HP Visualize c160L HP-UX DMI 2.0 Developer's Guide: HP-UX/HP 9000 Computers, - Page 18
Service Provider to MIF Relationship
 |
View all HP Visualize c160L manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
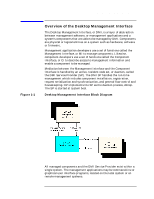
Figure 1-2 Introduction Overview of the Desktop Management Interface The relationships among management applications, the DMI SP and component instrumentation may be many-to-one. There may be many management applications issuing commands through a single DMI SP to manage many components. Within DMI, information about all components is defined in a language called the Management Interface Format (MIF) and stored by the DMI SP in a MIF database. Each component has a unique MIF file which describes its manageable characteristics. Each component's MIF file is registered in a MIF database, and owned by the DMI SP. For more information on MIF files, see Writing Component MIF Files in the Component section of this Developer's Guide. Within DMI, information about all components is defined in a language called the Management Interface Format (MIF) and stored by the DMI SP in a MIF database. Each component has a unique MIF file which describes its manageable characteristics. Each component's MIF file is registered in a MIF database, and owned by the DMI SP. For more information on MIF files, see Writing Component MIF Files in the Component section of this Developer's Guide. Service Provider to MIF Relationship 18 Chapter 1