3Com 3CDSG10PWR User Guide - Page 216
Electrical, Switch Features, Line Frequency, Input Voltage, Current Rating, Maximum Power, Consumption
 |
UPC - 662705520902
View all 3Com 3CDSG10PWR manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 216 highlights
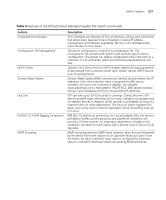
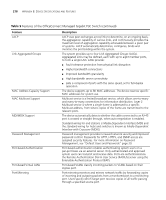
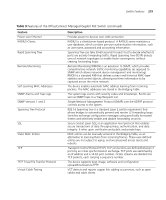
216 APPENDIX B: DEVICE SPECIFICATIONS AND FEATURES Electrical Line Frequency Input Voltage Current Rating Maximum Power Consumption Max Heat Dissipation 50/60 Hz 100-240 Vac (auto range) 2 Amp (Max) 358.4 BTU/hr (114 Watts) 79 BTU/hr Switch Features This section describes the device features. The system supports the following features: Table 9 Features of the OfficeConnect Managed Gigabit PoE Switch Feature Auto Negotiation Automatic MAC Addresses Aging Back Pressure Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Class Of Service (CoS) Description The purpose of auto negotiation is to allow a device to advertise modes of operation. The auto negotiation function provides the means to exchange information between two devices that share a point-to-point link segment, and to automatically configure both devices to take maximum advantage of their abilities. Auto negotiation is performed totally within the physical layers during link initiation, without any additional overhead to either the MAC or higher protocol layers. Auto negotiation allows the ports to do the following: ■ Advertise their abilities ■ Acknowledge receipt and understanding of the common modes of operation that both devices share ■ Reject the use of operational modes that are not shared by both devices ■ Configure each port for the highest-level operational mode that both ports can support MAC addresses from which no traffic is received for a given period are aged out. This prevents the Bridging Table from overflowing. On half duplex links, the receiver may employ back pressure (i.e. occupy the link so it is unavailable for additional traffic), to temporarily prevent the sender from transmitting additional traffic. This is used to prevent buffer overflows. ARP converts between IP addresses and MAC (i.e., hardware) addresses. ARP is used to locate the MAC address corresponding to a given IP address. This allows the switch to use IP addresses for routing decisions and the corresponding MAC addresses to forward packets from one hop to the next. Provide traffic belonging to a group preferential service (in terms of allocation of system resources), possibly at the expense of other traffic.