HP Professional 8000 Highly Parallel System Architecture for Compaq Profession - Page 11
Crossbar Switch Architecture, Crossbar, Switch
 |
View all HP Professional 8000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
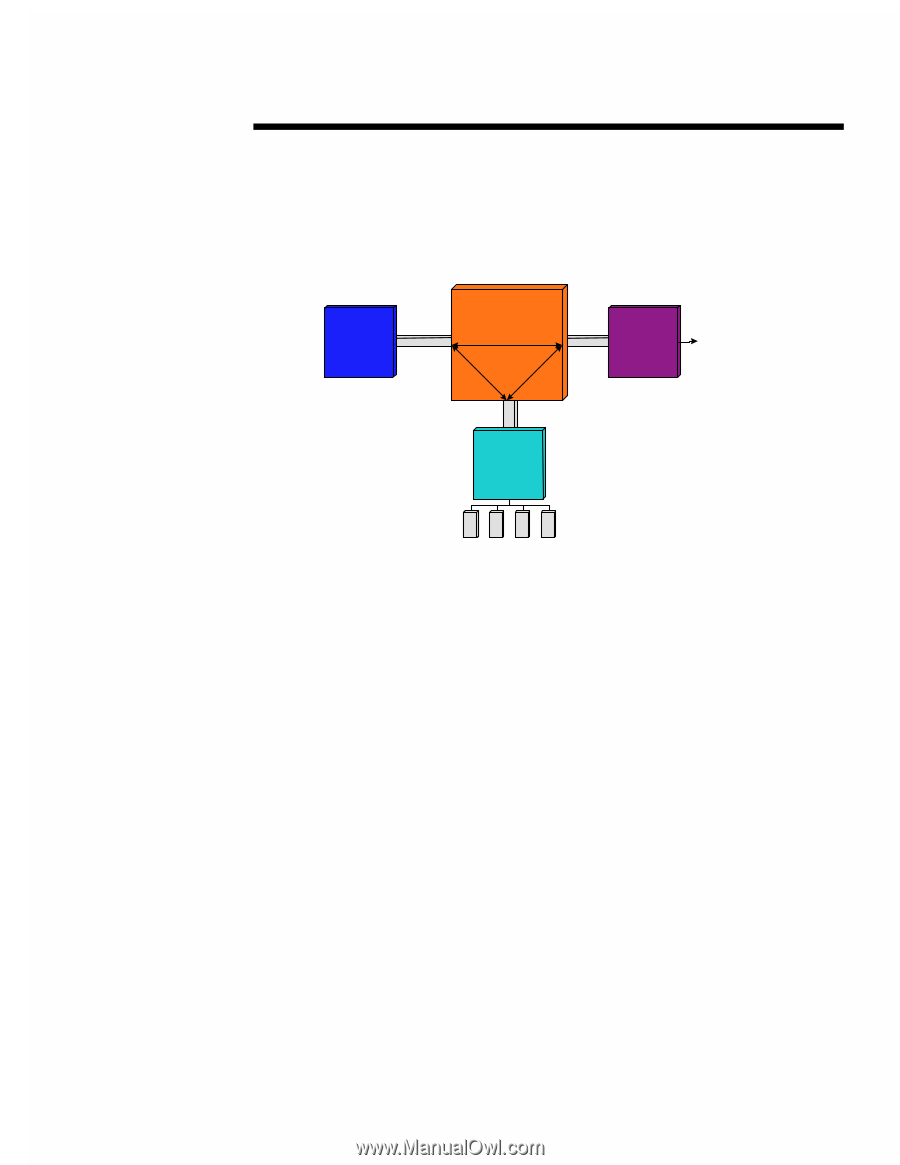
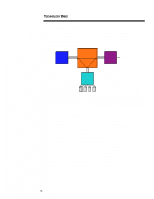
ECG066/1198 TECHNOLOGY BRIEF (cont.) ... Crossbar Switch Architecture A crossbar switch architecture provides multiple, independent paths to system memory. As Figure 8 illustrates, individual paths can be established to memory from each processor or I/O bus. Thus, a crossbar switch can avoid contention of multiple memory requests on a given bus. This style of crossbar switch is used in the Sun Microsystems Unified Port Architecture (UPA) and the Compaq TriFlex architectures. CPU Crossbar Switch PCI Controller PCI Slots and other Devices Memory Controller Figure 8. Crossbar switch architecture. The Sun UPA provides a peak memory bandwidth of 1.2 GB/s in its full implementation. In other Sun implementations, however, memory bandwidth is half that or less. The actual memory throughput of a Sun system with UPA architecture will be limited by the same DRAM constraints identified earlier in the section "Dual Memory Buses." By allowing separate paths to system memory, this style of crossbar switch can improve performance of both I/O traffic and processor cycles. A crossbar switch for a single processor bus, memory bus, and I/O bus can be implemented cost effectively. However, a crossbar switch is an expensive solution in a system with several buses. The reason is that all the buses must go into a single chip that has sufficient pins for each bus. This requires a large and expensive chip when several buses are implemented in the crossbar switch. A crossbar switch supporting the processor bus, two PCI buses, and two memory buses is not cost effective with today's silicon technology. Compaq chose not to use a crossbar switch because a better architectural solution was possible for the following reasons. First, the Pentium Pro processor bus is capable of running up to eight transactions simultaneously. Since the I/O cycle can be run simultaneously with processor cycles on the shared processor bus, independent paths to memory are not as critical. Furthermore, the I/O cache significantly reduces the amount of bandwidth required by each PCI bus on the processor bus. Second, having dual-peer PCI buses and two memory buses can produce significant performance increases. The new architecture using dual-peer PCI buses and dual memory controllers on a shared processor bus gives better performance than a crossbar switch with a single memory controller and a single PCI bus. Moreover, the higher performance comes at a price point well below that of a crossbar switch with dual memory controllers and dual PCI buses. 11