HP ML350 HP ProLiant Firmware Maintenance CD User Guide - Page 55
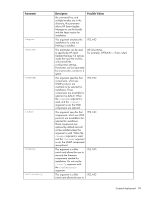
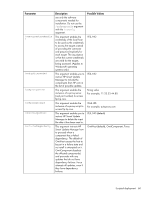
Input file format and rules, DRYRUN = YES, SILENT = YES, TARGETS], HOST = BL465C-01
 |
View all HP ML350 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 55 highlights
[TARGETS] HOST = schinta1 HOST = schinta2 UID = root PWD = root123 HOST = 234.567.765.432 [END] Example 1: The two targets are passed to be updated. The targets do not necessarily have to be OAs. They can be any target supported by HP Smart Update Manager. DRYRUN = YES SILENT = YES [TARGETS] HOST = BL465C-01 HOST = 192.168.1.2 [END] Example 2: A host is passed along with the user ID and password to use. DRYRUN = YES SILENT = YES [TARGETS] HOST=BL685cG6 UID = Bigboss2 PWD = password [END] NOTE: The credentials can be left out of the file for greater security and passed on the command line to HP Smart Update Manager. The only limitation of this is that the userID and credentials must be the same on all. When the file has been created, to use it with HP Smart Update Manager, add it as the inputfile parameter to a normal HP Smart Update Manager command line. For example, if the name of the input file is hpsum.in, the command line syntax is hpsum --inputfile hpsum.in. Full paths can be added to the input file location if it is not stored in the same location as the HP Smart Update Manager executables. The field may be enclosed in double quotes to allow for paths with spaces. Also, the input file itself may contain the same flags on the command line. The usual command line flags may still be used with the -inputfile flag, and takes precedence over any given input file. Input file format and rules The input file is divided into two sections: Scripted deployment 55