Lacie 4big Quadra White Paper - Page 2
Standard Raid Levels - spare drive
 |
View all Lacie 4big Quadra manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 2 highlights
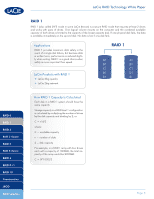
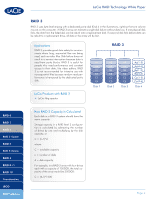
LaCie RAID Technology White Paper RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 3 RAID 3+Spare RAID 5 RAID 5+Spare RAID 6 RAID 0+1 RAID 10 Concatenation JBOD RAID Selection Standard RAID levels RAID 0 RAID 0 (also called FAST mode in some LaCie devices), is the fastest RAID mode. Requiring at least 2 drives, RAID 0 stripes data onto each disk. The available capacities of each disk are added together so that one logical volume mounts on the computer. If one physical disk in the array fails, the data of all disks becomes inaccessible because parts of the data have been written to all disks. Applications RAID 0 is ideal for users who need maximum speed and capacity. Video editors working with very large files may use RAID 0 when editing multiple streams of video for optimal playback performance. A RAID 0 array is more suited for actively working with files (editing video, for example) and should not be used as a single storage backup solution or on mission critical systems. LaCie Products with RAID 0 ✦✦ LaCie 2big quadra ✦✦ LaCie 4big quadra ✦✦ LaCie big disk quadra (built-in) ✦✦ LaCie little big disk quadra (built-in) ✦✦ LaCie 5big network RAID 0 A1 B1 C1 D1 Disk 1 A2 B2 C2 D2 Disk 2 A3 B3 C3 D3 Disk 3 A4 B4 C4 D4 Disk 4 How RAID 0 Capacity Is Calculated Each disk in a RAID 0 system should have the same capacity. Storage capacity in a RAID level 0 configuration is calculated by multiplying the number of drives by the disk capacity, or C = n*d, where: C = available capacity n = number of disks d = disk capacity For example, in a RAID 0 array with four drives each with a capacity of 1000GB, the total capacity of the array would be 4000GB: C = (4*1000) Page 2