Konica Minolta bizhub PRESS C70hc IC-601 Color Centro User Guide - Page 275
The acronym for Line Printer Request/Line Printer Daemon. This is a printing method
 |
View all Konica Minolta bizhub PRESS C70hc manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 275 highlights
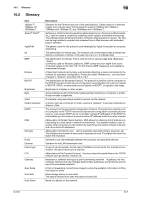
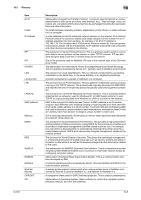
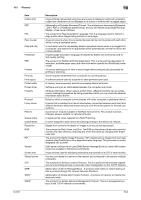
16.2 Glossary Item HTTP Install IP Address IPP IPX IPX/SPX LAN Local printer LPD LPR/LPD MAC address Memory NDPS NDS NetBEUI NetBIOS NetWare Nprinter/ Rprinter OHP/OHT OS 16 Description Abbreviation of HyperText Transfer Protocol. A protocol used to transmit or receive data between a web server and client (web browser, etc.). Files of image, voice, animation, etc. correlated with the document can be exchanged including the expression form and other information. To install hardware, operating systems, applications, printer drivers, or other software on to a computer. A code (address) to identify individual network devices on the Internet. IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4), a protocol widely used today, adopts a 32-bit number for an IP address separated into four sections. An example of an IPv4 IP address is: 192.168.1.10. On the other hand, IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6), the next generation protocol, adopts 128-bit IP addresses. An IP address is allocated to all computers and other devices connected to the Internet. The acronym for Internet Printing Protocol. This is a protocol used to send or receive print data or control printers via the Internet or other TCP/IP network. IPP can also send and print data to printers in remote areas via the Internet. One of the protocols used for NetWare. IPX runs in the network layer of the OSI reference model. The abbreviation for Internetwork Packet Exchange/Sequenced Packet Exchange. This is a protocol developed by Novell, Inc., typically used in NetWare environments. The acronym for Local Area Network. This is a network constructed by connecting computers on the same floor, in the same building, or in neighboring buildings. A printer connected to a parallel or USB port of a computer. The acronym for Line Printer Daemon. This is a platform-independent printer protocol running on the TCP/IP network. The protocol was originally developed for BSD UNIX, and has become one of the printing protocols typically used among general computers. The acronym for Line Printer Request/Line Printer Daemon. This is a printing method implemented via networks, used for Windows NT or UNIX based systems. It uses TCP/IP to output printing data from Windows or UNIX to a printer on the network. MAC is the acronym for Media Access Control. A MAC address is an ID number unique to each Ethernet card, enabling sending or receiving data to or from other Ethernet cards. A Mac address is a 48-bit number. The first 24 bits are controlled by IEEE and used to allocate a unique number to each manufacture, whereas the latter 24 bits are used by each manufacturer to assign a unique number to each card. Unit to save data temporarily. Some types of memory retain data even after the power is turned off, while others not. The acronym for Novell Distributed Print Services. This provides a high performance printing solution in NDS environments. Using NDPS for the print server simplifies and automates complicated management activities related to printer use. For example, you can print to a desired printer or automatically download the printer driver for a newly installed printer. NDPS print servers also integrate management related to the network printers. The acronym for Novell Directory Services. This allows the centralized management in a hierarchical structure of shared resources such as servers, printers and users information on the network, as well as the access privilege and other information related to the users. The abbreviation for NetBIOS Extended User Interface. This is a network protocol developed by IBM. NetBEUI enables you to construct a small-scale network simply by configuring computer names. Abbreviation of Network Basic Input Output System. This is a communication interface developed by IBM. A network operating system developed by Novell. This uses NetWare IPX/SPX for the communication protocol. A remote printer support module used when using a printer server in NetWare environments. Rprinter is used for NetWare 3.x, and Nprinter for NetWare 4.x. A transparent sheet used for OHP (Overhead projector). This is used for presentations. Abbreviation of Operating System. Basic software to control the computer system. Windows, MacOS, and Unix are examples. IC-601 16-8