Dell Vostro 15 3568 Vostro 15-3568 Owners Manual - Page 59
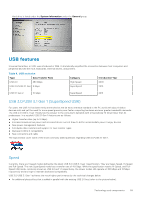
USB features, USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 SuperSpeed USB, Speed
 |
View all Dell Vostro 15 3568 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 59 highlights
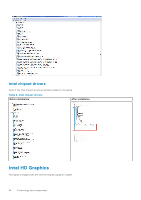
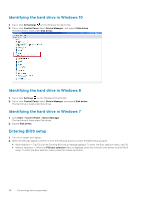
Hard drive is listed under the System Information under the General group. USB features Universal Serial Bus, or USB, was introduced in 1996. It dramatically simplified the connection between host computers and peripheral devices like mice, keyboards, external drivers, and printers. Table 4. USB evolution Type Data Transfer Rate USB 2.0 480 Mbps USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 5 Gbps 1 USB 3.1 Gen 2 10 Gbps Category High Speed SuperSpeed SuperSpeed Introduction Year 2000 2010 2013 USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 (SuperSpeed USB) For years, the USB 2.0 has been firmly entrenched as the de facto interface standard in the PC world with about 6 billion devices sold, and yet the need for more speed grows by ever faster computing hardware and ever greater bandwidth demands. The USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 finally has the answer to the consumers' demands with a theoretically 10 times faster than its predecessor. In a nutshell, USB 3.1 Gen 1 features are as follows: ● Higher transfer rates (up to 5 Gbps) ● Increased maximum bus power and increased device current draw to better accommodate power-hungry devices ● New power management features ● Full-duplex data transfers and support for new transfer types ● Backward USB 2.0 compatibility ● New connectors and cable The topics below cover some of the most commonly asked questions regarding USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1. Speed Currently, there are 3 speed modes defined by the latest USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 specification. They are Super-Speed, Hi-Speed and Full-Speed. The new SuperSpeed mode has a transfer rate of 4.8 Gbps. While the specification retains Hi-Speed, and FullSpeed USB mode, commonly known as USB 2.0 and 1.1 respectively, the slower modes still operate at 480 Mbps and 12 Mbps respectively and are kept to maintain backward compatibility. USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 achieves the much higher performance by the technical changes below: ● An additional physical bus that is added in parallel with the existing USB 2.0 bus (refer to the picture below). Technology and components 59