Lacie 4big Quadra White Paper - Page 9
Nested Raid Levels
 |
View all Lacie 4big Quadra manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
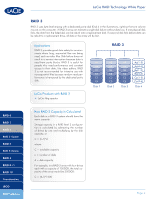
LaCie RAID Technology White Paper RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 3 RAID 3+Spare RAID 5 RAID 5+Spare RAID 6 RAID 0+1 RAID 10 Concatenation JBOD RAID Selection Nested RAID Levels RAID 0+1 RAID 0+1 is a secure RAID mode that is composed of a mirror of striped sets. RAID 0+1 arrays should have disks in multiples of four. For LaCie products with five disks, in a RAID 0+1 array, the fifth disk will either be a spare or will be unused. In the diagram, at right, array B is a mirror of array A. Up to two disks can fail in a RAID 0+1 array without loss of data, as long as the failed disks are not part of different RAID 0 pairs. In reference to the diagram, disk 1 and disk 2 could fail and the data would be preserved on disks 3 and 4. Applications RAID 0+1 provides good speeds because of RAID 0 striping, but cuts the available capacity of a device in half (assume all disks in the array have the same capacity). LaCie Products with RAID 0+1 ✦✦ Currently, no LaCie products How RAID 0+1 Capacity Is Calculated Each disk in a RAID 0+1 system should have the same capacity. Storage capacity in a RAID 0+1 configuration is calculated by multiplying the number of drives by the disk capacity and dividing by 2, or C = n*d/2 where: C = available capacity n = number of disks d = disk capacity For example, in a RAID 0+1 array with four drives each with a capacity of 1000GB, the total capacity of the array would be 2000GB: C = (4*1000)/2 RAID 0+1 RAID1 RAID0 A A1 B1 C1 D1 Disk 1 A2 B2 C2 D2 Disk 2 RAID0 B A1 B1 C1 D1 Disk 3 A2 B2 C2 D2 Disk 4 Page 9