HP BL260c HP Server Automation complements HP Insight Control to manage HP Bla - Page 17
Server Automation Compliance Check
 |
UPC - 883585668663
View all HP BL260c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
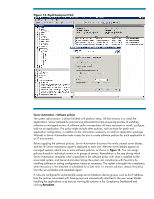
Figure 8: Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager Server connection profiles specify the specific network and storage connections, including boot settings that a server blade will use. Unlike traditional network connections, Virtual Connect server connection profiles are assigned to an enclosure bay and not tied to individual server hardware, which means that servers can be replaced or upgraded and the network connections for the enclosure remain constant. When you insert a server blade into an enclosure bay, it powers up and follows the profile boot settings to connect to its communication networks and storage. Based on the boot settings, it could obtain its operating system through several methods including Pre-boot Execution Environment (PXE) boot or a pre-existing image on its primary local or SAN-based boot partition. In this example, inactive server profiles in VCEM have been configured, set up, and tested as part of the Oracle RAC cluster. During normal operations, inactive profiles are disassociated from the server hardware, freeing the server for other uses, but the profiles remain available for immediate use. The administrator identifies an available server blade in another enclosure and uses VCEM to assign one of the inactive server blade profiles for the Oracle RAC cluster and then boots the server blade. Server Automation Compliance Check The server blade profile is configured to boot the server from a pre-existing SAN-based boot partition that contains an image of the desired operating system and application, so the additional server blade can be added to the cluster quickly. Because this instance has been inactive, you must verify that the configuration is in compliance with current operating system, application, and security policies. The system administrator consults the Server Automation server compliance view (Figure 9). If there have been changes to the production application configuration policies since the last time this image was used, which is the case in this example, the system administrator can click Remediate to immediately bring the instance into compliance. This server can now be safely added into the production Oracle RAC cluster. 17