Cisco SPA901-UK Provisioning Guide - Page 14
Configuration Access Control, Configuration Profiles - factory reset
 |
UPC - 745883570751
View all Cisco SPA901-UK manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
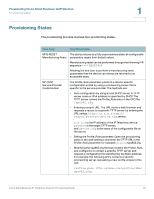
Provisioning Cisco Small Business VoIP Devices Provisioning Overview 1 Configuration Access Control Besides configuration parameters that control resync and upgrade behavior, the IP Telephony device firmware provides mechanisms for restricting end-user access to some parameters. The firmware provides specific privileges for login to an Admin account and a User account. Each can be independently password protected.: • Admin Account-Allows the service provider full access to all interactive voice response (IVR) functions and to all administration web server parameters. • User Account-Allows the user of a device to access basic IVR functions and to configure a subset of the administration web server parameters. The service provider can restrict the user account in the following ways: • Choose which configuration parameters are available to the User account. • Disable user access to the administration web server. • Disable the factory reset control using the IVR. • Restrict the Internet domains accessed by the device for resync, upgrades, or SIP registration for Line 1. Configuration Profiles The configuration profile defines the parameter values for a specific IP Telephony device. The configuration profile can be used in two formats: • Open (XML-style) The XML format uses standard tools to compile the parameters and values. To protect confidential information in the configuration profile, this type of file is generally delivered from the provisioning server to the IP Telephony device over a secure channel provided by HTTPS. • Proprietary, plain-text The plain-text configuration file uses a proprietary format that can be encrypted by using the SIP Profile Compiler (SPC) to prevent the unauthorized use of confidential information. By convention, the encrypted profile is named with the extension .cfg (for example, spa962.cfg). Cisco Small Business IP Telephony Devices Provisioning Guide 13