HP 800 HP DTC Cabling and Racking Guide - Page 80
Environmental effects, Shielded cables
 |
View all HP 800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 80 highlights
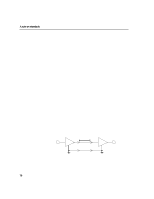
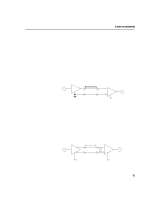
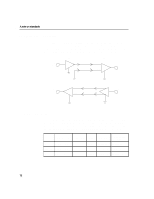
8 A note on standards Environmental effects Environmental effects, such as device-to-device ground shifts and conducted emissions can affect the reliable operation of RS-422 and RS-423 interfaces. The best measure of these effects is the common-mode voltage. Common mode voltage is defined differently for RS-422 and RS-423. According to the RS-422 standard, the common mode voltage at the receiver must be less than 7 volts to ensure reliable operation. The common mode voltage is defined by the sum of ground potential difference between the driver and receiver ground points, common mode noise, and the common mode offset (the drivers common mode voltage). The RS-423 standard specifies a common mode voltage of 4 volts. In this case, the common mode voltage is defined by the sum of the ground potential difference between the driver and receiver ground points and common mode noise. Shielded cables Shielded cables increase the immunity of data communications cables to electromagnetic energy and reduce common mode noise seen by the receiver. They also decrease emissions from the data communications cable. When using shielded cables, it is advisable to connect the shield to the chassis on the system side only. Shielded cables are not required by the RS-422 or RS-423 standards. Limiting the difference between the ground points at the system and the peripheral is important to ensure that the common mode range of the receiver is not exceeded. This is more difficult as distance sbecome greater between the system and the peripheral, and is highly dependent on the environment. It is often necessary to connect the system and peripheral to the same ground point. Otherwise, a large difference in ground potential may develop. A large ground potential difference may cause permanent damage to a system or to peripherals. Whilst Hewlett-Packard equipment is protected against this kind of damage, no such protection can be one hundred percent effective. 74