Lacie 4big Quadra White Paper - Page 5
RAID 3+ Spare - replace drive
 |
View all Lacie 4big Quadra manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
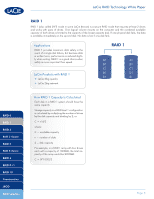
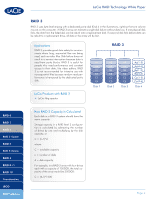
LaCie RAID Technology White Paper RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 3 RAID 3+Spare RAID 5 RAID 5+Spare RAID 6 RAID 0+1 RAID 10 Concatenation JBOD RAID Selection RAID 3+Spare In RAID 3+Spare, one disk in the array is left empty. If a drive in the array fails, the data from the failed disk is automatically rebuilt to the empty or "spare" disk. Applications In RAID 3+Spare disk failure does not require immediate attention because the system rebuilds itself using the hot spare, but the failed disk should be replaced as soon as possible. LaCie Products with RAID 3+Space ✦✦ LaCie 4big quadra How RAID 3+Space Capacity Is Calculated Each disk in a RAID 3+Spare system should have the same capacity. Storage capacity in a RAID 3+Spare configuration is calculated by subtracting the number of drives by two and multiplying by the disk capacity, or C = (n-2)*d where: C = available capacity n = number of disks d = disk capacity For example, in a RAID 3+Spare array with four drives each with a capacity of 1000GB, the total capacity of the array would be 2000GB: C = (4-2)*1000 RAID 3+ Spare A1 A3 B1 B3 C1 C3 Disk 1 A2 A3 B2 B4 C2 C4 Disk 2 Ap(1-2) Ap(3-4) Bp(1-2) Bp(3-4) Cp(1-2) Cp(3-4) Disk 3 Spare Disk 4 Page 5