HP ProLiant BL660c HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 3
Processor drivers, HP Static High Performance mode, HP Static Low Power mode
 |
View all HP ProLiant BL660c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
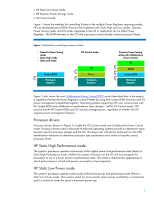
• HP Static Low Power mode • HP Dynamic Power Savings mode • OS Control mode Figure 1 shows the methods for controlling P-states in the multiple Power Regulator operating modes. HP has developed server ROM firmware that implements the Static High and Low modes, Dynamic Power Saving mode, and OS mode. Upgrades to the OS or application do not affect Power Regulator. The ROM firmware or the OS with a processor driver directly control processor P-states. Figure 1. Methods for controlling processor P-states • Dynamic Power Saving mode • Static High mode • Static Low mode OS Control mode System ROM Hardware Registers OS Driver Hardware Registers Dynamic Power Saving mode with Collaborative Power Control OS Driver System ROM Hardware Registers Figure 1 also shows the new Collaborative Power Control (CPC) mode (described later in the paper), a capability that lets the Power Regulator control P-states by using both system ROM firmware and OS power management capabilities together. Operating systems supporting CPC can communicate with the System ROM and collaborate on performance state changes. Unlike OS Control mode, CPC ensures that the HP System ROM and OS actively manage power, regardless of whether the OS supports power management features. Processor drivers Processor drivers (shown in Figure 1) enable the OS Control mode and Collaborative Power Control mode. Processor drivers used in Microsoft Windows® operating systems provide an abstraction layer between specific processor designs and the OS. Windows uses information obtained from the CPU Identification instruction to determine processor type and feature set in order to load the correct processor driver. HP Static High Performance mode The system's processors operate continuously at the highest power and performance state (Pmax) in Static High Performance mode. Neither the system's firmware nor the OS will ever program the processors to run in a lower power or performance state. This mode is important for applications in which performance is critical and power consumption is less important. HP Static Low Power mode The system's processors operate continuously at the lowest power and performance state (Pmin) in Static Low Power mode. This mode is useful for environments where power availability is constrained and it is critical to lower the server's maximum power use. 3