Lacie 4big Quadra White Paper - Page 6
Raid 5
 |
View all Lacie 4big Quadra manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
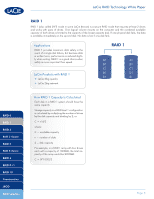
LaCie RAID Technology White Paper RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 3 RAID 3+Spare RAID 5 RAID 5+Spare RAID 6 RAID 0+1 RAID 10 Concatenation JBOD RAID Selection RAID 5 RAID 5 combines the striping of RAID 0 with data redundancy in an array with a minimum of three disks. The difference between RAID 3 and RAID 5 is that a RAID 3 configuration will offer better performance at the expense of slightly less overall capacity. Data is striped across all disks and a parity block (P) for each data block is written on the same stripe. If one physical disk fails, the data from the failed disk can be rebuilt onto a replacement disk. No data is lost in the case of a single disk failure, but if a second disk fails before data can be rebuilt to a replacement drive, all data in the array will be lost. Applications RAID 5 combines data safety with efficient use of disk space. Disk failure does not result in a service interruption because data is read from parity blocks. RAID 5 is useful for archiving and for people who need performance and constant access to their data, like video editors. LaCie Products with RAID 5 ✦✦ LaCie 4big quadra ✦✦ LaCie 5big network RAID 5 A1 B1 C1 Dp Disk 1 A2 B2 Cp D1 Disk 2 A3 Bp C2 D2 Disk 3 Ap B3 C3 D3 Disk 4 How RAID 5 Capacity Is Calculated Each disk in a RAID 5system should have the same capacity. Storage capacity in a RAID level 5 configuration is calculated by subtracting the number of drives by one and multiplying by the disk capacity, or C = (n-1)*d where: C = available capacity n = number of disks d = disk capacity For example, in a RAID 5 array with four drives each with a capacity of 1000GB, the total capacity of the array would be 3000GB: C = (4-1)*1000 Page 6