridges when an insufficient | number of DKs have been pre-generated. The DK is sent to the LTO 4 or the LTO 5 tape drive in encrypted or wrapped form by the Encryption Key Manager. The | LTO 4 and LTO 5 tape drives unwrap this DK and use it to perform encryption or | decryption. However, no wrapped key is stored anywhere on the LTO 4 or the | LTO 5 tape cartridges. After the encrypted volume is written, the DK must be accessible based on the alias or key label, and available to the Encryption Key Manager in order for the volume to be read. Figure 1-3 illustrates this process. The Dell Encryption Key Manager also gives you the ability to organize your symmetric keys for LTO encryption into key groups. In this way, you can group keys according to the type of data they encrypt, the users who have access to them, or by any other meaningful characteristic. See "Creating and Managing Key Groups" on page 3-14 for more information. Encryption Key Processing by Other Applications | In application-managed tape encryption, unencrypted data is sent to the LTO 4 and | LTO 5 Tape Drives and converted to ciphertext using a symmetric DK provided by the application, and is then written to tape. The DK is not stored anywhere on the tape cartridge. Once the encrypted volume is written, the DK must be in a location available to the application, a server database, for example, in order for the volume to be read. | LTO 4 and LTO 5 Tape Drives can use applications such as Yosemite (for Dell PowerVault TL2000 and TL4000 Tape Libraries), CommVault, and Symantec Backup Exec for application-managed encryption. | Alternatively, LTO 4 and LTO 5 Tape Drives can be used by applications that use the T10 command set to perform encryption. The T10 command set uses symmetric 256-bit AES keys provided by the application. T10 can use multiple, unique DKs per tape cartridge, and even write encrypted data and clear data to the same tape cartridge. When the application encrypts a tape cartridge, it selects or generates a DK using a method determined by the application and sends it to the tape drive. The key is not wrapped with an asymmetric public key and it is not stored on the tape cartridge. Once the encrypted data is written to tape, the DK must be in a location available to the application in order for the data to be read. The process for application-managed and library-managed encryption tape encryption is shown in Figure 1-3. a14m0236 Clear Data DK Esym{data,DK} Cipher Text Encrypted Tape Figure 1-3. Encryption Using Symmetric Encryption Keys. Library-Managed and Application-Managed Encryption on | LTO 4 and LTO 5 Tape Drives. 1-6 Dell Encryption Key Mgr User's Guide