Lowrance HDS-9 Gen2 Touch Installation Manual - Page 25
Micro-C T junctions
 |
View all Lowrance HDS-9 Gen2 Touch manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 25 highlights
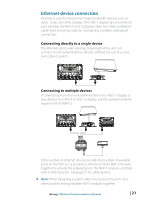
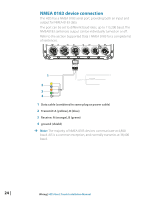
In smaller NMEA 2000 systems, the power connection may be made anywhere in the system, For larger systems introduce power at a central point in the backbone to 'balance' the voltage drop of the network. Use a power cable without termination. ¼¼ Note: When joining a NMEA 2000 network with a Simrad SimNet network, it is important that you do not introduce power to both. ¼¼ Note: Do not connect the power cable to the same terminals as the autopilot computer, pulse radar, bow thruster or other high current devices - the network may be affected by voltage drop when these devices are operated. Avoid connection to the engine starting batteries where possible. The following diagram demonstrates a typical small NMEA 2000 network: 1 2 3 5 _+ 12 V DC 6 T 9 7 8 1 GPS antenna 2 HDS Display 3 Broadband radar interface 4 SonicHub 5 'Drop' cables (should not exceed 6m (20') each) 6 Power cable 7 Micro-C T junctions 8 Backbone 9 Micro-C terminator (one male, one female) 4 T 9 Wiring | HDS Gen2 Touch Installation Manual | 23