TP-Link TL-SL3452 User Guide - Page 42
Defining Authentication Hosts
 |
UPC - 845973020507
View all TP-Link TL-SL3452 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 42 highlights
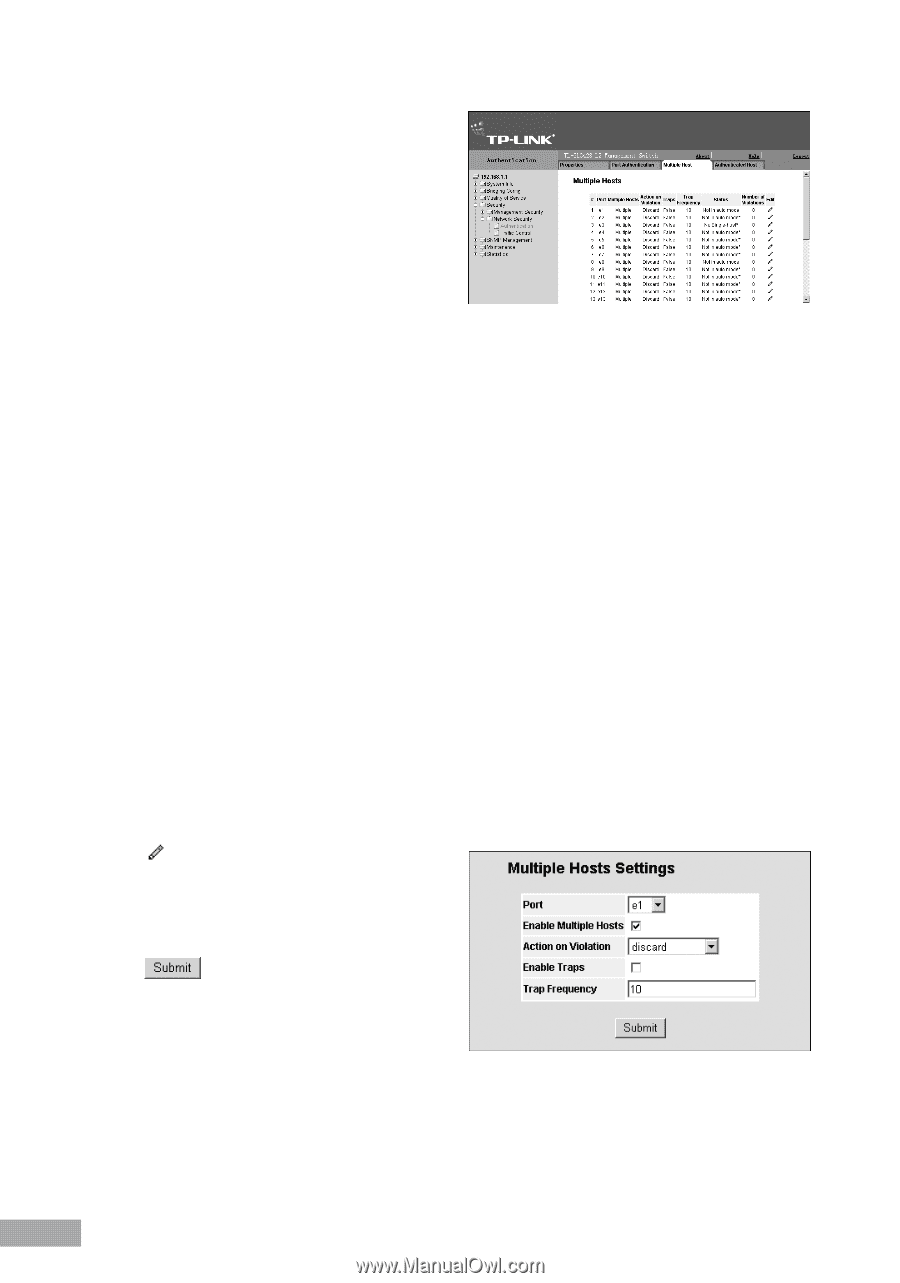
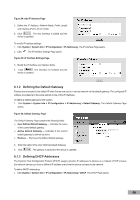
Figure 46: Multiple Hosts Page The Multiple Hosts Page contains the following fields: Port - Displays the port number for which advanced port-based authentication is enabled. Multiple Hosts - Indicates whether multiple hosts are enabled. Multiple hosts must be enabled in order to either disable the ingress-filter, or to use port-lock security on the selected port. The possible field values are: - Multiple - Multiple hosts are enabled. - Disable - Multiple hosts are disabled. Action on Violation - Defines the action to be applied to packets arriving in single-host mode, from a host whose MAC address is not the supplicant MAC address. The possible field values are: - Forward - Forwards the packet. - Discard - Discards the packets. This is the default value. - Shutdown - Discards the packets and shuts down the port. The port remains shut down until reactivated, or until the device is reset. Traps - Indicates if traps are enabled for Multiple Hosts. The possible field values are: - True - Indicates that traps are enabled for Multiple hosts. - False - Indicates that traps are disabled for Multiple hosts. Trap Frequency - Defines the time period by which traps are sent to the host. The Trap Frequency (1-1000000) field can be defined only if multiple hosts are disabled. The default is 10 seconds. Status - Indicates the host status. If there is an asterisk (*), the port is either not linked or is down. The possible field values are: - Unauthorized - Indicates that either the port control is Force Unauthorized and the port link is down, or the port control is Auto but a client has not been authenticated via the port. - Not in Auto Mode - Indicates that the port control is Forced Authorized, and clients have full port access. - Single-host Lock - Indicates that the port control is Auto and a single client has been authenticated via the port. - No Single Host - Indicates that Multiple Host is enabled. Number of Violations - Indicates the number of packets that arrived on the interface in single-host mode, from a host whose MAC address is not the supplicant MAC address. 2. Click . The Multiple Host Settings Page opens: Figure 47: Multiple Host Settings Page 3. Define the fields. 4. Click . The multiple host settings are saved, and the device is updated. 5.2.2.3 Defining Authentication Hosts The Authenticated Hosts Page contains a list of authenticated users. To define authenticated users: 1. Click System > Network Security > Authentication > Authenticated Hosts. The Authenticated Hosts Page opens: 35