IBM IC35L040AVVN07-0 Hard Drive Specifications - Page 109
Command Protocol
 |
UPC - 683728124212
View all IBM IC35L040AVVN07-0 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 109 highlights
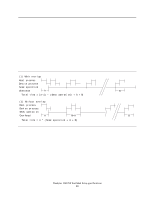
10.0 Command Protocol The commands are grouped into different classes according to the protocols followed for command execution. The command classes with their associated protocols are defined below. For all commands, the host must first check if BSY=1, and should proceed no further unless and until BSY=0. For all commands, the host must also wait for RDY=1 before proceeding. A device must maintain either BSY=1 or DRQ=1 at all times until the command is completed. The INTRQ signal is used by the device to signal most, but not all, times when the BSY bit is changed from one to zero during command execution. A command shall only be interrupted with a hardware or software reset. The result of writing to the Command register while BSY=1 or DRQ=1 is unpredictable and may result in data corruption. A command should only be interrupted by a reset at times when the host thinks there may be a problem, such as a device that is no longer responding. Interrupts are cleared when the host reads the Status Register, issues a reset, or writes to the Command Register. Figure 160 on page 193 shows the device time-out values. Deskstar 120GXP hard disk drive specifications 95