Fujitsu ST5111 User Guide - Page 60
Before Using the Wireless LAN
 |
UPC - 611343078443
View all Fujitsu ST5111 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 60 highlights
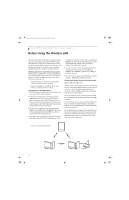
Osian_UG.book Page 48 Monday, October 9, 2006 1:24 PM Stylistic ST5100 Series Tablet PC User's Guide - Appendix A Before Using the Wireless LAN This manual describes the procedures required to properly setup and configure the integrated Wireless LAN Mini-PCI device (referred to as "WLAN device" in the rest of the manual). Before using the WLAN device, read this manual carefully to ensure it's correct operation. Keep this manual in a safe place for future reference. Wireless LAN Devices Covered by this Document This document is applicable to systems containing one of the following two devices. Most of the procedures are identical. Sections that differ between the two devices have been noted in the text: ■ Intel® PRO/Wireless 3945ABG (WM3945ABG) Network Connection (802.11a+b/g) ■ Atheros® AR5006EXS (AR5BXB6) Mini-Card Wireless network card (802.11a+b/g) Characteristics of the WLAN Device ■ The WLAN device is a Mini-PCI card attached to the main board of the mobile computer. ■ It operates in two license-free RF bands, therefore eliminating the need to procure an FCC license to operate. It operates in the 2.4GHz Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) RF band and in the lower and middle bands of the 5GHz Unlicensed National Information Infrastructure (UNII) bands. ■ The WLANs are capable of three operating modes, IEEE802.11a, IEEE802.11b and IEEE802.11g, wireless LAN standards governed by the IEEE (Institute of Electronics and Electrical Engineers). ■ Encoding of data is modulated using Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Complementary Code Keying (CCK) when the WLAN device is operating in IEEE 802.11b mode and Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) when operating in IEEE802.11a or IEEE802.11g mode. ■ The WLAN device is Wi-Fi certified and operates at the maximum data transfer rate of 54 Mbps in IEEE802.11a or IEEE802.11g mode and 11 Mbps in IEEE802.11b mode. ■ The WLAN device supports the following encryption methods - WEP, TKIP, and AES encryption. Wireless LAN Modes Using this Wireless Module Ad Hoc Mode (See Figure A-1) "Ad Hoc Mode" refers to a type of wireless network that involves connecting multiple computers without the use of an Access Point. Network connectivity between computers can be established using only wireless LAN cards in a peer-to-peer fashion. Ad Hoc networks are an easy and inexpensive method for establishing network connectivity between multiple computers. In Ad Hoc mode, you can use Microsoft Network functions, such as File and Print Sharing to share folders, printers, or other peripheral devices, and exchange files with other computers. To use Ad Hoc Mode, you must set the same SSID and the same encryption key for all the computers that are connected. Communication between computers in an Ad Hoc network will occur provided they are within each other's RF coverage area. Figure A-1. Ad Hoc Mode Network 48