Meade Scope 80mm User Manual - Page 13
Place the object to be viewed at
 |
View all Meade Scope 80mm manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
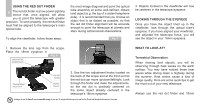
objects will seem to move through the field of when reading star maps, or inspecting the view of the eyepiece more rapidly. telescope. Do not use a regular flashlight or turn on other lights when observing with a Place the object to be viewed at the edge of the field and, without touching the telescope, watch it drift through the field to the other side before repositioning the telescope so that the object to be viewed is again placed at the edge of the field, ready to be further observed. Vibrations: Avoid touching the eyepiece while observing through the telescope. Vibrations group of other astronomers. You can make your own red filtered flashlight by taping red cellophane over a flashlight lens. Viewing through windows: Avoid setting up the telescope inside a room and observing through an opened or closed window pane. Images may appear blurred or distorted due to temperature differences between inside and outside air. Also, it is a good idea to allow resulting from such contact will cause the image to move. Avoid observing sites where vibrations cause image movement (for example, near railroad tracks). Viewing from the upper floors of a building may also cause image movement. Let your eyes "dark-adapt": Allow five or ten minutes for your eyes to become "dark adapted" before observing. Use a red TOO MUCH POWER? Can you ever have too much power? If the type of power you're referring to is eyepiece magnification, yes you can! The most common mistake of the beginning observer is to "overpower" a telescope by using high magnifications which the telescope's aperture and atmospheric conditions cannot reasonably support. Keep in mind that a smaller, but bright and well-resolved image is far superior to one that is larger, but dim and poorly resolved. Powers above 400x should be employed only under the steadiest atmospheric conditions. filtered flashlight to protect your night vision Looking at or near the Sun will cause irreversible damage to your eye. Do not point this telescope at or near the Sun. Do not look through the telescope as it is moving. your telescope to reach the ambient (surrounding) outside temperature before starting an observing session. 11 When to observe: Planets and other objects viewed low on the horizon often lack sharpness the same object, when observed higher in the sky, will appear sharper and have greater contrast. Try reducing power (change your eyepiece) if your image is fuzzy or shimmers. Keep in mind that a bright, clear, but smaller image is more interesting than a larger, dimmer, fuzzy one. Using too high a power eyepiece is one of the most common mistakes made by new astronomers. Surf the Web and visit your local library: We recommend to go to your library or check out the internet for more information about astronomy. Learn about the basics: light years, orbits, star colors, how stars and planets are formed, red shift, the big bang, the different kinds of nebula, what are comets, asteroids and meteors and what is