Sanyo DP55360 Internet Use Guide - Page 6
Glossary - ethernet
 |
View all Sanyo DP55360 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
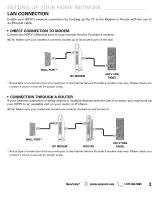
GLOSSARY Bandwidth: Digital bandwith, network bandwith or just bandwidth is a measure of available or consumed data communication resources expressed in bit/s (bits per second) or multiples of it (kbit/s, Mbit/s, etc.) Buffer: Memory used to temporarily hold data. In streaming, the buffer allows conent to continue playing uninterrupted during minor fluctuations in band width. If the buffer runs our before the connection stabilizes, the stream will have to rebuffer, or pause to allow the buffer to refill. Codec: A codec is a device or program capable of performing encoding and decoding on a digital data stream or signal. DHCP: Dynamic Host Control Protocol, DHCP, is a protocol where a DHCP server on a network hands out IP address automatically to devices that request one. Dolby Digital: Dolby Digital, or AC-3, is the common version containing up to six discrete channels of sound, with five channels for normal-range speakers. Dolby Digital Plus: Dolby Digital Plus (DD+ or E-AC-3 (Enhanced AC-3)), is a digital audio compression scheme. E-AC-3 has a number of improvements aimed at increasing quality at a given bitrate compared with legacy Dolby Digital (AC-3). Ethernet: A way of connecting equipment together in a local area network or LAN. Ethernet cables look like thick telephone cables and connect computers and other internet ready devices together or to devices like modems, routers, switches, etc. Physically the Ethernet cable consists of twisted pair copper cables (usually Cat-5 or Cat6 in home networks) terminated with RJ-45 connectors. H.264: H.264 is a state-of-the-art digital encoding format for high definition video and provides powerful compression technology that delivers a superior video experience at a low bit rate. HDMI: High-Definition Multimedia Interface. A connection type that transmits uncompressed digital video and audio signals between devices, such as: a Blu-ray Disc player and HDTV. HDMI connections process a special authorization signal between the equipment and use HDCP to encrypt the transmission. Hub: Similar to a switch except that traffic from one connection point is broadcast to all others. Internet: The internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) to serve billions of users worldwide. It carries a vast array of information resources and services, most notably the inter-linked hypertext documents of the World Wide Web (WWW) and the infrastructure to support electronic mail. IP Address: Internet Protocol Address. An IP address is numerical sets of numbers consisting of four (4) blocks of up to three (3) digits each in the range of 0 to 254. Every device on a network must have its own unique IP address. For LANs there are special sets of IPs that are used. These consist of the following blocks: 10.x.x.x - where x = a number from 0 to 254. ISP: An Internet Service Provider (ISP), usually for a monthly subscription fee, will allow a user to connect to the Internet. Some ISPs directly put their users on the Internet, while others will send a connection through its or a different company's servers. LAN: Local Area Network- A high speed data network installed in a small area such as a home or office. Multiple devices can be connected to share information and the Internet. LANs can be wired (by Ethernet cable) or wireless (Wi-Fi) Media Streaming: The process of receiving and playing back audio, video, and photos in real time from a remote source over the Internet. Examples of media streaming include: Videos on demand, Internet radio stations, Music services, and Photostreams. 6 Need help? www.sanyoctv.com 1-877-864-9604