Asus D1T D1T Hardware User Manual English - Page 47
Power Management Modes - cpu support
 |
View all Asus D1T manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 47 highlights
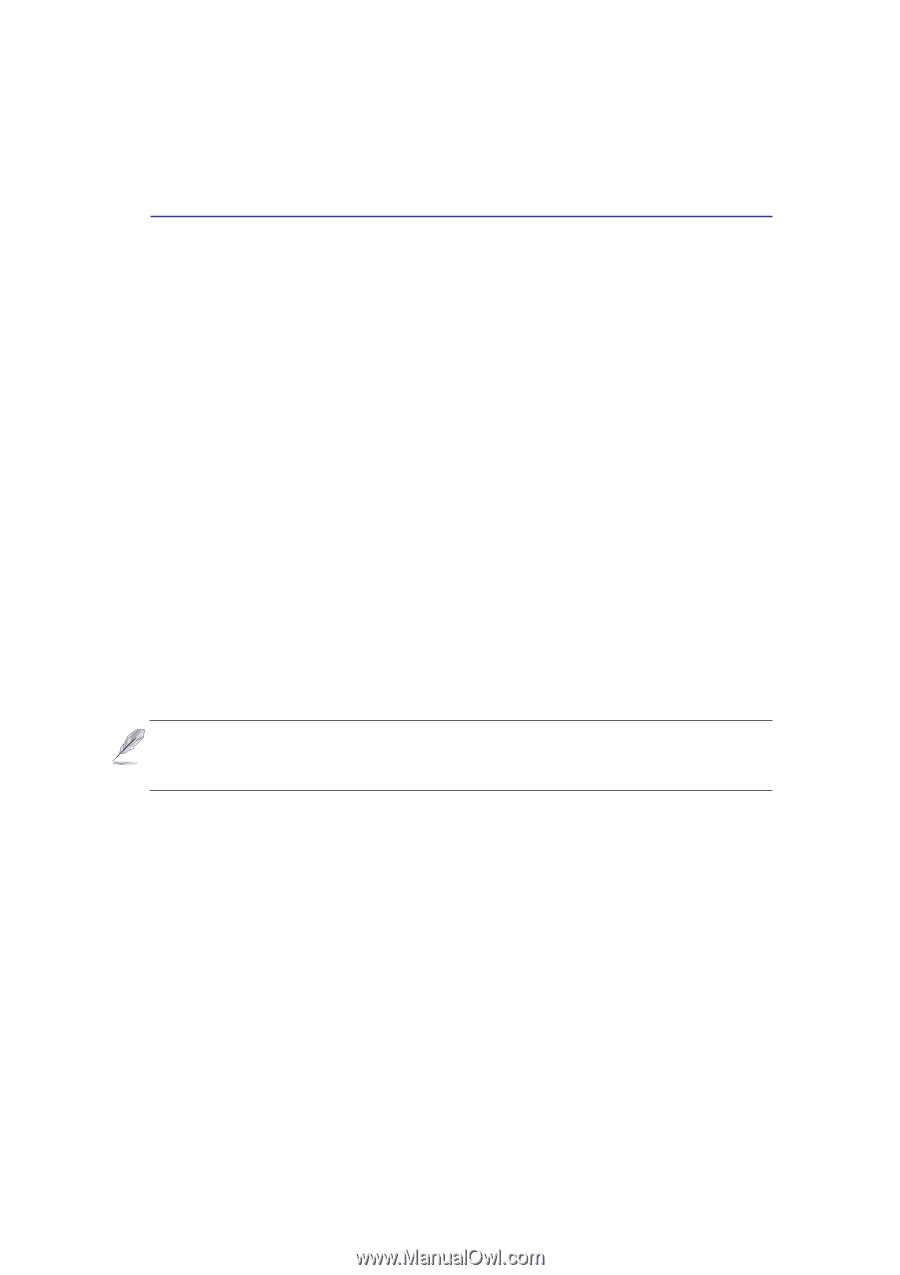
4 Using the Portable Desktop PC Power Management Modes The Portable Desktop PC has a number of automatic or adjustable power saving features that you can use to maximize battery life and lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). You can control some of these features through the Power menu in the BIOS Setup. ACPI power management settings are made through the operating system. The power management features are designed to save as much electricity as possible by putting components into a low power consumption mode as often as possible but also allow full operation on demand. These low power modes are referred to as Standby (or Suspend-to-RAM) and Hibernation mode or Suspend-to-Disk (STD). The Standby mode is a simple function provided by the operating system. When the Portable Desktop PC is in either one of the power saving modes, the status will be shown by the following: Standby: Power LED Blinks and Hibernation: Power LED OFF. Full Power Mode & Maximum Performance The Portable Desktop PC operates in Full Power mode when the power management function is disabled by configuring Windows power management and Speedstep (see Driver & Utility manual). When the Portable Desktop PC is operating in Full Power Mode, the Power LED remains ON. If you are conscious of both system performance and power consumption, select "Maximum Performance" instead of disabling all power management features. ACPI Advanced Configuration and Power Management (ACPI) was developed by Intel, Microsoft, and Toshiba especially for Windows and later to control power management and Plug and Play features. ACPI is the new standard in power management for Portable Desktop PCs. If installing Windows 98 using a BIOS dated 12/1/1999 or later, ACPI is automatically installed. NOTE: APM was used in older operating systems like Windows NT4 and Windows 98. Because newer operating systems like Windows 2000 and Windows ME utilize ACPI, APM is no longer fully supported on this Portable Desktop PC. Suspend Mode In Standby and Hibernation, the CPU clock is stopped and most of the Portable Desktop PC devices are put in their lowest active state. The suspend mode is the lowest power state of the Portable Desktop PC. The Portable Desktop PC enters Suspend when the system remains idle for a specified amount of time or manually using the [Fn][F1] keys. The Power LED blinks when the Portable Desktop PC is in STR mode. In STD mode, the Portable Desktop PC will appear to be powered OFF. Recover from STR by pressing any keyboard button (except Fn). Recover from STD by using the power switch (just like powering ON the Portable Desktop PC). 47