| Section |
Page |
| Contents |
3 |
| Chapter 1: Extending Fireworks Overview |
5 |
| Prerequisites |
5 |
| Installing an extension |
5 |
| What’s new in Extending Fireworks CS3 |
6 |
| Conventions used in this guide |
6 |
| Additional resources for extension writers |
7 |
| Chapter 2: The Fireworks Object Model |
8 |
| Using the Fireworks Object Model |
8 |
| Accessing a Fireworks document |
8 |
| Passing values |
8 |
| Fireworks Object Model calls and API calls |
9 |
| Formatting nonstandard data types |
9 |
| Color string data type |
9 |
| Mask data type |
9 |
| Matrix data type |
10 |
| Point data type |
10 |
| Rectangle data type |
10 |
| Resolution data type |
10 |
| Using Fireworks API functions |
10 |
| Zero-based indexes |
10 |
| Passing null values |
10 |
| Working with selected elements |
10 |
| Palette or panel |
11 |
| Using the common API |
11 |
| app.toggleFloater() |
11 |
| app.setFloaterVisibility() |
11 |
| app.getRootDirectory() |
11 |
| app.browseDocument() |
11 |
| Working with selected objects |
11 |
| Working with properties for any selected object |
12 |
| elementMask |
12 |
| effectList |
12 |
| Working with specific properties for selected elements |
13 |
| Hotspot |
13 |
| SliceHotspot |
13 |
| Path |
13 |
| Group |
14 |
| Instance |
14 |
| Text |
14 |
| RectanglePrimitive |
14 |
| pathAttributes |
15 |
| Global methods |
15 |
| alert(message) |
15 |
| confirm(message) |
16 |
| prompt(caption, text) |
16 |
| write(arg1, arg2, ..., argN) |
16 |
| WRITE_CSS |
17 |
| WRITE_HTML(arg1, arg2, ..., argN) |
17 |
| Core objects |
17 |
| Errors object |
18 |
| Files object |
18 |
| File Reference object |
20 |
| Find object |
21 |
| Finding and replacing text |
21 |
| Finding and replacing fonts and styles |
21 |
| Finding and replacing colors, fills, strokes, and effects |
22 |
| Finding and replacing URLs |
22 |
| Finding and replacing non-websafe colors with the closest websafe color |
22 |
| System object |
22 |
| Chapter 3: The Document object |
24 |
| The pngText property |
27 |
| Document functions |
27 |
| dom.addBehavior() |
27 |
| Using the dom.addBehavior() function |
28 |
| MM_nbGroup [down] |
28 |
| MM_nbGroup [highlight] |
29 |
| MM_nbGroup [image] |
29 |
| MM_nbGroup [out] |
30 |
| MM_simpleRollover |
30 |
| MM_statusMessage |
30 |
| MM_swapImage |
31 |
| MM_swapImgRestore |
31 |
| dom.addElementMask() |
31 |
| dom.addFrames() |
32 |
| dom.addGuide() |
32 |
| dom.addMasterPageLayer() |
33 |
| dom.addNewHotspot() |
33 |
| dom.addNewImage() |
34 |
| dom.addNewImageViaCopy() |
34 |
| dom.addNewImageViaCut() |
35 |
| dom.addNewLayer() |
35 |
| dom.addNewLine() |
36 |
| dom.addNewOval() |
36 |
| dom.addNewPage() |
37 |
| dom.addNewRectangle() |
37 |
| dom.addNewRectanglePrimitive() |
38 |
| dom.addNewSinglePointPath() |
38 |
| dom.addNewStar() |
39 |
| dom.addNewSubLayer() |
39 |
| dom.addNewSymbol() |
40 |
| dom.addNewText() |
40 |
| dom.addSwapImageBehaviorFromPoint() |
41 |
| dom.adjustExportToSize() |
41 |
| dom.adjustFontSize() |
42 |
| dom.align() |
42 |
| dom.appendPointToHotspot() |
43 |
| dom.appendPointToPath() |
43 |
| dom.appendPointToSlice() |
44 |
| dom.applyCharacterMarkup() |
44 |
| dom.applyCurrentFill() |
44 |
| dom.applyEffects() |
45 |
| dom.applyFontMarkup() |
45 |
| dom.applyStyle() |
46 |
| dom.arrange() |
46 |
| dom.attachTextToPath() |
47 |
| dom.changeCurrentPage() |
47 |
| dom.changeGuide() |
47 |
| dom.changeNineScaleGuide() |
48 |
| dom.changeSliceGuide() |
49 |
| dom.clearJPEGMask() |
49 |
| dom.clipCopy() |
50 |
| dom.clipCopyAsPaths() |
50 |
| dom.clipCopyFormats() |
51 |
| dom.clipCut() |
51 |
| dom.clipPaste() |
51 |
| dom.clipPasteAsMask() |
52 |
| dom.clipPasteAttributes() |
53 |
| dom.clipPasteFromChannelToChannel() |
53 |
| dom.clipPasteInside() |
54 |
| dom.cloneSelection() |
54 |
| dom.close() |
55 |
| dom.convertAnimSymbolToGraphicSymbol() |
55 |
| dom.convertMarqueeToPath() |
56 |
| dom.convertPathToMarquee() |
56 |
| dom.convertToAnimSymbol() |
56 |
| dom.convertToPaths() |
57 |
| dom.convertToSymbol() |
58 |
| dom.convolveSelection() |
58 |
| dom.copyHtmlWizard() |
59 |
| dom.copyToHotspot() |
59 |
| dom.cropSelection() |
60 |
| dom.deleteAllInDocument() |
60 |
| dom.deleteFrames() |
61 |
| dom.deleteLayer() |
61 |
| dom.deletePageAt() |
62 |
| dom.deletePointOnPath() |
62 |
| dom.deleteSavedSelection() |
62 |
| dom.deleteSelection() |
63 |
| dom.deleteSymbol() |
63 |
| dom.detachInstanceFromSymbol() |
64 |
| dom.detachSharedLayer() |
65 |
| dom.distribute() |
65 |
| dom.distributeLayerToFrames() |
66 |
| dom.distributeSelectionToFrames() |
66 |
| dom.dragControlPoint() |
66 |
| dom.duplicateFrame() |
67 |
| dom.duplicateLayer() |
67 |
| dom.duplicatePage() |
68 |
| dom.duplicateSelection() |
68 |
| dom.duplicateSelectionToFrameRange() |
69 |
| dom.duplicateSelectionToFrames() |
69 |
| dom.duplicateSymbol() |
70 |
| dom.duplicateSymbolForAlias() |
70 |
| dom.elementsAt() |
70 |
| dom.enableElementMask() |
71 |
| dom.enableNineScale() |
71 |
| dom.enableTextAntiAliasing() |
72 |
| dom.enterElementMaskEditMode() |
72 |
| dom.enterPaintMode() |
73 |
| dom.exitElementMaskEditMode() |
73 |
| dom.exitPaintMode() |
73 |
| dom.exportOptions.loadColorPalette() |
74 |
| dom.exportOptions.saveColorPalette() |
74 |
| dom.exportTo() |
74 |
| dom.fillSelectedPixels() |
75 |
| dom.filterSelection() |
76 |
| dom.filterSelectionByID() |
76 |
| dom.filterSelectionByName() |
77 |
| dom.findNamedElements() |
77 |
| dom.flattenDocument() |
77 |
| dom.flattenSelection() |
78 |
| dom.getFontMarkup() |
78 |
| dom.getParentLayerNum() |
79 |
| dom.getPixelMask() |
79 |
| dom.getSelectionBounds() |
79 |
| dom.getShowGrid() |
80 |
| dom.getShowGuides() |
80 |
| dom.getShowRulers() |
80 |
| dom.getSnapToGuides() |
81 |
| dom.getSnapToGrid() |
81 |
| dom.getTextAlignment() |
81 |
| dom.group() |
82 |
| dom.hasCharacterMarkup() |
82 |
| dom.hasMasterPage() |
83 |
| dom.hideSelection() |
83 |
| dom.importFile() |
83 |
| dom.importSymbol() |
84 |
| dom.importSymbolButNotAsAlias() |
84 |
| dom.inLaunchAndEdit() |
85 |
| dom.insertPointInPath() |
85 |
| dom.insertSmartShapeAt() |
86 |
| dom.insertSymbolAt() |
86 |
| dom.isMasterPageLayer() |
87 |
| dom.isSelectionDirectlyAboveBitmapObject() |
87 |
| dom.joinPaths() |
88 |
| dom.knifeElementsFromPoint() |
88 |
| dom.knifeElementsFromPoints() |
88 |
| dom.linkElementMask() |
89 |
| dom.lockNineScale() |
89 |
| dom.lockSelection() |
90 |
| dom.makeFind() |
90 |
| dom.makeActive() |
91 |
| dom.mergeDown() |
91 |
| dom.modifyPointOnPath() |
91 |
| dom.motionBlurSelection() |
92 |
| dom.moveBezierHandleBy() |
92 |
| dom.moveElementMaskBy() |
93 |
| dom.moveFillVectorHandleBy() |
93 |
| dom.moveMaskGroupContentsBy() |
94 |
| dom.movePixelMaskBy() |
94 |
| dom.movePointOnHotspotBy() |
95 |
| dom.movePointOnHotspotByWithFlags() |
95 |
| dom.moveSelectedBezierPointsBy() |
96 |
| dom.moveSelectionBy() |
96 |
| dom.moveSelectionMaskBy() |
97 |
| dom.moveSelectionTo() |
97 |
| dom.moveSelectionToFrame() |
98 |
| dom.moveSelectionToLayer() |
98 |
| dom.moveSelectionToNewLayer() |
99 |
| dom.pageName() |
99 |
| dom.pathCrop() |
99 |
| dom.pathExpand() |
100 |
| dom.pathInset() |
100 |
| dom.pathIntersect() |
101 |
| dom.pathPunch() |
101 |
| dom.pathSimplify() |
101 |
| dom.pathUnion() |
102 |
| dom.previewInBrowser() |
102 |
| dom.rebuildColorTable() |
102 |
| dom.redo() |
103 |
| dom.redraw() |
103 |
| dom.redrawSmartShape() |
103 |
| dom.reflectSelection() |
104 |
| dom.removeAllGuides() |
104 |
| dom.removeBehavior() |
105 |
| dom.removeBrush() |
105 |
| dom.removeCharacterMarkup() |
105 |
| dom.removeElementMask() |
106 |
| dom.removeFontMarkup() |
106 |
| dom.removeFill() |
107 |
| dom.removeGuide() |
107 |
| dom.removeNineScale() |
107 |
| dom.removeTransformation() |
108 |
| dom.reorderFrame() |
108 |
| dom.reorderLayer() |
109 |
| dom.reorderPages() |
109 |
| dom.replaceButtonTextStrings() |
109 |
| dom.replaceButtonTextStringsInInstances() |
110 |
| dom.replaceTextString() |
110 |
| dom.resetNineScale() |
111 |
| dom.resizeSelection() |
111 |
| dom.restoreJPEGMask() |
112 |
| dom.restoreSelection() |
112 |
| dom.reversePathTextDirection() |
113 |
| dom.rotateDocument() |
113 |
| dom.rotateSelection() |
113 |
| dom.save() |
114 |
| dom.saveCopyAs() |
114 |
| dom.saveJPEGMask() |
115 |
| dom.saveSelection() |
115 |
| dom.scaleSelection() |
116 |
| dom.scalingGridRect() |
116 |
| dom.selectAdjustPixelSel() |
117 |
| dom.selectAll() |
117 |
| dom.selectAllOnLayer() |
117 |
| dom.selectChildren() |
118 |
| dom.selectFeather() |
118 |
| dom.selectInverse() |
119 |
| dom.selectNone() |
119 |
| dom.selectParents() |
119 |
| dom.selectSimilar() |
120 |
| dom.selectSimilarFromPoint() |
120 |
| dom.sendEmail() |
121 |
| dom.setAllLayersDisclosure() |
121 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceLoopCount() |
122 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceNumFrames() |
122 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceOffsetDist() |
123 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceRotationAmount() |
123 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceScaleAmount() |
124 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceStartEndOpacity() |
124 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceStartFrame() |
125 |
| dom.setBlendMode() |
125 |
| dom.setBrush() |
125 |
| dom.setBrushColor() |
126 |
| dom.setBrushName() |
126 |
| dom.setBrushNColor() |
127 |
| dom.setBrushNColorNTexture() |
127 |
| dom.setBrushPlacement() |
127 |
| dom.setButtonAutoSlice() |
128 |
| dom.setButtonIncludeDownState() |
128 |
| dom.setButtonIncludeOverWhileDownState() |
128 |
| dom.setButtonShowDownOnLoad() |
129 |
| dom.setButtonOptions() |
129 |
| dom.setDefaultBrushAndFillColors() |
130 |
| dom.setDefaultFillVector() |
130 |
| dom.setDocumentCanvasColor() |
130 |
| dom.setDocumentCanvasSize() |
131 |
| dom.setDocumentCanvasSizeToDocumentExtents() |
131 |
| dom.setDocumentCanvasSizeToSelection() |
132 |
| dom.setDocumentImageSize() |
132 |
| dom.setDocumentResolution() |
133 |
| dom.setEffectName() |
133 |
| dom.setElementLocked() |
134 |
| dom.setElementLockedByName() |
134 |
| dom.setElementMaskMode() |
135 |
| dom.setElementMaskShowAttrs() |
135 |
| dom.setElementName() |
135 |
| dom.setElementVisible() |
136 |
| dom.setElementVisibleByName() |
137 |
| dom.setExportOptions() |
137 |
| dom.setExportSettings() |
137 |
| dom.setFill() |
138 |
| dom.setFillColor() |
138 |
| dom.setFillEdgeMode() |
138 |
| dom.setFillNColor() |
139 |
| dom.setFillNColorNTexture() |
139 |
| dom.setFillPlacement() |
140 |
| dom.setFillVector() |
140 |
| dom.setFillVectorStart() |
141 |
| dom.setGradientName() |
141 |
| dom.setGridOrigin() |
141 |
| dom.setGridSize() |
142 |
| dom.setGridColor() |
142 |
| dom.setGroupType() |
142 |
| dom.setGuideColor() |
143 |
| dom.setHotspotAltTag() |
143 |
| dom.setHotspotColor() |
144 |
| dom.setHotspotRectangle() |
144 |
| dom.setHotspotShape() |
145 |
| dom.setHotspotTarget() |
145 |
| dom.setHotspotText() |
145 |
| dom.setLayerDisclosure() |
146 |
| dom.setLayerLocked() |
147 |
| dom.setLayerName() |
147 |
| dom.setLayerSharing() |
148 |
| dom.setLayerVisible() |
148 |
| dom.setMasterPage() |
149 |
| dom.setMatteColor() |
149 |
| dom.setPixelMask() |
150 |
| dom.setOnionSkinning() |
150 |
| dom.setOpacity() |
151 |
| dom.setPageName() |
151 |
| dom.setQuadrangle() |
152 |
| dom.setRectRoundness() |
152 |
| dom.setRectSides() |
153 |
| dom.setSelectionBounds() |
153 |
| dom.setSelectionMask() |
153 |
| dom.setShowEdges() |
154 |
| dom.setShowGammaPreview() |
154 |
| dom.setShowGrid() |
155 |
| dom.setShowGuides() |
155 |
| dom.setShowRulers() |
155 |
| dom.setShowSliceGuides() |
156 |
| dom.setShowSliceOverlay() |
156 |
| dom.setSliceAutonaming() |
156 |
| dom.setSliceExportOptions() |
157 |
| dom.setSliceFilename() |
157 |
| dom.setSliceGuideColor() |
157 |
| dom.setSliceHtml() |
158 |
| dom.setSliceIsHtml() |
158 |
| dom.setSnapToGrid() |
159 |
| dom.setSnapToGuides() |
159 |
| dom.setSymbolProperties() |
159 |
| dom.setTextAlignment() |
160 |
| dom.setTextAntiAliasing() |
160 |
| dom.setTextAutoKern() |
161 |
| dom.setTextCharSpacing() |
161 |
| dom.setTextCustomAntiAliasOverSample() |
161 |
| dom.setTextCustomAntiAliasSharpness() |
162 |
| dom.setTextCustomAntiAliasStrength() |
162 |
| dom.setTextFlow() |
162 |
| dom.setTextHorizontalScale() |
163 |
| dom.setTextLeading() |
163 |
| dom.setTextOnPathMode() |
164 |
| dom.setTextOnPathOffset() |
164 |
| dom.setTextOrientation() |
164 |
| dom.setTextParaIndent() |
165 |
| dom.setTextParaSpacingAfter() |
165 |
| dom.setTextParaSpacingBefore() |
165 |
| dom.setTextRuns() |
166 |
| dom.setTransformMode() |
166 |
| dom.setTextRectangle() |
166 |
| dom.setTextRectangleAuto() |
167 |
| dom.setTextRectangleAutoFromPoint() |
167 |
| dom.setWebObjectsVisibility() |
168 |
| dom.shareLayerToPages() |
168 |
| dom.shareWebLayerToPages() |
169 |
| dom.showAllHidden() |
169 |
| dom.splitPaths() |
170 |
| dom.swapBrushAndFillColors() |
170 |
| dom.transformSelection() |
170 |
| dom.tween() |
171 |
| dom.undo() |
171 |
| dom.updateSymbol() |
171 |
| dom.ungroup() |
172 |
| dom.unsetMasterPage() |
172 |
| Chapter 4: The Fireworks Object |
174 |
| Fireworks functions |
178 |
| fw.browseDocument() |
178 |
| fw.browseForFileURL() |
178 |
| fw.browseForFolderURL() |
178 |
| fw.browseHelp() |
179 |
| fw.checkFwJsVersion() |
179 |
| fw.chooseBrowser() |
180 |
| fw.chooseScriptTargetDialog() |
180 |
| fw.closeDocument() |
180 |
| fw.createDocument() |
181 |
| fw.createDocumentWithDialog() |
181 |
| fw.createFireworksDocument() |
182 |
| fw.dialogs.runEditGrids() |
182 |
| fw.dialogs.runEditGuides() |
183 |
| fw.dialogs.runNumericTransform() |
183 |
| fw.disableFlashDebugging() |
183 |
| fw.dismissBatchDialogWhenDone() |
184 |
| fw.enableFlashDebugging() |
184 |
| fw.exportAndCopyHTMLCode() |
184 |
| fw.exportDirectorAsLayers() |
185 |
| fw.exportDirectorAsSlices() |
185 |
| fw.exportDocumentAs() |
186 |
| fw.exportFrames() |
186 |
| fw.exportHtmlAndImages() |
187 |
| fw.exportIllustrator() |
187 |
| fw.exportLayers() |
188 |
| fw.exportPSD() |
188 |
| fw.exportSWF() |
190 |
| fw.findApp() |
191 |
| fw.findNext() |
191 |
| fw.findOpenDocument() |
192 |
| fw.getDocumentDOM() |
192 |
| fw.getDocumentPath() |
193 |
| fw.getFloaterGroupings() |
193 |
| fw.getFloaterPosition() |
193 |
| fw.getFloaterVisibility() |
194 |
| fw.getHideAllFloaters() |
194 |
| fw.getHTMLFileForScript() |
195 |
| fw.getNumberOfTables() |
195 |
| fw.getPref() |
195 |
| fw.launchApp() |
196 |
| fw.launchBrowserTo() |
196 |
| fw.locateDocDialog() |
197 |
| fw.openDocument() |
198 |
| fw.popupColorPicker() |
198 |
| fw.popupColorPickerOverMouse() |
199 |
| fw.quit() |
199 |
| fw.quitApplication() |
200 |
| fw.readNthTable() |
200 |
| fw.readPanelStateFromFile() |
200 |
| fw.replace() |
201 |
| fw.replaceAll() |
201 |
| fw.revertDocument() |
202 |
| fw.runScript() |
202 |
| fw.saveAll() |
202 |
| fw.saveDocument() |
203 |
| fw.saveDocumentAs() |
203 |
| fw.saveDocumentCopyAs() |
204 |
| fw.saveJsCommand() |
204 |
| fw.setActiveViewScale() |
205 |
| fw.setActiveWindow() |
205 |
| fw.setFloaterGrouping() |
206 |
| fw.setFloaterPosition() |
206 |
| fw.setFloaterVisibility() |
207 |
| fw.setHideAllFloaters() |
207 |
| fw.setPref() |
208 |
| fw.setUpFindReplace() |
208 |
| fw.toggleFloater() |
208 |
| fw.ungroupPrimitives() |
209 |
| fw.updateHTML() |
209 |
| fw.writePanelStateToFile() |
210 |
| fw.yesNoDialog() |
210 |
| Chapter 5: Objects within Fireworks documents |
212 |
| Behavior object |
212 |
| Brush object |
212 |
| Contour object |
215 |
| ContourNode object |
215 |
| ContourNodeDynamicInfo object |
216 |
| ControlPoint object |
217 |
| Effect object |
218 |
| Bevel object |
218 |
| Blur object |
220 |
| Blur More object |
220 |
| Brightness/Contrast object |
220 |
| Convert to Alpha object |
221 |
| Curves object |
221 |
| Drop Shadow object |
221 |
| Find Edges object |
222 |
| Gaussian Blur object |
222 |
| Hue/Saturation object |
222 |
| Inner Shadow object |
222 |
| Invert object |
223 |
| Levels object |
223 |
| Sharpen object |
224 |
| Sharpen More object |
224 |
| Unsharp Mask object |
224 |
| EffectList object |
225 |
| Element object |
225 |
| Group object |
226 |
| Image object |
227 |
| Instance object |
227 |
| Hotspot object |
228 |
| SliceHotspot object |
228 |
| Path object |
229 |
| Text object |
229 |
| Texture object |
230 |
| ElementMask object |
230 |
| ExportFrameInfo object |
231 |
| ExportOptions object |
231 |
| ExportPaletteInfo object |
233 |
| ExportSettings object |
234 |
| Fill object |
237 |
| Frame object |
238 |
| FrameNLayerIntersection object |
238 |
| Gradient object |
239 |
| GradientNode object |
239 |
| Guides object |
239 |
| Layer object |
240 |
| PathAttrs object |
240 |
| Pattern object |
241 |
| RectanglePrimitive object |
241 |
| RegisterMoveParms object |
242 |
| SingleTextRun object |
245 |
| SmartShape object |
245 |
| Style object |
246 |
| TextAttrs object |
247 |
| TextRuns object |
248 |
| Widget object |
249 |
| Chapter 6: HTML export objects |
251 |
| BehaviorInfo object |
251 |
| BehaviorsList object |
254 |
| exportDoc object |
254 |
| ImageMap object |
256 |
| ImagemapList object |
257 |
| SliceInfo object |
257 |
| Slices object |
259 |
| Chapter 7: Cross-Product Extensions |
261 |
| Cross-product architecture |
261 |
| XML and remote procedure calls |
261 |
| RPC client XML requests |
262 |
| Object IDs |
263 |
| Data node |
264 |
| Parameters |
265 |
| RPC server XML replies |
265 |
| Error codes |
265 |
| RPC and the Fireworks JavaScript DOM |
266 |
| Generating stubs for nonstandard client types |
266 |
| Security |
268 |
| RPCMethods class |
269 |
| RPCMethods.CreateAutoReleasePool() |
269 |
| RPCMethods.DestroyAutoReleasePool() |
269 |
| RPCMethods.AddToAutoReleasePool() |
270 |
| RPCMethods.RemoveFromAutoReleasePool() |
270 |
| RPCMethods.ReleaseObject() |
270 |
| Creating auto-release blocks |
270 |
| Accessing proxy objects |
271 |
| A simple RPC example |
271 |
| Flash panels |
273 |
| How Flash panels and commands work |
273 |
| Embedding API commands |
274 |
| MMExecute() |
274 |
| MMEndCommand() |
274 |
| Using the API wrapper extension in Adobe Flash |
275 |
| Working with ActionScript files |
275 |
| Guidelines for creating panels and commands |
275 |
| Events |
276 |
| How event handlers work |
276 |
| Creating event handlers |
276 |
| Publishing |
277 |
| Debugging |
278 |
| Chapter 8: Auto Shapes |
279 |
| How Auto Shapes work |
279 |
| Creating an Auto Shape |
279 |
| Defining the shape |
280 |
| Adding control points |
282 |
| Handling the user interaction |
282 |
| Fireworks messages |
282 |
| Message handler functions |
283 |
| Switch statements |
284 |
| Supporting functions and methods |
286 |
| Chapter 9: Rich symbols |
287 |
| How Rich symbols work |
287 |
| Supported attributes for rich symbols |
288 |
| MXML Export |
292 |
| Flex Component Definitions for MXML and Images Export |
293 |
| flexClassName |
293 |
| flexClassDefinition |
293 |
| Example script |
296 |
| Chapter 10: Additional Fireworks Functions |
298 |
| Property inspector functions |
298 |
| fw.showPIWindow() |
298 |
| fw.hidePIWindow() |
298 |
| fw.isPIExpanded() |
299 |
| fw.isPIVisible() |
299 |
| fw.growPIWindow() |
299 |
| fw.shrinkPIWindow() |
300 |
| fw.setPIPosition() |
300 |
| fw.getPIPosition() |
300 |
| History panel functions |
301 |
| fw.historyPalette.clearSteps() |
301 |
| fw.historyPalette.copySteps() |
301 |
| fw.historyPalette.getSelection() |
302 |
| fw.historyPalette.getStepCount() |
302 |
| fw.historyPalette.getStepsAsJavaScript() |
302 |
| fw.historyPalette.getUndoState() |
303 |
| fw.historyPalette.replaySteps() |
303 |
| fw.historyPalette.saveAsCommand() |
304 |
| fw.historyPalette.setSelection() |
304 |
| fw.historyPalette.setUndoState() |
304 |
| Static Document Functions |
305 |
| document.findExportFormatOptionsByName() |
305 |
| document.makeGoodNativeFilePath() |
305 |
| Index |
307 |
| A |
307 |
| ActionScript 269 |
307 |
| cross-product extensions 257 |
307 |
| addBehavior() 23, 24 |
307 |
| addElementMask() 27 |
307 |
| addFrames() 28 |
307 |
| addGuide() 28 |
307 |
| addNewHotspot() 29 |
307 |
| addNewImage() 30, 31 |
307 |
| addNewImageViaCopy() 30 |
307 |
| addNewImageViaCut() 31 |
307 |
| addNewLayer() 31, 35 |
307 |
| addNewLine() 32 |
307 |
| addNewOval() 32 |
307 |
| addNewRectangle() 33 |
307 |
| addNewRectanglePrimitive() 34 |
307 |
| addNewSinglePointPath() 34 |
307 |
| addNewStar() 35 |
307 |
| addNewSymbol() 36 |
307 |
| addNewText() 36 |
307 |
| addSwapImageBehaviorFromPoint() 37 |
307 |
| AddToAutoReleasePool() 266 |
307 |
| adjustExportToSize() 37 |
307 |
| adjustFontSize() 38 |
307 |
| align() 38 |
307 |
| API wrapper 271 |
307 |
| App object. See Fireworks object |
307 |
| app.browseDocument() 7 |
307 |
| app.getRootDirectory() 7 |
307 |
| app.setFloaterVisibility() 7 |
307 |
| app.toggleFloater() 7 |
307 |
| appendPointToHotspot() 39 |
307 |
| appendPointToPath() 39 |
307 |
| appendPointToSlice() 40 |
307 |
| applyCharacterMarkup() 40 |
307 |
| applyCurrentFill() 40 |
307 |
| applyEffects() 41 |
307 |
| applyFontMarkup() 41 |
307 |
| applyStyle() 42 |
307 |
| arrange() 42 |
307 |
| attachTextToPath() 43 |
307 |
| Auto Shapes 275 |
307 |
| defining 275, 283 |
307 |
| helper functions 277 |
307 |
| icons 275 |
307 |
| switch statement 280 |
307 |
| B |
307 |
| BeginDragControlPoint 278 |
307 |
| BeginDragInsert 278 |
307 |
| Behavior object 208 |
307 |
| BehaviorInfo object 247 |
307 |
| BehaviorsList object 250 |
307 |
| Bevel properties (Effect object) 214 |
307 |
| Blur More properties (Effect object) 216 |
307 |
| Blur properties (Effect object) 216 |
307 |
| Brightness properties (Effect object) 216 |
307 |
| browseDocument() 7, 174 |
307 |
| browseForFileURL() 174 |
307 |
| browseForFolderURL() 174 |
307 |
| browseHelp() 175 |
307 |
| Brush object 208 |
307 |
| C |
307 |
| changeGuide() 43, 44, 45 |
307 |
| changeSliceGuide() 45 |
307 |
| checkFwJsVersion() 175 |
307 |
| chooseBrowser() 176 |
307 |
| chooseScriptTargetDialog() 176 |
307 |
| clearJPEGMask() 45 |
307 |
| clearSteps() 297 |
307 |
| clipCopy() 46, 47 |
307 |
| clipCopyAsPaths() 46 |
307 |
| clipCopyFormats() 47 |
307 |
| clipCut() 47 |
307 |
| clipPaste() 47 |
307 |
| clipPasteAsMask() 48 |
307 |
| clipPasteAttributes() 49 |
307 |
| clipPasteFromChannelToChannel() 49 |
307 |
| clipPasteInside() 50 |
307 |
| cloneSelection() 50 |
307 |
| close() 51 |
307 |
| closeDocument() 176 |
307 |
| color string 5 |
307 |
| colors, finding and replacing 18 |
307 |
| Common Application API 7 |
307 |
| Contour object 211 |
307 |
| ContourNode object 211 |
307 |
| ContourNodeDynamicInfo object 212 |
307 |
| Contrast properties (Effect object) 216 |
307 |
| ControlPoint object 213 |
307 |
| conventions, in book 2 |
307 |
| Convert to Alpha properties (Effect object) 217 |
307 |
| convertAnimSymbolToGraphicSym bol() 51 |
307 |
| convertToAnimSymbol() 52 |
307 |
| convertToPaths() 53 |
307 |
| convertToSymbol() 54 |
307 |
| convolveSelection() 54 |
307 |
| copyHtmlWizard() 55 |
307 |
| copySteps() 297 |
307 |
| copyToHotspot() 55 |
307 |
| core objects 13 |
307 |
| CreateAutoReleasePool() 265 |
307 |
| createDocument() 177 |
307 |
| createDocumentWithDialog() 177 |
307 |
| createFireworksDocument() 178 |
307 |
| cropSelection() 56 |
307 |
| Curves properties (Effect object) 217 |
307 |
| D |
307 |
| data types |
307 |
| color string 5 |
307 |
| mask 5 |
307 |
| matrix 6 |
307 |
| non-standard 5 |
307 |
| point 6 |
307 |
| rectangle 6 |
307 |
| resolution 6 |
307 |
| deleteAllInDocument() 56 |
307 |
| deleteFrames() 57 |
307 |
| deleteLayer() 57 |
307 |
| deletePointOnPath() 58 |
307 |
| deleteSelection() 59 |
307 |
| deleteSymbol() 59 |
307 |
| deprecated functions or arguments |
307 |
| dom.clipPasteInside() 50 |
307 |
| dom.getPixelMask 75 |
307 |
| dom.group() 78 |
308 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceStartFrame( ) 121 |
308 |
| dom.setGroupType() 138 |
308 |
| dom.setPixelMask() 146 |
308 |
| mask to image 222 |
308 |
| mask to path 222 |
308 |
| DestroyAutoReleasePool() 265 |
308 |
| detachInstanceFromSymbol() 60 |
308 |
| detachTextFromPath() 60 |
308 |
| disableFlashDebugging() 179 |
308 |
| dismissBatchDialogWhenDone() 18 0 |
308 |
| distribute() 61 |
308 |
| distributeLayerToFrames() 62 |
308 |
| distributeSelectionToFrames() 62 |
308 |
| documents, accessing objects 208 |
308 |
| DOM (Document Object Model) 4 |
308 |
| dom.addBehavior() 23 |
308 |
| dom.addElementMask() 27 |
308 |
| dom.addFrames() 28 |
308 |
| dom.addGuide() 28 |
308 |
| dom.addNewHotspot() 29 |
308 |
| dom.addNewImage() 30 |
308 |
| dom.addNewImageViaCopy() 30 |
308 |
| dom.addNewImageViaCut() 31 |
308 |
| dom.addNewLayer() 31, 35 |
308 |
| dom.addNewLine() 32 |
308 |
| dom.addNewOval() 32 |
308 |
| dom.addNewRectangle() 33 |
308 |
| dom.addNewRectanglePrimitive() 3 4 |
308 |
| dom.addNewSinglePointPath() 34 |
308 |
| dom.addNewStar() 35 |
308 |
| dom.addNewSymbol() 36 |
308 |
| dom.addNewText() 36 |
308 |
| dom.addSwapImageBehaviorFromP oint() 37 |
308 |
| dom.adjustExportToSize() 37 |
308 |
| dom.adjustFontSize() 38 |
308 |
| dom.align() 38 |
308 |
| dom.appendPointToHotspot() 39 |
308 |
| dom.appendPointToPath() 39 |
308 |
| dom.appendPointToSlice() 40 |
308 |
| dom.applyCharacterMarkup() 40 |
308 |
| dom.applyCurrentFill() 40 |
308 |
| dom.applyEffects() 41 |
308 |
| dom.applyFontMarkup() 41 |
308 |
| dom.applyStyle() 42 |
308 |
| dom.arrange() 42 |
308 |
| dom.attachTextToPath() 43 |
308 |
| dom.changeGuide() 43, 44 |
308 |
| dom.changeSliceGuide() 45 |
308 |
| dom.clearJPEGMask() 45 |
308 |
| dom.clipCopy() 46 |
308 |
| dom.clipCopyAsPaths() 46 |
308 |
| dom.clipCopyFormats() 47 |
308 |
| dom.clipCut() 47 |
308 |
| dom.clipPaste() 47 |
308 |
| dom.clipPasteAsMask() 48 |
308 |
| dom.clipPasteAttributes() 49 |
308 |
| dom.clipPasteFromChannelToChan nel() 49 |
308 |
| dom.clipPasteInside() 50 |
308 |
| dom.cloneSelection() 50 |
308 |
| dom.close() 51 |
308 |
| dom.convertAnimSymbolToGraphic Symbol() 51 |
308 |
| dom.convertToAnimSymbol() 52 |
308 |
| dom.convertToPaths() 53 |
308 |
| dom.convertToSymbol() 54 |
308 |
| dom.convolveSelection() 54 |
308 |
| dom.copyHtmlWizard() 55 |
308 |
| dom.copyToHotspot() 55 |
308 |
| dom.cropSelection() 56 |
308 |
| dom.deleteAllInDocument() 56 |
308 |
| dom.deleteFrames() 57 |
308 |
| dom.deleteLayer() 57 |
308 |
| dom.deletePointOnPath() 58 |
308 |
| dom.deleteSelection() 59 |
308 |
| dom.deleteSymbol() 59 |
308 |
| dom.detachInstanceFromSymbol() 6 0 |
308 |
| dom.detachTextFromPath() 60 |
308 |
| dom.distribute() 61 |
308 |
| dom.distributeLayerToFrames() 62 |
308 |
| dom.distributeSelectionToFrames() 62 |
308 |
| dom.dragControlPoint() 62 |
308 |
| dom.duplicateFrame() 63 |
308 |
| dom.duplicateLayer() 43, 63, 64, 79, 95, 145, 147, 168 |
308 |
| dom.duplicateSelection() 64 |
308 |
| dom.duplicateSelectionToFrameRan ge() 65 |
308 |
| dom.duplicateSelectionToFrames() 6 5 |
308 |
| dom.duplicateSymbol() 66 |
308 |
| dom.duplicateSymbolForAlias() 66 |
308 |
| dom.elementsAt() 66 |
308 |
| dom.enableElementMask() 67, 85, 103, 107, 112 |
308 |
| dom.enableTextAntiAliasing() 68 |
308 |
| dom.enterElementMaskEditMode() 68 |
308 |
| dom.enterPaintMode() 69 |
308 |
| dom.exitElementMaskEditMode() 6 9 |
308 |
| dom.exitPaintMode() 69 |
308 |
| dom.exportOptions.loadColorPalett e() 70 |
308 |
| dom.exportOptions.saveColorPalette () 70 |
308 |
| dom.exportTo() 70 |
308 |
| dom.fillSelectedPixels() 71 |
308 |
| dom.filterSelection() 72 |
308 |
| dom.filterSelectionByName() 72, 73 |
308 |
| dom.findExportFormatOptionsByN ame() 301 |
308 |
| dom.findNamedElements() 73 |
308 |
| dom.flattenDocument() 73 |
308 |
| dom.flattenSelection() 74 |
308 |
| dom.getFontMarkup() 74, 75 |
308 |
| dom.getPixelMask() 75 |
308 |
| dom.getSelectionBounds() 75 |
308 |
| dom.getShowGrid() 76 |
308 |
| dom.getShowRulers() 76 |
308 |
| dom.getSnapToGrid() 77 |
308 |
| dom.getTextAlignment() 77 |
308 |
| dom.group() 78 |
308 |
| dom.hasCharacterMarkup() 78 |
308 |
| dom.hideSelection() 79 |
308 |
| dom.importFile() 79 |
308 |
| dom.importSymbol() 80 |
308 |
| dom.importSymbolButNotAsAlias() 80 |
308 |
| dom.inLaunchAndEdit() 81 |
308 |
| dom.insertPointInPath() 81 |
308 |
| dom.insertSmartShapeAt() 82 |
308 |
| dom.isSelectionDirectlyAboveBitma pObject() 83 |
308 |
| dom.joinPaths() 84 |
308 |
| dom.knifeElementsFromPoint() 84 |
308 |
| dom.knifeElementsFromPoints() 84 |
308 |
| dom.linkElementMask() 85 |
308 |
| dom.makeActive() 87 |
308 |
| dom.makeFind() 86 |
308 |
| dom.makeGoodNativeFilePath() 301 |
308 |
| dom.mergeDown() 87 |
308 |
| dom.modifyPointOnPath() 87 |
308 |
| dom.motionBlurSelection() 88 |
308 |
| dom.moveBezierHandleBy() 88 |
309 |
| dom.moveElementMaskBy() 89 |
309 |
| dom.moveFillVectorHandleBy() 89 |
309 |
| dom.moveMaskGroupContentsBy() 90 |
309 |
| dom.movePixelMaskBy() 90 |
309 |
| dom.movePointOnHotspotBy() 91 |
309 |
| dom.movePointOnHotspotByWithF lags() 91 |
309 |
| dom.moveSelectedBezierPointsBy() 92 |
309 |
| dom.moveSelectionBy() 92 |
309 |
| dom.moveSelectionMaskBy() 93 |
309 |
| dom.moveSelectionTo() 93 |
309 |
| dom.moveSelectionToFrame() 94 |
309 |
| dom.moveSelectionToLayer() 94 |
309 |
| dom.moveSelectionToNewLayer() 9 5 |
309 |
| dom.pathCrop() 95 |
309 |
| dom.pathExpand() 96 |
309 |
| dom.pathInset() 96 |
309 |
| dom.pathIntersect() 97 |
309 |
| dom.pathPunch() 97 |
309 |
| dom.pathSimplify() 97 |
309 |
| dom.pathUnion() 98 |
309 |
| dom.previewInBrowser() 98 |
309 |
| dom.rebuildColorTable() 98 |
309 |
| dom.redo() 99 |
309 |
| dom.redraw() 99 |
309 |
| dom.reflectSelection() 100 |
309 |
| dom.removeAllGuides() 100 |
309 |
| dom.removeBehavior() 101 |
309 |
| dom.removeBrush() 101 |
309 |
| dom.removeCharacterMarkup() 101 |
309 |
| dom.removeElementMask() 102 |
309 |
| dom.removeFill() 103 |
309 |
| dom.removeFontMarkup() 102 |
309 |
| dom.removeGuide() 103 |
309 |
| dom.removeTransformation() 104 |
309 |
| dom.reorderFrame() 104 |
309 |
| dom.reorderLayer() 105 |
309 |
| dom.replaceButtonTextStrings() 105 |
309 |
| dom.replaceButtonTextStringsInInst ances() 106 |
309 |
| dom.replaceTextString() 106 |
309 |
| dom.resizeSelection() 107 |
309 |
| dom.restoreJPEGMask() 108 |
309 |
| dom.restoreSelection() 108 |
309 |
| dom.reversePathTextDirection() 109 |
309 |
| dom.rotateDocument() 109 |
309 |
| dom.rotateSelection() 109 |
309 |
| dom.save() 110 |
309 |
| dom.saveCopyAs() 110 |
309 |
| dom.saveJPEGMask() 111 |
309 |
| dom.saveSelection() 111 |
309 |
| dom.scaleSelection() 112 |
309 |
| dom.selectAdjustPixelSel() 113 |
309 |
| dom.selectAll() 113 |
309 |
| dom.selectAllOnLayer() 113 |
309 |
| dom.selectChildren() 114 |
309 |
| dom.selectFeather() 114 |
309 |
| dom.selectInverse() 115 |
309 |
| dom.selectNone() 115 |
309 |
| dom.selectParents() 115 |
309 |
| dom.selectSimilar() 116 |
309 |
| dom.selectSimilarFromPoint() 116 |
309 |
| dom.sendEmail() 117 |
309 |
| dom.setAllLayersDisclosure() 117 |
309 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceLoopCount() 118 |
309 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceNumFrames() 118 |
309 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceOffsetDist() 11 9 |
309 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceRotationAmo unt() 119 |
309 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceScaleAmount( ) 120 |
309 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceStartEndOpaci ty() 120 |
309 |
| dom.setAnimInstanceStartFrame() 1 21 |
309 |
| dom.setBlendMode() 121 |
309 |
| dom.setBrush() 121 |
309 |
| dom.setBrushColor() 122 |
309 |
| dom.setBrushName() 122 |
309 |
| dom.setBrushNColorNTexture() 123 |
309 |
| dom.setBrushPlacement() 123 |
309 |
| dom.setButtonAutoSlice() 124 |
309 |
| dom.setButtonIncludeDownState() 1 24 |
309 |
| dom.setButtonIncludeOverWhileDo wnState() 124 |
309 |
| dom.setButtonOptions() 125 |
309 |
| dom.setButtonShowDownOnLoad() 125 |
309 |
| dom.setDefaultBrushAndFillColors( ) 126 |
309 |
| dom.setDefaultFillVector() 126 |
309 |
| dom.setDocumentCanvasColor() 12 6 |
309 |
| dom.setDocumentCanvasSize() 127 |
309 |
| dom.setDocumentCanvasSizeToDoc umentExtents() 127 |
309 |
| dom.setDocumentCanvasSizeToSele ction() 128 |
309 |
| dom.setDocumentImageSize() 128 |
309 |
| dom.setDocumentResolution() 129 |
309 |
| dom.setEffectName() 129, 130, 131 |
309 |
| dom.setElementMaskMode() 130, 131 |
309 |
| dom.setElementMaskShowAttrs() 13 1 |
309 |
| dom.setElementName() 131 |
309 |
| dom.setElementVisible() 132 |
309 |
| dom.setElementVisibleByName() 13 3 |
309 |
| dom.setExportOptions() 133 |
309 |
| dom.setExportSettings() 133 |
309 |
| dom.setFill() 134 |
309 |
| dom.setFillColor() 134 |
309 |
| dom.setFillEdgeMode() 134 |
309 |
| dom.setFillNColor() 135 |
309 |
| dom.setFillNColorNTexture() 135 |
309 |
| dom.setFillPlacement() 136 |
309 |
| dom.setFillVector() 136 |
309 |
| dom.setFillVectorStart() 137 |
309 |
| dom.setGradientName() 137 |
309 |
| dom.setGridColor() 138 |
309 |
| dom.setGridOrigin() 137 |
309 |
| dom.setGridSize() 138 |
309 |
| dom.setGroupType() 138 |
309 |
| dom.setGuideColor() 139 |
309 |
| dom.setHotspotAltTag() 139 |
309 |
| dom.setHotspotColor() 140 |
309 |
| dom.setHotspotRectangle() 140 |
309 |
| dom.setHotspotShape() 141 |
309 |
| dom.setHotspotTarget() 141 |
309 |
| dom.setHotspotText() 141 |
309 |
| dom.setLayerDisclosure() 142 |
309 |
| dom.setLayerLocked() 143 |
309 |
| dom.setLayerName() 143 |
309 |
| dom.setLayerSharing() 144 |
309 |
| dom.setLayerVisible() 144 |
309 |
| dom.setMatteColor() 145 |
309 |
| dom.setOnionSkinning() 146 |
309 |
| dom.setOpacity() 147 |
309 |
| dom.setPixelMask() 146 |
309 |
| dom.setQuadrangle() 148 |
309 |
| dom.setRectRoundness() 148 |
309 |
| dom.setRectSides() 149 |
309 |
| dom.setSelectionBounds() 149 |
309 |
| dom.setSelectionMask() 149 |
310 |
| dom.setShowEdges() 150 |
310 |
| dom.setShowGammaPreview() 150 |
310 |
| dom.setShowGrid() 151 |
310 |
| dom.setShowGuides() 151 |
310 |
| dom.setShowRulers() 151 |
310 |
| dom.setShowSliceGuides() 152 |
310 |
| dom.setShowSliceOverlay() 152 |
310 |
| dom.setSliceAutonaming() 152 |
310 |
| dom.setSliceExportOptions() 153 |
310 |
| dom.setSliceFilename() 153 |
310 |
| dom.setSliceGuideColor() 153 |
310 |
| dom.setSliceHtml() 154 |
310 |
| dom.setSliceIsHtml() 154 |
310 |
| dom.setSnapToGrid() 155 |
310 |
| dom.setSnapToGuides() 155 |
310 |
| dom.setSymbolProperties() 155 |
310 |
| dom.setTextAlignment() 156 |
310 |
| dom.setTextAntiAliasing() 156 |
310 |
| dom.setTextAutoKern() 157 |
310 |
| dom.setTextCharSpacing() 157 |
310 |
| dom.setTextCustomAntiAliasOverS ample() 157 |
310 |
| dom.setTextCustomAntiAliasSharpn ess() 158 |
310 |
| dom.setTextCustomAntiAliasStrengt h() 158 |
310 |
| dom.setTextFlow() 158 |
310 |
| dom.setTextHorizontalScale() 159 |
310 |
| dom.setTextLeading() 159 |
310 |
| dom.setTextOnPathMode() 160 |
310 |
| dom.setTextOnPathOffset() 160 |
310 |
| dom.setTextOrientation() 160 |
310 |
| dom.setTextParaIndent() 161 |
310 |
| dom.setTextParaSpacingAfter() 161 |
310 |
| dom.setTextParaSpacingBefore() 16 1 |
310 |
| dom.setTextRectangle() 162 |
310 |
| dom.setTextRectangleAuto() 163 |
310 |
| dom.setTextRectangleAutoFromPoi nt() 29, 33, 58, 61, 83, 105, 163, 164, 165 |
310 |
| dom.setTextRuns() 162 |
310 |
| dom.setTransformMode() 162 |
310 |
| dom.showAllHidden() 165 |
310 |
| dom.splitPaths() 166 |
310 |
| dom.swapBrushAndFillColors() 166 |
310 |
| dom.transformSelection() 166 |
310 |
| dom.tween() 167 |
310 |
| dom.undo() 167 |
310 |
| dom.ungroup() 168 |
310 |
| dom.updateSymbol() 167 |
310 |
| DragControlPoint 278 |
310 |
| dragControlPoint() 62 |
310 |
| DragInsert 278 |
310 |
| Drop Shadow (Effect object) 217 |
310 |
| duplicateFrame() 63 |
310 |
| duplicateLayer() 43, 63, 64, 79, 95, 145, 147, 168 |
310 |
| duplicateSelection() 64 |
310 |
| duplicateSelectionToFrameRange() 65 |
310 |
| duplicateSelectionToFrames() 65 |
310 |
| duplicateSymbol() 66 |
310 |
| duplicateSymbolForAlias() 66 |
310 |
| E |
310 |
| EAppAlreadyRunning 14 |
310 |
| EAppNotSerialized 14 |
310 |
| EArrayIndexOutOfBounds 14 |
310 |
| EBadFileContents 14 |
310 |
| EBadJsVersion 14 |
310 |
| EBadNesting 14 |
310 |
| EBadParam 14 |
310 |
| EBadParamType 14 |
310 |
| EBadSelection 14 |
310 |
| EBufferTooSmall 14 |
310 |
| ECharConversionFailed 14 |
310 |
| EDatabaseError 14 |
310 |
| EDeletingLastMasterChild 14 |
310 |
| EDiskFull 14 |
310 |
| EDuplicateFileName 14 |
310 |
| Effect object 214, 220 |
310 |
| EffectList object 221 |
310 |
| effectList property 8 |
310 |
| effects, finding and replacing 18 |
310 |
| EFileIsReadOnly 14 |
310 |
| EFileNotFound 14 |
310 |
| EGenericErrorOccurred 14 |
310 |
| EGroupDepth 14 |
310 |
| EIllegalThreadAccess 14 |
310 |
| EInternalError 14 |
310 |
| Element object 221 |
310 |
| ElementMask object 226 |
310 |
| elements, changing 4 |
310 |
| elementsAt() 66 |
310 |
| ELowOnMem 14 |
310 |
| enableElementMask() 67, 85, 103, 107, 112 |
310 |
| enableFlashDebugging() 180 |
310 |
| enableTextAntiAliasing() 68 |
310 |
| EndDragControlPoint 279 |
310 |
| EndDragInsert 278 |
310 |
| end-of-line character 16 |
310 |
| ENoActiveDocument 14 |
310 |
| ENoActiveSelection 14 |
310 |
| ENoFilesSelected 14 |
310 |
| ENoNestedMastersOrAliases 14 |
310 |
| ENoNestedPasting 14 |
310 |
| ENoSliceableElems 14 |
310 |
| ENoSuchElement 14 |
310 |
| ENotImplemented 14 |
310 |
| ENotMyType 14 |
310 |
| enterElementMaskEditMode() 68 |
310 |
| enterPaintMode() 69 |
310 |
| EOutOfMem 14 |
310 |
| EResourceNotFound 14 |
310 |
| error 261 |
310 |
| Errors object (core object) 14 |
310 |
| ESharingViolation 14 |
310 |
| EUnknownReaderFormat 14 |
310 |
| EUserCanceled 14 |
310 |
| EUserInterrupted 14 |
310 |
| EWrongType 14 |
310 |
| exitElementMaskEditMode 69 |
310 |
| exitPaintMode() 69 |
310 |
| exportAndCopyHTMLCode() 180 |
310 |
| exportDirectorAsLayers() 181 |
310 |
| exportDirectorAsSlices() 181 |
310 |
| exportDoc object 250 |
310 |
| exportDocumentAs() 182 |
310 |
| ExportFrameInfo object 227 |
310 |
| exportFrames() 182 |
310 |
| exportHtmlAndImages() 183 |
310 |
| exportIllustrator() 183 |
310 |
| exporting HTML and sliced images 247 |
310 |
| exportLayers() 184 |
310 |
| ExportOptions object 227, ??-229 |
310 |
| exportOptions.loadColorPalette() 70 |
310 |
| exportOptions.saveColorPalette() 70 |
310 |
| ExportPaletteInfo object 229 |
310 |
| exportPSD() 184 |
310 |
| ExportSettings object 230 |
310 |
| exportSWF() 186 |
310 |
| exportTo() 70 |
310 |
| F |
310 |
| Files object 14, 18 |
310 |
| Fill object 233 |
311 |
| fills, finding and replacing 18 |
311 |
| fillSelectedPixels() 71 |
311 |
| filterSelection() 72 |
311 |
| filterSelectionByName() 72, 73 |
311 |
| Find (core object) 17 |
311 |
| Find Edges (Effect object) 218 |
311 |
| findApp() 187 |
311 |
| findExportFormatOptionsByName() 301 |
311 |
| finding and replacing |
311 |
| colors 18 |
311 |
| effects 18 |
311 |
| fills 18 |
311 |
| fonts and styles 17 |
311 |
| strokes 18 |
311 |
| styles 17 |
311 |
| text 17 |
311 |
| URLs 18 |
311 |
| findNamedElements() 73 |
311 |
| findNext() 187 |
311 |
| findOpenDocument() 188 |
311 |
| fireworks and fw class names 174 |
311 |
| Fireworks Object Model |
311 |
| compared to API calls 5 |
311 |
| using the 4 |
311 |
| Flash debugging |
311 |
| disable 179 |
311 |
| enable 180 |
311 |
| Flash document, exporting as 186 |
311 |
| Flash extensions 257 |
311 |
| Flash panels 269 |
311 |
| Actionscript compatibility 271 |
311 |
| event handlers 272 |
311 |
| Flash wrapper extension 271 |
311 |
| flattenDocument() 73 |
311 |
| flattenSelection() 74 |
311 |
| fonts, finding and replacing 17 |
311 |
| Frame object 234 |
311 |
| frameIndex argument 6 |
311 |
| FrameNLayerIntersection object 234 |
311 |
| func 259 |
311 |
| fw and fireworks class names 174 |
311 |
| fw.browseDocument() 174 |
311 |
| fw.browseForFileURL() 174 |
311 |
| fw.browseForFolderURL() 174 |
311 |
| fw.browseHelp() 175 |
311 |
| fw.checkFwJsVersion() 175 |
311 |
| fw.chooseBrowser() 176 |
311 |
| fw.chooseScriptTargetDialog() 176 |
311 |
| fw.closeDocument() 176 |
311 |
| fw.createDocument() 177 |
311 |
| fw.createDocumentWithDialog() 17 7 |
311 |
| fw.createFireworksDocument() 178 |
311 |
| fw.disableFlashDebugging() 179 |
311 |
| fw.dismissBatchDialogWhenDone() 180 |
311 |
| fw.enableFlashDebugging() 180 |
311 |
| fw.exportAndCopyHTMLCode() 18 0 |
311 |
| fw.exportDirectorAsLayers() 181 |
311 |
| fw.exportDirectorAsSlices() 181 |
311 |
| fw.exportDocumentAs() 182 |
311 |
| fw.exportFrames() 182 |
311 |
| fw.exportHtmlAndImages() 183 |
311 |
| fw.exportIllustrator() 183 |
311 |
| fw.exportLayers() 184 |
311 |
| fw.exportPSD() 184 |
311 |
| fw.exportSWF() 186 |
311 |
| fw.findApp() 187 |
311 |
| fw.findNext() 187 |
311 |
| fw.findOpenDocument() 188 |
311 |
| fw.getDocumentDOM() 188 |
311 |
| fw.getDocumentPath() 189 |
311 |
| fw.getFloaterGroupings() 189 |
311 |
| fw.getFloaterPosition() 189 |
311 |
| fw.getFloaterVisibility() 190 |
311 |
| fw.getHideAllFloaters() 190 |
311 |
| fw.getHTMLFileForScript() 191 |
311 |
| fw.getNumberOfTables() 191 |
311 |
| fw.getPIPosition() 296 |
311 |
| fw.getPref() 191 |
311 |
| fw.growPIWindow() 295 |
311 |
| fw.hidePIWindow() 294 |
311 |
| fw.historyPalette.clearSteps() 297 |
311 |
| fw.historyPalette.copySteps() 297 |
311 |
| fw.historyPalette.getSelection() 298 |
311 |
| fw.historyPalette.getStepCount() 298 |
311 |
| fw.historyPalette.getStepsAsJavaScri pt() 298 |
311 |
| fw.historyPalette.getUndoState() 299 |
311 |
| fw.historyPalette.replaySteps() 299 |
311 |
| fw.historyPalette.saveAsCommand() 300 |
311 |
| fw.historyPalette.setSelection() 300 |
311 |
| fw.historyPalette.setUndoState() 300 |
311 |
| fw.isPIExpanded() 295 |
311 |
| fw.isPIVisible() 295 |
311 |
| fw.launchApp() 192 |
311 |
| fw.launchBrowserTo() 192 |
311 |
| fw.locateDocDialog() 193 |
311 |
| fw.openDocument() 194 |
311 |
| fw.popupColorPicker() 194 |
311 |
| fw.popupColorPickerOverMouse() 1 95 |
311 |
| fw.quit() 195 |
311 |
| fw.quitApplication() 196 |
311 |
| fw.readNthTable() 196 |
311 |
| fw.readPanelStateFromFile() 196 |
311 |
| fw.replace() 197 |
311 |
| fw.replaceAll() 197 |
311 |
| fw.revertDocument() 198 |
311 |
| fw.runScript() 198 |
311 |
| fw.saveAll() 198 |
311 |
| fw.saveDocument() 199 |
311 |
| fw.saveDocumentAs() 199 |
311 |
| fw.saveDocumentCopyAs() 200 |
311 |
| fw.saveJsCommand() 200 |
311 |
| fw.setActiveViewScale() 201 |
311 |
| fw.setActiveWindow() 201 |
311 |
| fw.setFloaterGrouping() 202 |
311 |
| fw.setFloaterPosition() 202 |
311 |
| fw.setFloaterVisibility() 203 |
311 |
| fw.setHideAllFloaters() 203 |
311 |
| fw.setPIPosition() 296 |
311 |
| fw.setPref() 204 |
311 |
| fw.setUpFindReplace() 204 |
311 |
| fw.showPIWindow() 294 |
311 |
| fw.shrinkPIWindow() 296 |
311 |
| fw.toggleFloater() 204 |
311 |
| fw.ungroupPrimitives() 205 |
311 |
| fw.updateHTML() 205 |
311 |
| fw.writePanelStateToFile() 206 |
311 |
| fw.yesNoDialog() 206 |
311 |
| G |
311 |
| Gaussian Blur property (Effect object) 218 |
311 |
| get 259 |
311 |
| GetDefaultMoveParms() 242 |
311 |
| getDocumentDOM() 188 |
311 |
| getDocumentPath() 189 |
311 |
| getFloaterGroupings() 189 |
311 |
| getFloaterPosition() 189 |
311 |
| getFloaterVisibility() 190 |
311 |
| getFontMarkup() 74, 75 |
311 |
| getHideAllFloaters() 190 |
311 |
| getHTMLFileForScript() 191 |
312 |
| getNumberOfTables() 191 |
312 |
| getPIPosition() 296 |
312 |
| getPixelMask() 75 |
312 |
| getPref() 191 |
312 |
| getRootDirectory() 7 |
312 |
| getSelection() 298 |
312 |
| getSelectionBounds() 75 |
312 |
| getShowGrid() 76 |
312 |
| getShowRulers() 76 |
312 |
| getSnapToGrid() 77 |
312 |
| getStepCount() 298 |
312 |
| getStepsAsJavaScript() 298 |
312 |
| getTextAlignment() 77 |
312 |
| getUndoState() 299 |
312 |
| Global methods 11 |
312 |
| Gradient object 235 |
312 |
| GradientNode object 235 |
312 |
| Group object 222 |
312 |
| group() 78 |
312 |
| growPIWindow() 295 |
312 |
| Guides object 235 |
312 |
| H |
312 |
| hasCharacterMarkup() 78 |
312 |
| hidePIWindow() 294 |
312 |
| hideSelection() 79 |
312 |
| History panel functions 297 |
312 |
| historyPalette.clearSteps() 297 |
312 |
| historyPalette.copySteps() 297 |
312 |
| historyPalette.getSelection() 298 |
312 |
| historyPalette.getStepCount() 298 |
312 |
| historyPalette.getStepsAsJavaScript() 298 |
312 |
| historyPalette.getUndoState() 299 |
312 |
| historyPalette.replaySteps() 299 |
312 |
| historyPalette.saveAsCommand() 30 0 |
312 |
| historyPalette.setSelection() 300 |
312 |
| historyPalette.setUndoState() 300 |
312 |
| Hotspot object 224 |
312 |
| HTML export objects 247 |
312 |
| Hue (Effect object) 218 |
312 |
| Hue/Saturation (Effect object) 218 |
312 |
| I |
312 |
| Image object 223 |
312 |
| ImageMap object 252, 253 |
312 |
| ImagemapList object 253 |
312 |
| importFile() 79 |
312 |
| importSymbol() 80 |
312 |
| importSymbolButNotAsAlias() 80 |
312 |
| index arguments 6 |
312 |
| inLaunchAndEdit() 81 |
312 |
| Inner Shadow (Effect object) 218 |
312 |
| insertPointInPath() 81 |
312 |
| InsertSmartShapeAt 278 |
312 |
| insertSmartShapeAt() 82 |
312 |
| installing an extension 1 |
312 |
| Instance object 223 |
312 |
| Invert property (Effect object) 219 |
312 |
| isPIExpanded() 295 |
312 |
| isPIVisible() 295 |
312 |
| isSelectionDirectlyAboveBitmapObj ect() 83 |
312 |
| J |
312 |
| JavaScript |
312 |
| books 1 |
312 |
| checking the API for incompatibilities 175 |
312 |
| executing steps from the History panel 299 |
312 |
| extensibility file 4 |
312 |
| returning steps from the History panel 298 |
312 |
| running a script file 198 |
312 |
| saving a string as a command file 201 |
312 |
| saving steps to a command file 300 |
312 |
| syntax 1 |
312 |
| undoing functions 167 |
312 |
| JavaScript wrapper 270 |
312 |
| joinPaths() 84 |
312 |
| K |
312 |
| knifeElementsFromPoint() 84 |
312 |
| knifeElementsFromPoints() 84 |
312 |
| L |
312 |
| launchApp() 192 |
312 |
| launchBrowserTo() 192 |
312 |
| Layer object 236 |
312 |
| layerIndex argument 6 |
312 |
| Levels (Effect object) 219 |
312 |
| linkElementMask() 85 |
312 |
| loadColorPalette() 70 |
312 |
| M |
312 |
| makeActive() 87 |
312 |
| makeFind() 86 |
312 |
| makeGoodNativeFilePath() 301 |
312 |
| mask 5 |
312 |
| matrix 6 |
312 |
| mergeDown() 87 |
312 |
| Metafile.htt 247 |
312 |
| methods,global 11 |
312 |
| MM_nbGroup |
312 |
| (down) 24 |
312 |
| (highlight) 25 |
312 |
| (image) 25 |
312 |
| (out) 26 |
312 |
| MM_simpleRollover 26 |
312 |
| MM_statusMessage 26 |
312 |
| MM_swapImage 27 |
312 |
| MM_swapImgRestore 27 |
312 |
| MMEndCommand() 270 |
312 |
| MMExecute() 270 |
312 |
| modifyPointOnPath() 87 |
312 |
| motionBlurSelection() 88 |
312 |
| moveBezierHandleBy() 88 |
312 |
| moveElementMaskBy() 89 |
312 |
| moveFillVectorHandleBy() 89 |
312 |
| moveMaskGroupContentsBy() 90 |
312 |
| movePixelMaskBy() 90 |
312 |
| movePointOnHotspotBy() 91 |
312 |
| movePointOnHotspotByWithFlags() 91 |
312 |
| moveSelectedBezierPointsBy() 92 |
312 |
| moveSelectionBy() 92 |
312 |
| moveSelectionMaskBy() 93 |
312 |
| moveSelectionTo() 93 |
312 |
| moveSelectionToFrame() 94 |
312 |
| moveSelectionToLayer() 94 |
312 |
| moveSelectionToNewLayer() 95 |
312 |
| N |
312 |
| new features 2 |
312 |
| null values 6 |
312 |
| O |
312 |
| object |
312 |
| Behavior 208 |
312 |
| BehaviorInfo 247 |
312 |
| BehaviorsList 250 |
312 |
| Brush 208 |
312 |
| Contour 211 |
312 |
| ContourNode 211 |
313 |
| ContourNodeDynamicInfo 212 |
313 |
| ControlPoint 213 |
313 |
| Effect 214 |
313 |
| EffectList 221 |
313 |
| Element 221 |
313 |
| ElementMask 226 |
313 |
| Errors 14 |
313 |
| exportDoc 250 |
313 |
| ExportFrameInfo 227 |
313 |
| ExportOptions 227 |
313 |
| ExportPaletteInfo 229 |
313 |
| ExportSettings 230 |
313 |
| Files 14, 18 |
313 |
| Fill 233 |
313 |
| Find 17 |
313 |
| Frame 234 |
313 |
| FrameNLayerIntersection 234 |
313 |
| Gradient 235 |
313 |
| GradientNode 235 |
313 |
| Group 222 |
313 |
| Guides 235 |
313 |
| Hotspot 224 |
313 |
| Image 223 |
313 |
| ImageMap 252 |
313 |
| ImagemapList 253 |
313 |
| Instance 223 |
313 |
| Layer 236 |
313 |
| Path 225 |
313 |
| PathAttrs 236 |
313 |
| Pattern 237 |
313 |
| pngText 23 |
313 |
| SingleTextRun 241 |
313 |
| SliceHotspot 224 |
313 |
| SliceInfo 253 |
313 |
| Slices 255 |
313 |
| Style 242 |
313 |
| Text 225 |
313 |
| TextAttrs 243 |
313 |
| TextRuns 244 |
313 |
| Texture 226 |
313 |
| objects |
313 |
| accessing within documents 208 |
313 |
| classification 7 |
313 |
| core objects 13 |
313 |
| selected 7 |
313 |
| openDocument() 194 |
313 |
| P |
313 |
| palette 7 |
313 |
| panel 7 |
313 |
| panels, custom 269 |
313 |
| Path object 225 |
313 |
| PathAttrs object 236 |
313 |
| pathCrop() 95 |
313 |
| pathExpand() 96 |
313 |
| pathInset() 96 |
313 |
| pathIntersect() 97 |
313 |
| pathPunch() 97 |
313 |
| pathSimplify() 97 |
313 |
| pathUnion() 98 |
313 |
| Pattern object 237 |
313 |
| Photoshop document, exporting as 184 |
313 |
| pngText 23 |
313 |
| point 6 |
313 |
| popupColorPicker() 194 |
313 |
| popupColorPickerOverMouse() 195 |
313 |
| previewInBrowser() 98 |
313 |
| primitive 34 |
313 |
| property types |
313 |
| effectList 8 |
313 |
| PSD, exporting as 184 |
313 |
| Q |
313 |
| quit() 195 |
313 |
| quitApplication() 196 |
313 |
| R |
313 |
| readNthTable() 196 |
313 |
| readPanelStateFromFile() 196 |
313 |
| rebuildColorTable() 98 |
313 |
| rectangle 6 |
313 |
| rectangle primitive 34 |
313 |
| redo() 99 |
313 |
| redraw() 99 |
313 |
| reflectSelection() 100 |
313 |
| RegisterMoveParms 238 |
313 |
| release 259 |
313 |
| ReleaseObject() 266 |
313 |
| remote procedure calls 257 |
313 |
| auto-release blocks 266 |
313 |
| data node 260 |
313 |
| error codes 261 |
313 |
| object ID 259 |
313 |
| order 261 |
313 |
| parameters 261 |
313 |
| stubs 262 |
313 |
| removeAllGuides() 100 |
313 |
| removeBehavior() 101 |
313 |
| removeBrush() 101 |
313 |
| removeCharacterMarkup() 101 |
313 |
| removeElementMask() 102 |
313 |
| removeFill() 103 |
313 |
| removeFontMarkup() 102 |
313 |
| RemoveFromAutoReleasePool() 266 |
313 |
| removeGuide() 103 |
313 |
| removeTransformation() 104 |
313 |
| reorderFrame() 104 |
313 |
| reorderLayer() 105 |
313 |
| replace() 197 |
313 |
| replaceAll() 197 |
313 |
| replaceButtonTextStrings() 105 |
313 |
| replaceButtonTextStringsInInstances () 106 |
313 |
| replaceTextString() 106 |
313 |
| replaySteps() 299 |
313 |
| resizeSelection() 107 |
313 |
| resolution data type 6 |
313 |
| restoreJPEGMask() 108 |
313 |
| restoreSelection() 108 |
313 |
| reversePathTextDirection() 109 |
313 |
| revertDocument() 198 |
313 |
| rotateDocument() 109 |
313 |
| rotateSelection() 109 |
313 |
| RPCMethods 262, 265 |
313 |
| RPCMethods.AddToAutoReleasePo ol() 266 |
313 |
| RPCMethods.CreateAutoReleasePoo l() 265 |
313 |
| RPCMethods.DestroyAutoReleasePo ol() 265 |
313 |
| RPCMethods.ReleaseObject() 266 |
313 |
| RPCMethods.RemoveFromAutoRele asePool() 266 |
313 |
| runScript() 198 |
313 |
| S |
313 |
| Saturation properties (Effect object) 218 |
313 |
| save() 110 |
313 |
| saveAll() 198 |
313 |
| saveAsCommand() 300 |
313 |
| saveColorPalette() 70 |
313 |
| saveCopyAs() 110 |
313 |
| saveDocument() 199 |
313 |
| saveDocumentAs() 199 |
313 |
| saveDocumentCopyAs() 200 |
314 |
| saveJPEGMask() 111 |
314 |
| saveJsCommand() 200 |
314 |
| saveSelection() 111 |
314 |
| scaleSelection() 112 |
314 |
| selectAdjustPixelSel() 113 |
314 |
| selectAll() 113 |
314 |
| selectAllOnLayer() 113 |
314 |
| selectChildren() 114 |
314 |
| selected objects 7 |
314 |
| selectFeather() 114 |
314 |
| selectInverse() 115 |
314 |
| selectNone() 115 |
314 |
| selectParents() 115 |
314 |
| selectSimilar() 116 |
314 |
| selectSimilarFromPoint() 116 |
314 |
| sendEmail() 117 |
314 |
| set 259 |
314 |
| setActiveViewScale() 201 |
314 |
| setActiveWindow() 201 |
314 |
| setAllLayersDisclosure() 117 |
314 |
| setAnimInstanceLoopCount() 118 |
314 |
| setAnimInstanceNumFrames() 118 |
314 |
| setAnimInstanceOffsetDist() 119 |
314 |
| setAnimInstanceRotationAmount() 119 |
314 |
| setAnimInstanceScaleAmount() 120 |
314 |
| setAnimInstanceStartEndOpacity() 1 20 |
314 |
| setAnimInstanceStartFrame() 121 |
314 |
| setBlendMode() 121 |
314 |
| setBrush() 121 |
314 |
| setBrushColor() 122 |
314 |
| setBrushName() 122 |
314 |
| setBrushNColorNTexture() 123 |
314 |
| setBrushPlacement() 123 |
314 |
| setButtonAutoSlice() 124 |
314 |
| setButtonIncludeDownState() 124 |
314 |
| setButtonIncludeOverWhileDownSt ate 124 |
314 |
| setButtonIncludeOverWhileDownSt ate() 124 |
314 |
| setButtonOptions 125 |
314 |
| setButtonOptions() 125 |
314 |
| setButtonShowDownOnLoad() 125 |
314 |
| setDefaultBrushAndFillColors() 126 |
314 |
| setDefaultFillVector() 126 |
314 |
| setDocumentCanvasColor() 126 |
314 |
| setDocumentCanvasSize() 127 |
314 |
| setDocumentCanvasSizeToDocume ntExtents() 127 |
314 |
| setDocumentCanvasSizeToSelection () 128 |
314 |
| setDocumentImageSize() 128 |
314 |
| setDocumentResolution() 129 |
314 |
| setEffectName() 129, 130, 131 |
314 |
| setElementMaskMode() 130, 131 |
314 |
| setElementMaskShowAttrs() 131 |
314 |
| setElementName() 131 |
314 |
| setElementVisible() 132 |
314 |
| setElementVisibleByName() 133 |
314 |
| setExportOptions() 133 |
314 |
| setExportSettings() 133 |
314 |
| setFill() 134 |
314 |
| setFillColor() 134 |
314 |
| setFillEdgeMode() 134 |
314 |
| setFillNColor() 135 |
314 |
| setFillNColorNTexture() 135 |
314 |
| setFillPlacement() 136 |
314 |
| setFillVector() 136 |
314 |
| setFillVectorStart() 137 |
314 |
| setFloaterGrouping() 202 |
314 |
| setFloaterPosition() 202 |
314 |
| setFloaterVisibility() 7, 203 |
314 |
| setGradientName() 137 |
314 |
| setGridColor() 138 |
314 |
| setGridOrigin() 137 |
314 |
| setGridSize() 138 |
314 |
| setGroupType() 138 |
314 |
| setGuideColor() 139 |
314 |
| setHideAllFloaters() 203 |
314 |
| setHotspotAltTag() 139 |
314 |
| setHotspotColor() 140 |
314 |
| setHotspotRectangle() 140 |
314 |
| setHotspotShape() 141 |
314 |
| setHotspotTarget() 141 |
314 |
| setHotspotText() 141 |
314 |
| setLayerDisclosure() 142 |
314 |
| setLayerLocked() 143 |
314 |
| setLayerName() 143 |
314 |
| setLayerSharing() 144 |
314 |
| setLayerVisible() 144 |
314 |
| setMatteColor() 145 |
314 |
| setOnionSkinning() 146 |
314 |
| setOpacity() 147 |
314 |
| setPIPosition() 296 |
314 |
| setPixelMask() 146 |
314 |
| setPref() 204 |
314 |
| setQuadrangle() 148 |
314 |
| setRectRoundness() 148 |
314 |
| setRectSides() 149 |
314 |
| setSelection() 300 |
314 |
| setSelectionBounds() 149 |
314 |
| setSelectionMask() 149 |
314 |
| setShowEdges() 150 |
314 |
| setShowGammaPreview() 150 |
314 |
| setShowGrid() 151 |
314 |
| setShowGuides() 151 |
314 |
| setShowRulers() 151 |
314 |
| setShowSliceGuides() 152 |
314 |
| setShowSliceOverlay() 152 |
314 |
| setSliceAutonaming() 152 |
314 |
| setSliceExportOptions() 153 |
314 |
| setSliceFilename() 153 |
314 |
| setSliceGuideColor() 153 |
314 |
| setSliceHtml() 154 |
314 |
| setSliceIsHtml() 154 |
314 |
| setSnapToGrid() 155 |
314 |
| setSnapToGuides() 155 |
314 |
| setSymbolProperties() 155 |
314 |
| setTextAlignment() 156 |
314 |
| setTextAntiAliasing() 156 |
314 |
| setTextAutoKern() 157 |
314 |
| setTextCharSpacing() 157 |
314 |
| setTextCustomAntiAliasOverSample () 157 |
314 |
| setTextCustomAntiAliasSharpness() 158 |
314 |
| setTextCustomAntiAliasStrength() 1 58 |
314 |
| setTextFlow() 158 |
314 |
| setTextHorizontalScale() 159 |
314 |
| setTextLeading() 159 |
314 |
| setTextOnPathMode() 160 |
314 |
| setTextOnPathOffset() 160 |
314 |
| setTextOrientation() 160 |
314 |
| setTextParaIndent() 161 |
314 |
| setTextParaSpacingAfter() 161 |
314 |
| setTextParaSpacingBefore() 161 |
314 |
| setTextRectangle() 162 |
314 |
| setTextRectangleAuto() 163 |
314 |
| setTextRectangleAutoFromPoint() 2 9, 33, 58, 61, 83, 105, 163, 164, 165 |
314 |
| setTextRuns() 162 |
314 |
| setTransformMode() 162 |
314 |
| setUndoState() 300 |
314 |
| setUpFindReplace() 204 |
314 |
| Sharpen (Effect object) 220 |
315 |
| Sharpen More (Effect object) 220 |
315 |
| showAllHidden() 165 |
315 |
| showPIWindow() 294 |
315 |
| shrinkPIWindow() 296 |
315 |
| SingleTextRun object 241 |
315 |
| sliced images 247 |
315 |
| SliceHotspot object 224 |
315 |
| SliceInfo object 253 |
315 |
| Slices object 255 |
315 |
| Slices.htt 247 |
315 |
| smartShape 259 |
315 |
| smartShape object 275 |
315 |
| Auto Shapes 275 |
315 |
| SmartShapeEdited 279 |
315 |
| splitPaths() 166 |
315 |
| strokes, finding and replacing 18 |
315 |
| stubs 262 |
315 |
| Style object 242 |
315 |
| styles, finding and replacing 17 |
315 |
| swapBrushAndFillColors() 166 |
315 |
| SWF, exporting as 186 |
315 |
| syntax conventions 23 |
315 |
| T |
315 |
| templates 247 |
315 |
| Text object 225 |
315 |
| text, finding and replacing 17 |
315 |
| TextAttrs object 243 |
315 |
| TextRuns object 244 |
315 |
| Texture object 226 |
315 |
| toggleFloater() 7, 204 |
315 |
| transformSelection() 166 |
315 |
| tween() 167 |
315 |
| U |
315 |
| undo() 167 |
315 |
| ungroup() 168 |
315 |
| ungroupPrimitives() 205 |
315 |
| Unsharp Mask property (Effect object) 220 |
315 |
| updateHTML() 205 |
315 |
| updateSymbol() 167 |
315 |
| URLs, finding and replacing 18 |
315 |
| V |
315 |
| values 4 |
315 |
| W |
315 |
| Working with selected elements 6 |
315 |
| writePanelStateToFile() 206 |
315 |
| X |
315 |
| XML 257 |
315 |
| Y |
315 |
| yesNoDialog() 206 |
315 |
| Z |
315 |

 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21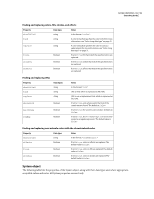 22
22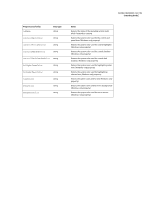 23
23 24
24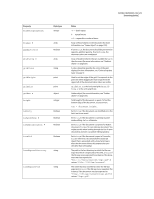 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60 61
61 62
62 63
63 64
64 65
65 66
66 67
67 68
68 69
69 70
70 71
71 72
72 73
73 74
74 75
75 76
76 77
77 78
78 79
79 80
80 81
81 82
82 83
83 84
84 85
85 86
86 87
87 88
88 89
89 90
90 91
91 92
92 93
93 94
94 95
95 96
96 97
97 98
98 99
99 100
100 101
101 102
102 103
103 104
104 105
105 106
106 107
107 108
108 109
109 110
110 111
111 112
112 113
113 114
114 115
115 116
116 117
117 118
118 119
119 120
120 121
121 122
122 123
123 124
124 125
125 126
126 127
127 128
128 129
129 130
130 131
131 132
132 133
133 134
134 135
135 136
136 137
137 138
138 139
139 140
140 141
141 142
142 143
143 144
144 145
145 146
146 147
147 148
148 149
149 150
150 151
151 152
152 153
153 154
154 155
155 156
156 157
157 158
158 159
159 160
160 161
161 162
162 163
163 164
164 165
165 166
166 167
167 168
168 169
169 170
170 171
171 172
172 173
173 174
174 175
175 176
176 177
177 178
178 179
179 180
180 181
181 182
182 183
183 184
184 185
185 186
186 187
187 188
188 189
189 190
190 191
191 192
192 193
193 194
194 195
195 196
196 197
197 198
198 199
199 200
200 201
201 202
202 203
203 204
204 205
205 206
206 207
207 208
208 209
209 210
210 211
211 212
212 213
213 214
214 215
215 216
216 217
217 218
218 219
219 220
220 221
221 222
222 223
223 224
224 225
225 226
226 227
227 228
228 229
229 230
230 231
231 232
232 233
233 234
234 235
235 236
236 237
237 238
238 239
239 240
240 241
241 242
242 243
243 244
244 245
245 246
246 247
247 248
248 249
249 250
250 251
251 252
252 253
253 254
254 255
255 256
256 257
257 258
258 259
259 260
260 261
261 262
262 263
263 264
264 265
265 266
266 267
267 268
268 269
269 270
270 271
271 272
272 273
273 274
274 275
275 276
276 277
277 278
278 279
279 280
280 281
281 282
282 283
283 284
284 285
285 286
286 287
287 288
288 289
289 290
290 291
291 292
292 293
293 294
294 295
295 296
296 297
297 298
298 299
299 300
300 301
301 302
302 303
303 304
304 305
305 306
306 307
307 308
308 309
309 310
310 311
311 312
312 313
313 314
314 315
315