D-Link DIR-632 Product Manual - Page 103
What.is.Wireless?, Why.D-Link.Wireless, How.does.wireless.work? - wireless range
 |
UPC - 790069336263
View all D-Link DIR-632 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 103 highlights
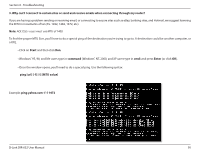
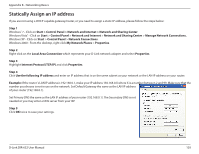
Appendix A - Wireless Basics What is Wireless? Wireless or Wi-Fi technology is another way of connecting your computer to the network without using wires. Wi-Fi uses radio frequency to connect wirelessly, so you have the freedom to connect computers anywhere in your home or office network. Why D-Link Wireless? D-Link is the worldwide leader and award winning designer, developer, and manufacturer of networking products. D-Link delivers the performance you need at a price you can afford. D-Link has all the products you need to build your network. How does wireless work? Wireless works similar to how cordless phone work, through radio signals to transmit data from one point A to point B. But wireless technology has restrictions as to how you can access the network. You must be within the wireless network range area to be able to connect your computer. There are two different types of wireless networks Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN), and Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN). Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) In a wireless local area network, a device called an Access Point (AP) connects computers to the network. The access point has a small antenna attached to it, which allows it to transmit data back and forth over radio signals. With an indoor access point as seen in the picture, the signal can travel up to 300 feet. With an outdoor access point the signal can reach out up to 30 miles to serve places like manufacturing plants, industrial locations, college and high school campuses, airports, golf courses, and many other outdoor venues. Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) Bluetooth is the industry standard wireless technology used for WPAN. Bluetooth devices in WPAN operate in a range up to 30 feet away. Compared to WLAN the speed and wireless operation range are both less than WLAN, but in return it doesn't use nearly as much power which makes it ideal for personal devices, such as mobile phones, PDAs, headphones, laptops, speakers, and other devices that operate on batteries. D-Link DIR-632 User Manual 98