Stihl MS 290 STIHL FARM BOSS Product Instruction Manual - Page 14
Reactive forces including kickback, Warning, Kickback, ANSI B 175.1-2000 chainsaw, kickback standard
 |
View all Stihl MS 290 STIHL FARM BOSS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
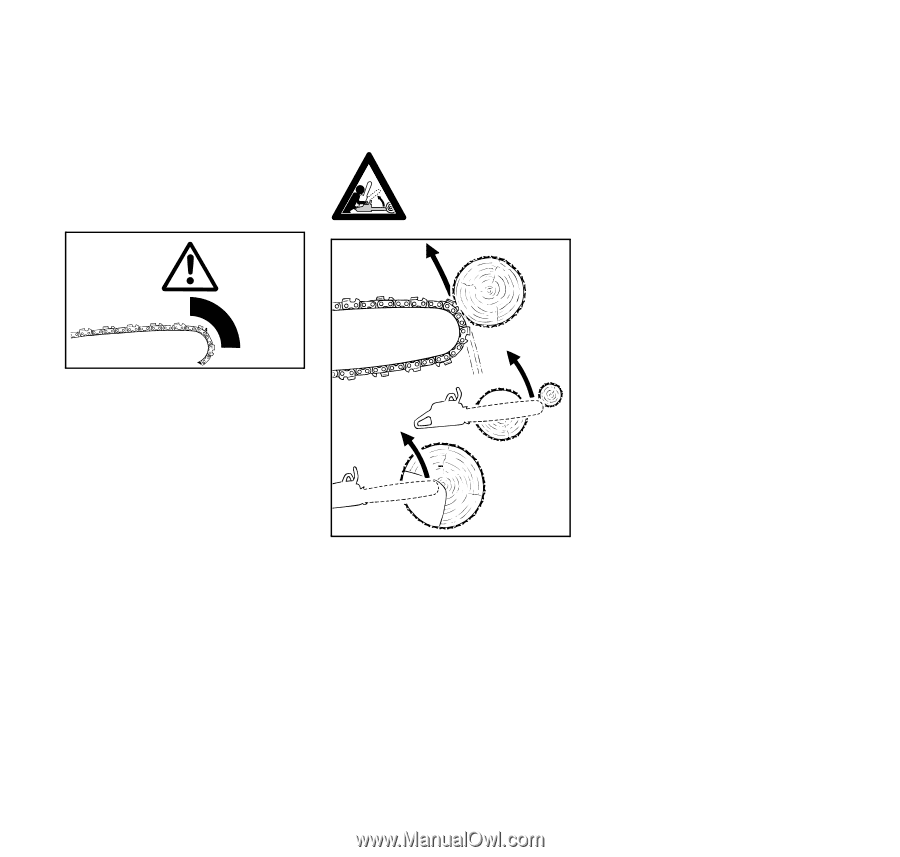
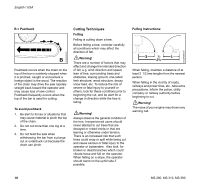
English / USA Reactive forces including kickback !Warning! Reactive forces may occur any time the chain is rotating. Reactive forces can cause serious personal injury. The powerful force used to cut wood can be reversed and work against the operator. If the rotating chain is suddenly stopped by contact with any solid object such as a log or branch or is pinched, the reactive forces may occur instantly. These reactive forces may result in loss of control, which, in turn, may cause serious or fatal injury. An understanding of the causes of these reactive forces may help you avoid the element of surprise and loss of control. Sudden surprise contributes to accidents. The most common reactive forces are: - kickback, - pushback, - pull-in. 001BA093 LÄ 001BA035 KN Kickback: Kickback may occur when the moving saw chain near the upper quadrant of the bar nose contacts a solid object or is pinched. The reaction of the cutting force of the chain causes a rotational force on the chainsaw in the direction opposite to the chain movement. This may fling the bar up and back in a ligtening fast reaction in an uncontrolled arc mainly in the plane of the bar. Under some cutting circumstances the bar moves towards the operator, who may suffer severe or fatal injury. Kickback may occur, for example, when the chain near the upper quadrant of the bar nose contacts the wood or is pinched during limbing or when it is incorrectly used to begin a plunge or boring cut. The greater the force of the kickback reaction, the more difficult it becomes for the operator to control the saw. Many factors influence the occurrence and force of the kickback reaction. These include chain speed, the speed at which the bar and chain contact the object, the angle of contact, the condition of the chain and other factors. The type of bar and saw chain you use is an important factor in the occurrence and force of the kickback reaction. Some STIHL bar and chain types are designed to reduce kickback forces. STIHL recommends the use of reduced kickback bars and low kickback chains. ANSI B 175.1-2000 chainsaw kickback standard Section 5.11 of ANSI standard B 175.1-2000, sets certain performance and design criteria related to chainsaw kickback. To comply with section 5.11 of ANSI B 175.1-2000: MS 290, MS 310, MS 390 13