Intel DZ68PL Technical product specification - Page 19
Memory Configurations - motherboard
 |
View all Intel DZ68PL manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
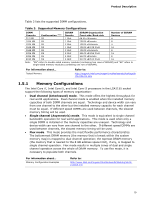
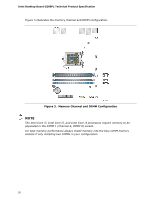
Product Description Table 3 lists the supported DIMM configurations. Table 3. Supported Memory Configurations DIMM Capacity SDRAM Configuration (Note) Density SDRAM Organization Front-side/Back-side Number of SDRAM Devices 512 MB SS 1 Gbit 64 M x16/empty 4 1024 MB SS 1 Gbit 128 M x8/empty 8 1024 MB SS 2 Gbit 128 M x16/empty 4 2048 MB DS 1 Gbit 128 M x8/128 M x8 16 2048 MB SS 2 Gbit 128 M x16/empty 8 4096 MB DS 2 Gbit 256 M x8/256 M x8 16 4096 MB SS 4 Gbit 512 M x8/empty 8 8192 MB DS 4 Gbit 512 M x8/512 M x8 16 Note: "DS" refers to double-sided memory modules (containing two rows of SDRAM) and "SS" refers to single-sided memory modules (containing one row of SDRAM). For information about... Tested Memory Refer to: http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/sb /CS-025414.htm 1.5.1 Memory Configurations The Intel Core i7, Intel Core i5, and Intel Core i3 processors in the LGA1155 socket support the following types of memory organization: • Dual channel (Interleaved) mode. This mode offers the highest throughput for real world applications. Dual channel mode is enabled when the installed memory capacities of both DIMM channels are equal. Technology and device width can vary from one channel to the other but the installed memory capacity for each channel must be equal. If different speed DIMMs are used between channels, the slowest memory timing will be used. • Single channel (Asymmetric) mode. This mode is equivalent to single channel bandwidth operation for real world applications. This mode is used when only a single DIMM is installed or the memory capacities are unequal. Technology and device width can vary from one channel to the other. If different speed DIMMs are used between channels, the slowest memory timing will be used. • Flex mode. This mode provides the most flexible performance characteristics. The bottommost DRAM memory (the memory that is lowest within the system memory map) is mapped to dual channel operation; the topmost DRAM memory (the memory that is nearest to the 8 GB address space limit), if any, is mapped to single channel operation. Flex mode results in multiple zones of dual and single channel operation across the whole of DRAM memory. To use flex mode, it is necessary to populate both channels. For information about... Memory Configuration Examples Refer to: http://www.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/sb/cs011965.htm 19