Samsung T240HD User Manual (ENGLISH) - Page 85
Terms, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa - composite
 |
UPC - 729507804521
View all Samsung T240HD manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 85 highlights
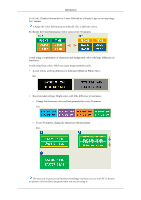
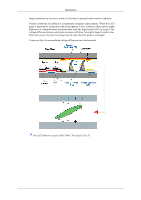
Appendix TAIWAN VIETNAM Asia Pacific 0800-329-999 1 800 588 889 http://www.samsung.com/tw http://www.samsung.com SOUTH AFRICA TURKEY U.A.E Middle East & Africa 0860-SAMSUNG(726-7864) http://www.samsung.com 444 77 11 http://www.samsung.com 800-SAMSUNG(726-7864) http://www.samsung.com 8000-4726 Terms Sync Signal Types of Sync Signals Sync (Synchronized) Signals refer to the standard signals that are required to display desired colors on the monitor. They are divided into Vertical and Horizontal Sync Signals. These signals display normal color images by the set resolution and frequency. Separate Composite This is a scheme of transmitting individual vertical and horizontal sync signals to the monitor. This is a scheme of combining vertical and horizontal sync signals into one composite signal and transmitting it to the monitor. The monitor displays the color signals by separating the composite signal into original color signals. Dot Pitch Vertical Frequency Horizontal Frequency Interlace and Non-Interlace Methods Plug & Play Resolution The image on a monitor is composed of red, green and blue dots. The closer the dots, the higher the resolution. The distance between two dots of the same color is called the 'Dot Pitch'. Unit: mm The screen must be redrawn several times per second in order to create and display an image for the user. The frequency of this repetition per second is called the Vertical Frequency or Refresh Rate. Unit: Hz Example: If the same light repeats itself 60 times per second, this is regarded as 60 Hz. The time to scan one line connecting the right edge to the left edge of the screen horizontally is called the Horizontal Cycle. The inverse number of the Horizontal Cycle is called Horizontal Frequency. Unit: kHz Showing the horizontal lines of the screen from the top to the bottom sequentially is called the Non-Interlace method while showing odd lines and then even lines in turn is called the Interlace method. The Non-Interlace method is used for the majority of monitors to ensure a clear image. The Interlace method is the same as that used in TVs. This is a function that provides the best quality screen for the user by allowing the computer and the monitor to exchange information automatically. This monitor follows the international standard VESA DDC for the Plug & Play function. The number of horizontal and vertical dots used to compose the screen image is called the 'resolution'. This number shows the ac-