HP StorageWorks P2000 HP StorageWorks P2000 G3 MSA System FC/iSCSI User Guide - Page 44
Setting Network port IP addresses using DHCP, The MSA Device Discovery Tool will run. - default ip address
 |
View all HP StorageWorks P2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 44 highlights
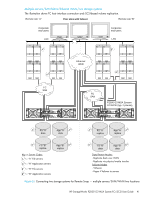
The MSA Device Discovery Tool will run. 4. Follow the instructions to discover the IP addresses of the controller or controllers. Record these IP addresses. You will use them when you want to log onto your controllers, so that you can manage them using SMU or CLI. Alternatively, you can set network port IP addresses using CLI on HP-UX, Windows, and Linux platforms. Setting Network port IP addresses using DHCP 1. Look in the DHCP server's pool of leased addresses for two IP addresses assigned to "HP StorageWorks MSA Storage." 2. Use a ping broadcast to try to identify the device through the host's ARP table. If you do not have a DHCP server, you will need to ask your system administrator to allocate two IP addresses and set them using the CLI during initial configuration (described below). Setting Network port IP addresses using the CLI If you did not use the MSA Device Discovery Tool to set network port IP values, set them manually using the CLI port and cable. If you have not done so already, you need to enable your system for using the CLI port. NOTE: For Linux systems, see Preparing a Linux computer before cabling to the CLI port on page 43. For Windows systems see Downloading a device driver for Windows computers on page 43. Network ports on controller module A and controller module B are configured with the following default values: • Management Port IP Address: 10.0.0.2 (controller A), 10.0.0.3 (controller B) • IP Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 • Gateway IP Address: 10.0.0.1 If the default IP addresses are not compatible with your network, you must set an IP address for each network port using the command-line interface (CLI) embedded in each controller module. The CLI enables you to access the system using the USB (universal serial bus) communication interface and terminal emulation software. The USB cable and CLI port support USB version 2.0. Use the CLI commands described in the steps below to set the IP address for the Network port on each controller module. Once new IP addresses are set, you can change them as needed using SMU. Be sure to change the IP address via SMU before changing the network configuration. NOTE: Changing IP settings can cause management hosts to lose access to the storage system. 1. From your network administrator, obtain an IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address for controller A, and another for controller B. Record these IP addresses so that you can specify them whenever you manage the controllers using SMU or the CLI. 2. Use the provided USB cable to connect controller A to a USB port on a host computer. The USB mini 5 male connector plugs into the CLI port as shown in Figure 15 (generic controller module is shown). 44 Connecting to the controller CLI port